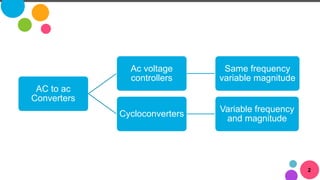
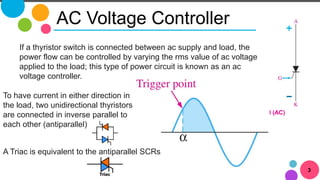
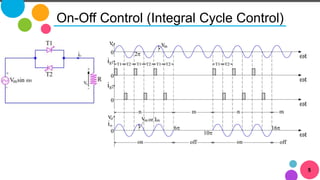
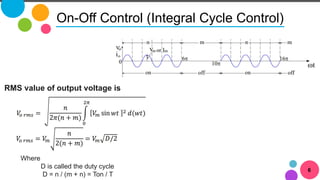
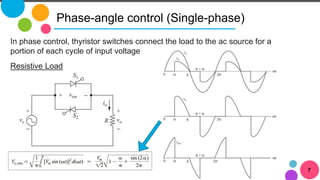
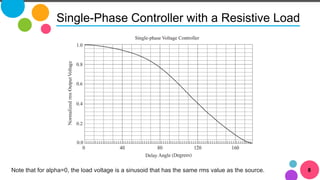
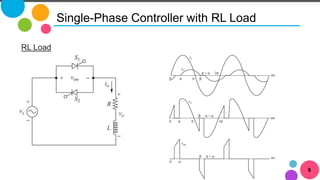
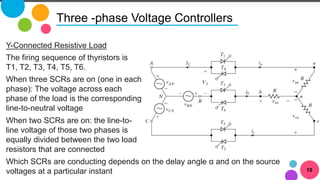
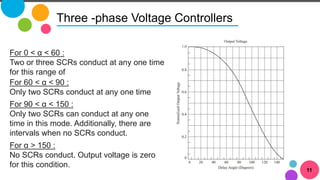
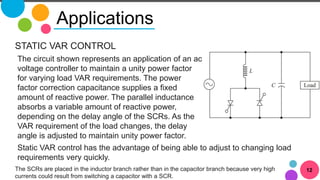
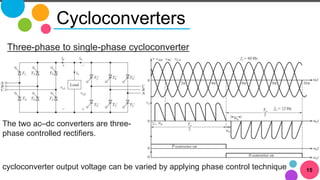
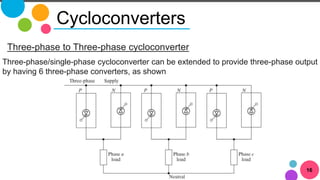
The document discusses AC to AC converters, detailing various types such as AC voltage controllers and cycloconverters. AC voltage controllers use thyristors for power flow control through on-off and phase-angle control methods. Cycloconverters convert AC power from one frequency to another without intermediate links and are classified based on their phase connections.