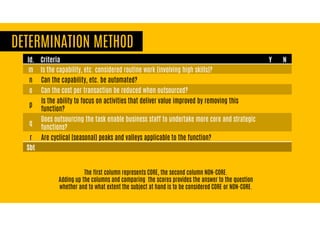
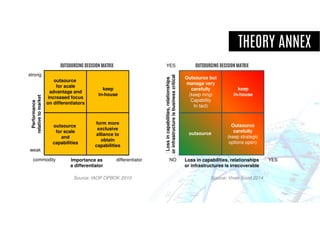
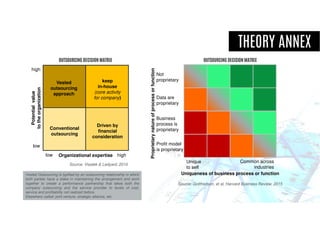
The document discusses criteria for determining whether business functions are core or non-core, emphasizing the importance of strategic capabilities and competitive advantages. It outlines various questions to help businesses assess their activities regarding in-sourcing or outsourcing decisions while cautioning against the potential pitfalls of strictly categorizing functions as core or non-core. Additionally, it highlights the evolving nature of outsourcing, where some routine tasks may be critical for development despite traditional views.