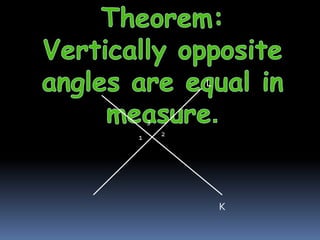
The document contains proofs of several geometric theorems:
1) Intersecting lines L and K have vertically opposite angles 1 and 2 that are equal.
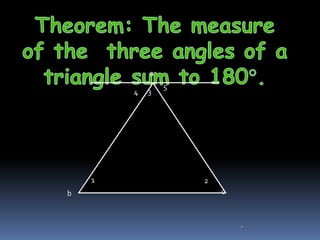
2) The interior angles of any triangle sum to 180 degrees.
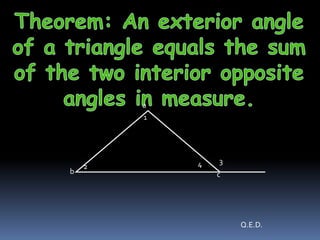
3) The exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two interior opposite angles.
4) In an isosceles triangle, the base angles are equal.
5) Corresponding angles are equal when two parallel lines are intersected by a transversal.
6) Angles opposite equal sides of a triangle are equal.
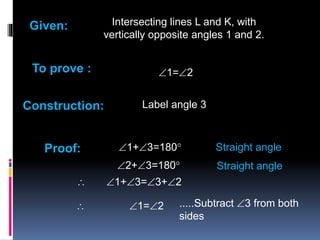





![Given: AB||CD and EFGH is a transversal.
To Prove: 1 = 2
Proof : 1= 5 [1] v .o .a
5= 2 [2] corresponding
angles
from equation 1 and 2 we get ,
1= 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-140829095529-phpapp02/85/a-very-nice-ppt-for-learning-theorems-10-320.jpg)


