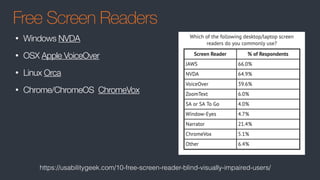
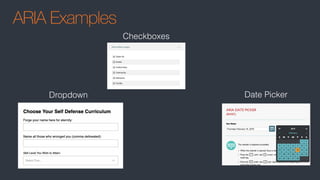
The document discusses web accessibility, highlighting the various disabilities it addresses and the importance of compliance with standards like WCAG 2.1. It outlines the legal landscape surrounding accessibility, emphasizing that while specific regulations may be pending, the need for accessible web design remains critical. Additionally, it provides a checklist for developers to implement best practices in web accessibility and references various resources and tools to assist in compliance.