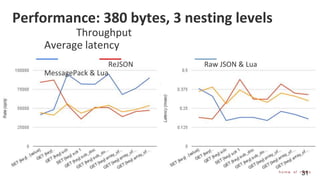
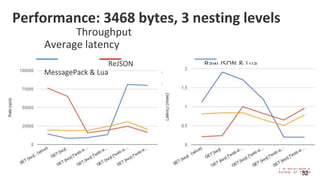
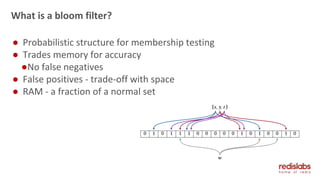
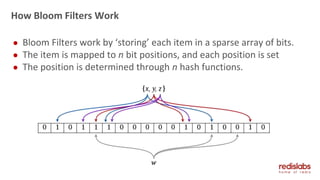
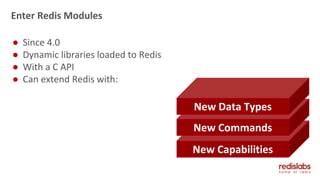
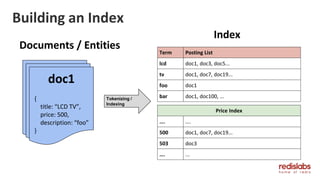
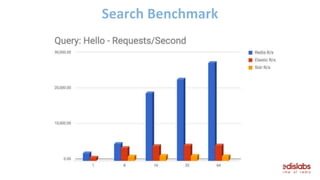
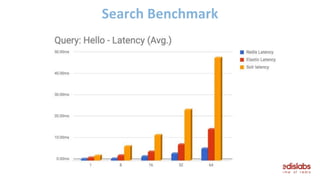
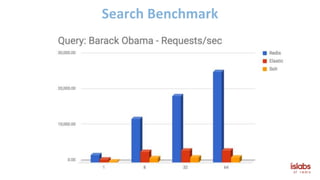
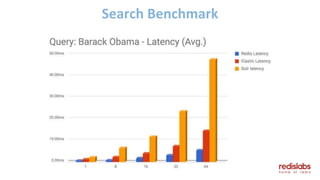
The document provides an overview of Redis Modules, which allow Redis to be extended through dynamically loaded libraries written in C. Some key modules discussed include ReJSON for storing and querying JSON documents natively in Redis, RediSearch for full-text search capabilities, and ReBloom for implementing scalable Bloom filters. Redis Modules can be used to add new data types, commands, and capabilities to Redis in order to adapt it to specific use cases and data models. Performance benchmarks show modules like ReJSON providing significant performance advantages over alternatives that rely on Redis' core data structures and Lua scripting.



![Simplicity: Data Structures - Redis’ Building Blocks
Lists
[ A → B → C → D → E ]
Hashes
{ A: “foo”, B: “bar”, C: “baz” }
Bitmaps
0011010101100111001010
Strings
"I'm a Plain Text String!”
Bit field
{23334}{112345569}{766538}
Key
6
2
Streams
→{id1=time1.seq1(A:“xyz”, B:“cdf”),
d2=time2.seq2(D:“abc”, )}→
Hyperloglog
00110101 11001110
Sorted Sets
{ A: 0.1, B: 0.3, C: 100 }
Sets
{ A , B , C , D , E }
Geospatial Indexes
{ A: (51.5, 0.12), B: (32.1, 34.7)
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/redislabsmodules-indiatour-oct2017-171115055318/85/Redis-Modules-Redis-India-Tour-2017-6-320.jpg)






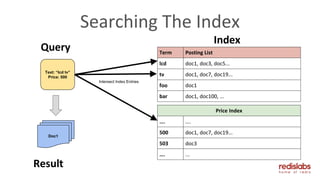



![Searching
FT.SEARCH products
“@title|body:(lcd 42|44|50)
@cats:(tvs|electronics )
@brand:(samsung|sony)
@price:[200 500]”
LIMIT 0 20
SORTBY price DESC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/redislabsmodules-indiatour-oct2017-171115055318/85/Redis-Modules-Redis-India-Tour-2017-20-320.jpg)




![ReJSON "demo"
29
> JSON.SET foo . '{"foo": "bar", "list": [1,2,3,4]}'
> JSON.GET foo .
"{"foo":"bar","list":[1,2,3,4]}"
> JSON.GET foo foo
""bar""
> JSON.GET foo .list[1]
"2"
> JSON.ARRAPPEND foo .list 1337
> JSON.ARRAPPEND foo .list 1337
> JSON.GET foo .list
"[1,2,3,4,1337,1337]"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/redislabsmodules-indiatour-oct2017-171115055318/85/Redis-Modules-Redis-India-Tour-2017-29-320.jpg)