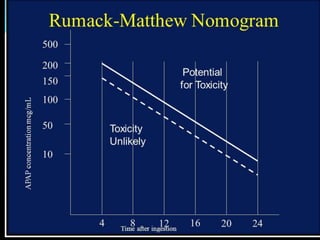
This presentation discusses paracetamol toxicity and provides information on its definition, history of use, therapeutic uses, toxicokinetics, mechanisms of toxicity, clinical features of acute and chronic overdose, diagnosis, and treatment including use of activated charcoal, N-acetylcysteine, methionine, and liver transplantation in severe cases. Key points covered include paracetamol's mechanism of hepatotoxicity through production of the reactive intermediate NAPQI, signs of liver damage that present 2-3 days after overdose, and the importance of administering N-acetylcysteine within 10 hours of ingestion to prevent liver injury.