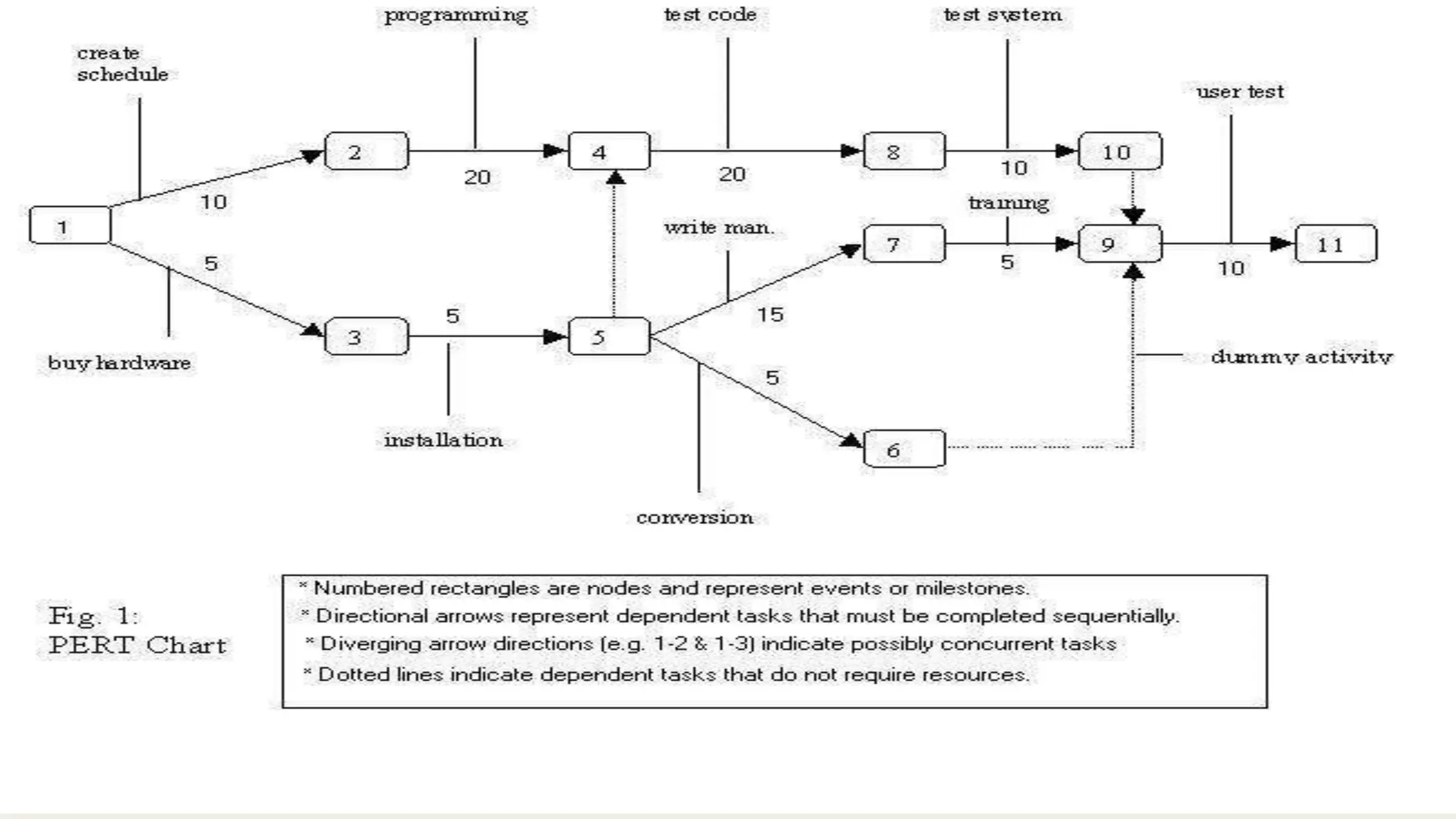
