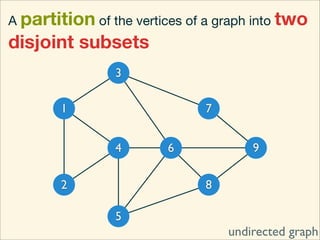
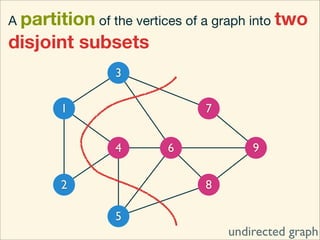
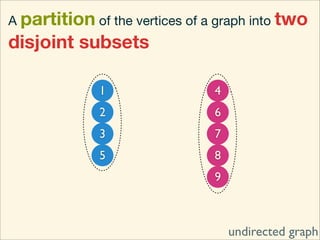
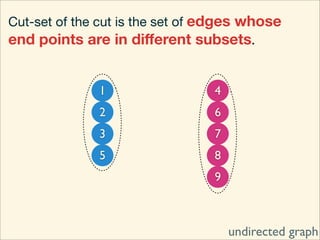
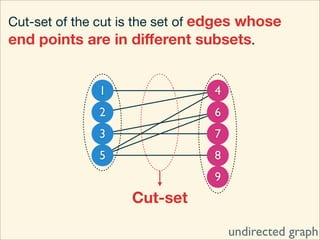
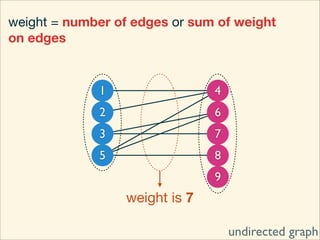
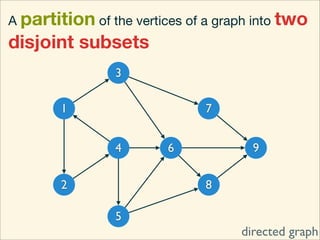
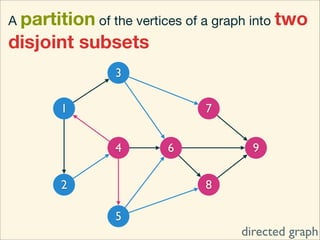
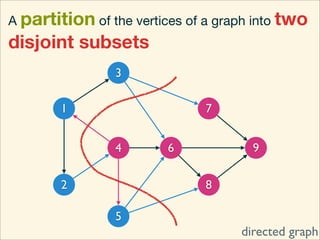
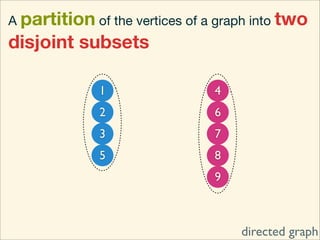
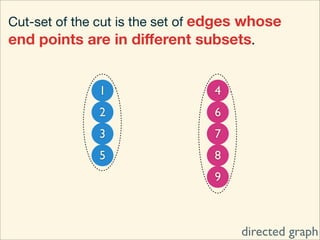
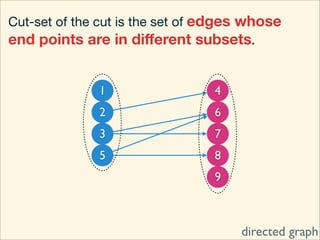
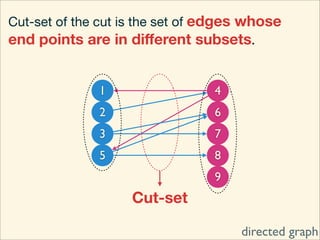
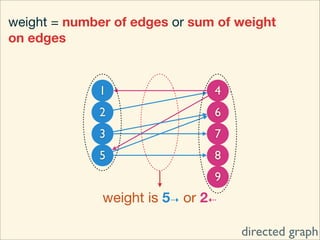
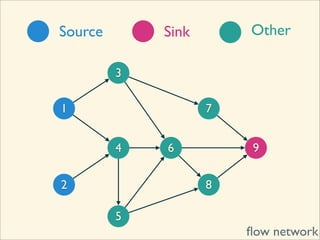
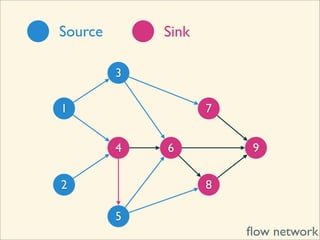
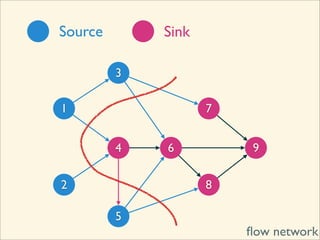
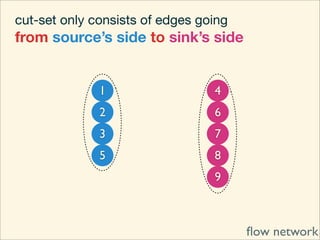
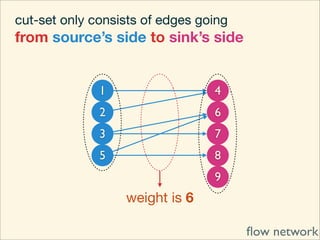
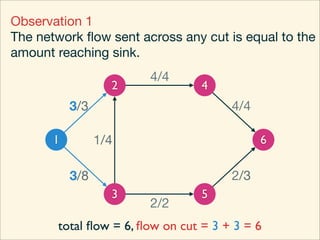
