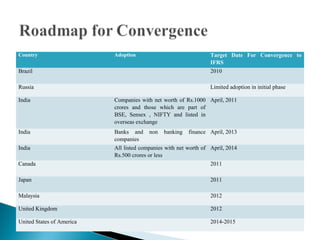
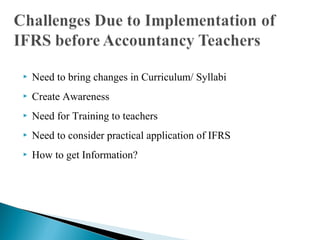
The document discusses the challenges that accountancy teachers in India face with the implementation of International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). IFRS adoption began in India on April 1, 2011, starting with large listed companies. This represents the beginning of a convergence process that will eventually require all companies in India to comply with IFRS. Some of the challenges mentioned include the need to revise curriculums and syllabi to include IFRS, provide training to teachers, develop study materials, and conduct research on applying IFRS in practice. Overall, Indian educational institutions need to better coordinate with standard-setting bodies to facilitate the transition to IFRS.