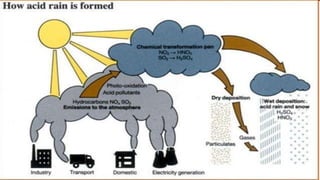
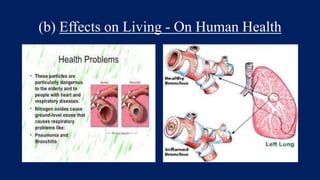
Acid rain is caused by sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides emitted from the burning of fossil fuels. It damages buildings, statues, and other structures made of materials like marble and limestone. It also harms plants and aquatic life by making soils and waters more acidic. The Taj Mahal has been affected by acid rain due to emissions from a nearby oil refinery, causing the marble to discolor. Remedial measures include installing scrubbers in factory chimneys and converting vehicles and energy production to less polluting methods.