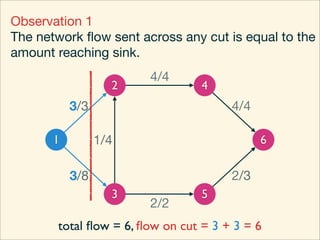
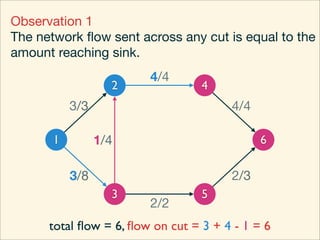
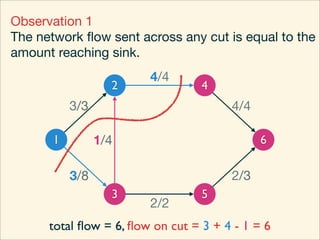
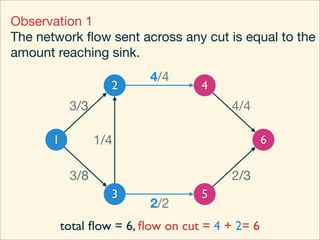
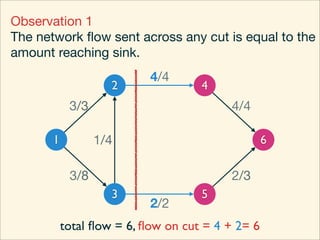
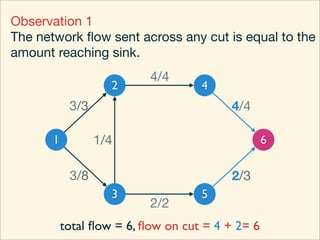
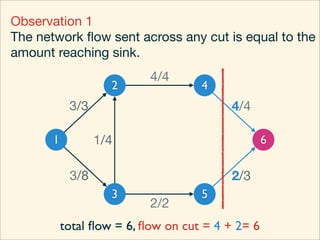
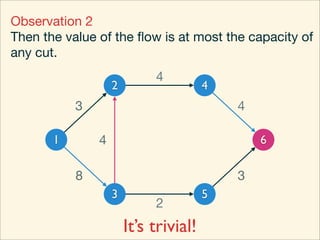
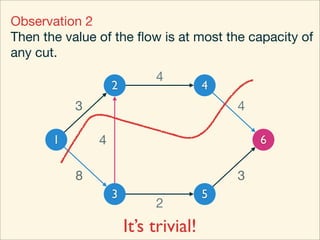
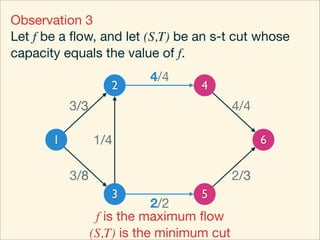
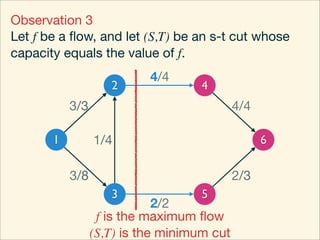
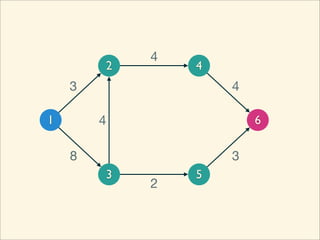
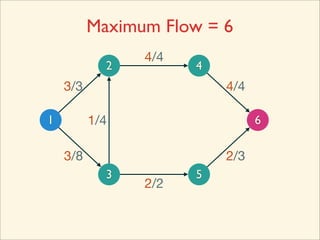
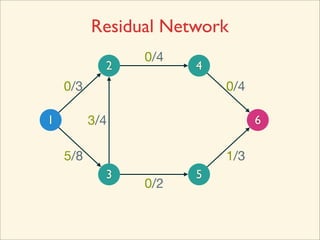
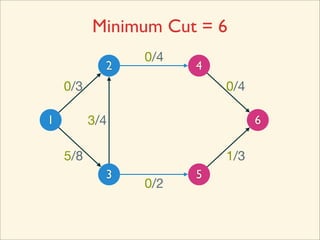
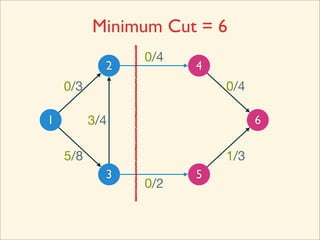
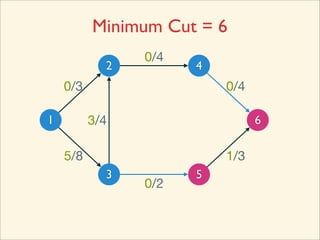
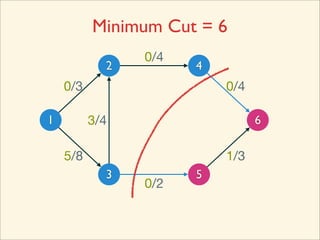
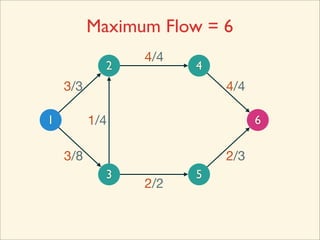
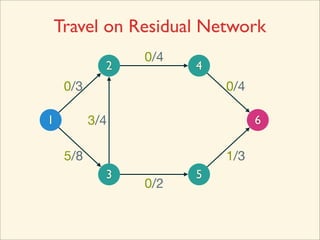
