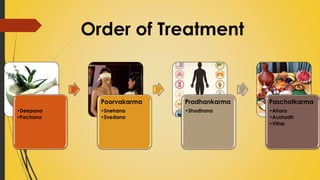
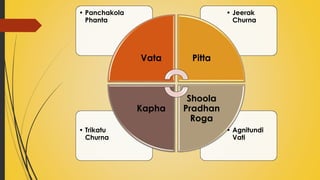
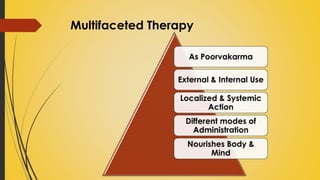
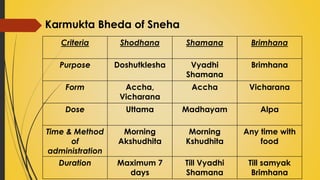
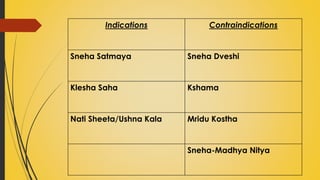
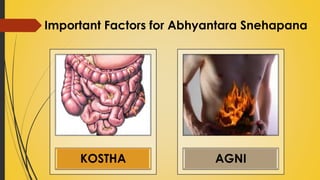
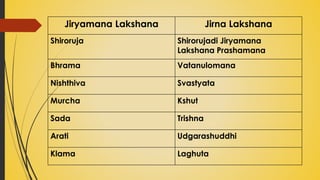
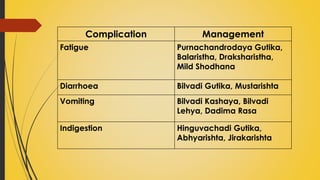
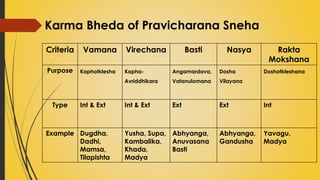
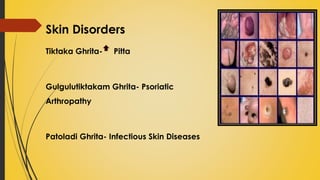
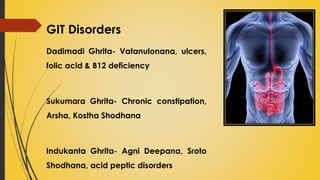
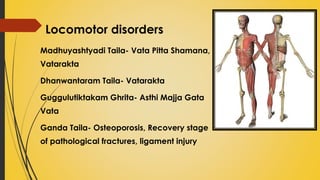
This document provides information on Abhyantara Snehapana (internal oleation therapy). It discusses the types of internal oleation including Accha Sneha (pure oleation), Pravicharana Sneha (oleation with adjuncts), and Sadhya Sneha (quick oleation). It outlines the procedures, indications, contraindications, dos and don'ts of internal oleation therapy based on Panchakarma principles. The key goal is to induce Samyak Snigdha Lakshanas (proper oleated features) through internal administration of oils and fats.