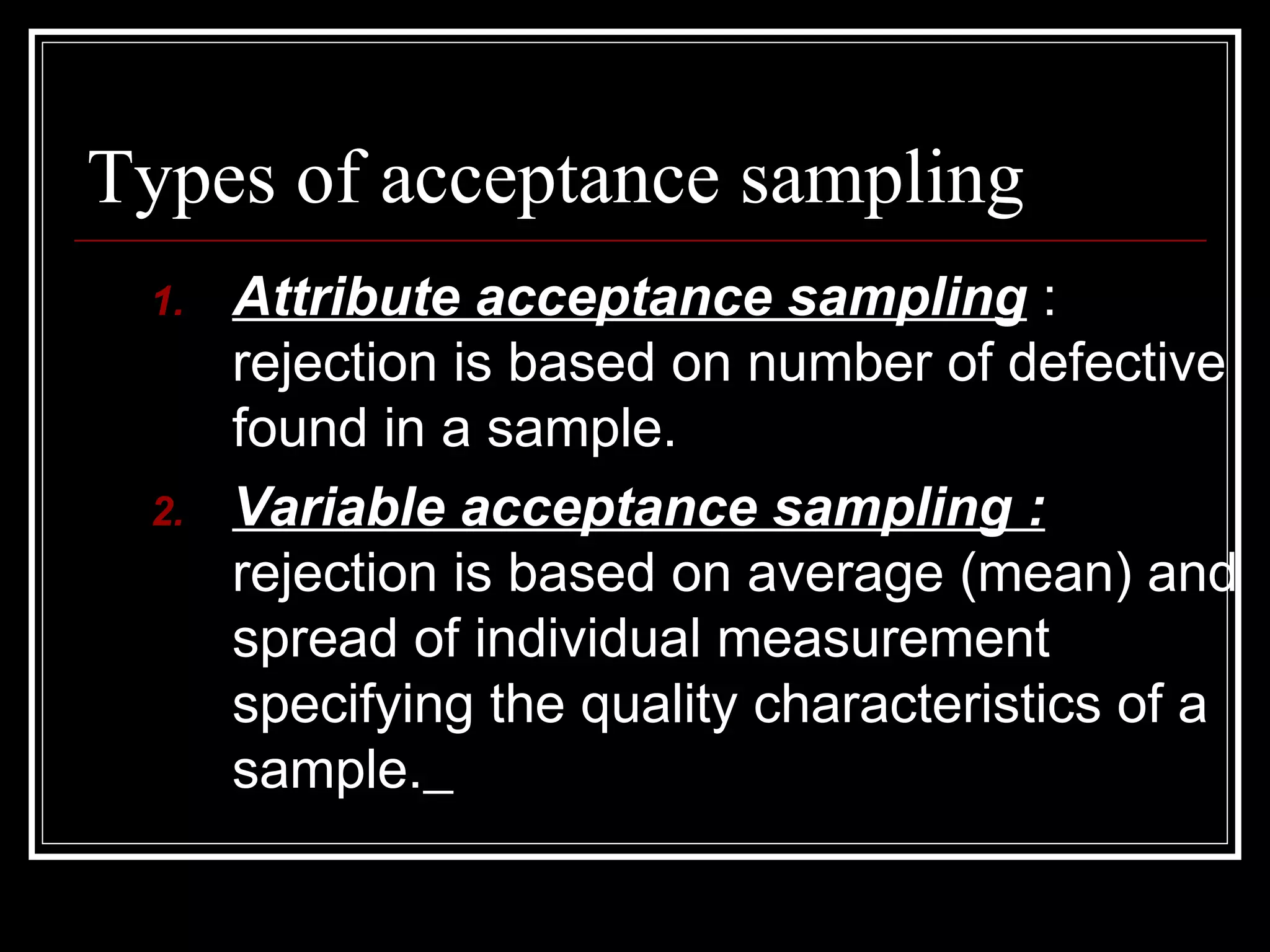
The document discusses acceptance sampling, a method for deciding whether to accept or reject lots based on sample inspection, emphasizing its cost-effectiveness compared to 100% inspection. It outlines the types of acceptance sampling, risks involved, advantages such as reduced production costs and improved efficiency, and limitations like the potential for incorrect decisions. The acceptance sampling procedure is detailed along with key terms associated with it.