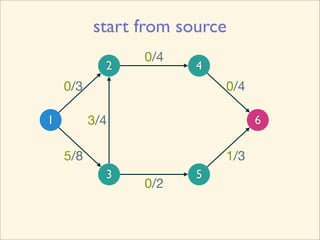
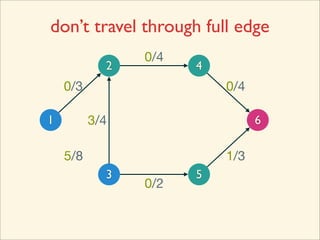
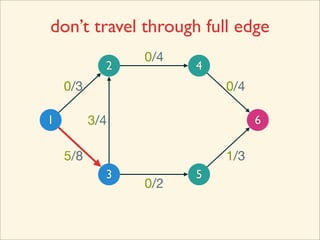
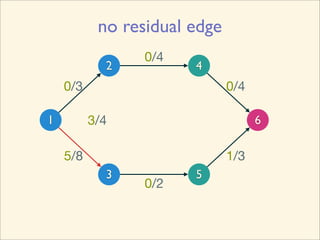
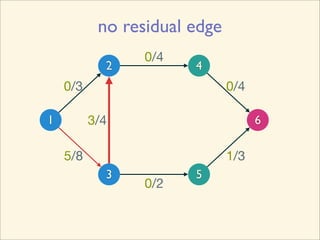
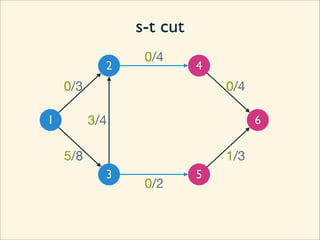
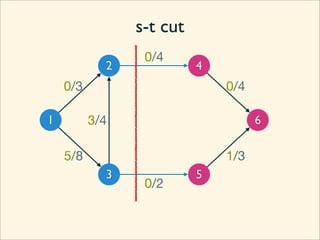
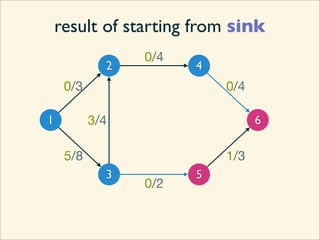
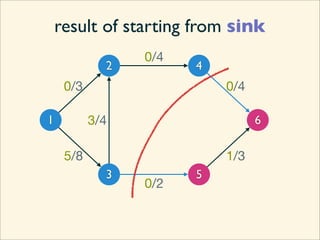
The document discusses minimum cuts in graphs. It defines a minimum cut as a partition of the vertices of a graph into two disjoint subsets such that the number/weight of edges between the two subsets is minimized. For directed graphs, the cut-set of a cut consists only of edges going from one subset to the other. The maximum flow minimum cut theorem states that the maximum amount of flow passing from a source to sink node is equal to the capacity of the minimum s-t cut.