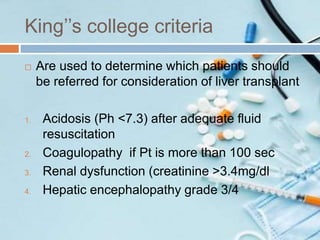
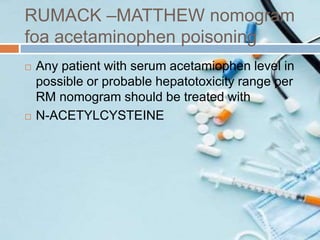
This document discusses acetaminophen poisoning, including its metabolism, toxicity, signs and symptoms, treatment with N-acetylcysteine, and prevention. Acetaminophen toxicity results from formation of a reactive intermediate metabolite, NAPQI, which can cause hepatocellular damage in overdose by overwhelming glutathione stores. A toxic dose is above 200mg/kg in children or supratherapeutic doses above 75mg/kg/day. Treatment involves decontamination, monitoring acetaminophen levels, and administering N-acetylcysteine to replenish glutathione if levels are above the toxic range or if liver enzymes are elevated. Education is needed to prevent misuse and overdose.









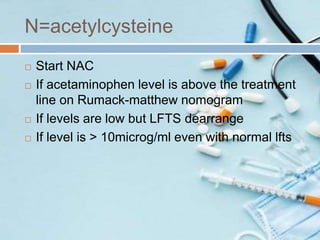

![NAC
Most effective when initiated within 8 hr of
ingestion
NAC available both oral and iv
DOSE ]ORAL :140mgKG loading,followed by
70mgkg every 4hr for 17 doses
(MUCOMYST)
DOSE IV:150mg/kg iv over 1 hr, followed by
50mg kg over 4 hours, followed by 100mg/kg
over 16 hrs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acetaminophenpoisoning-220309191657/85/Acetaminophen-poisoning-13-320.jpg)