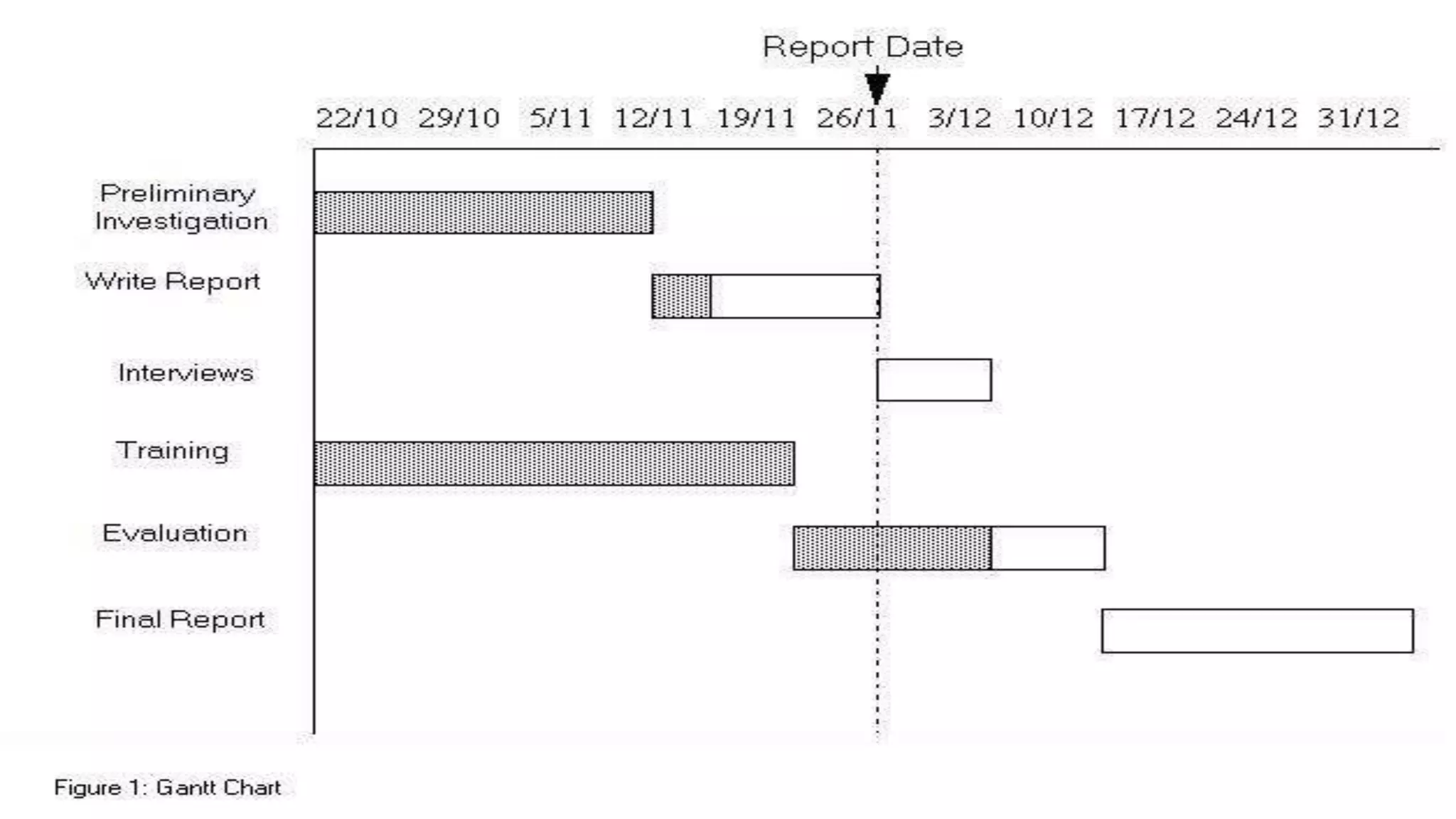
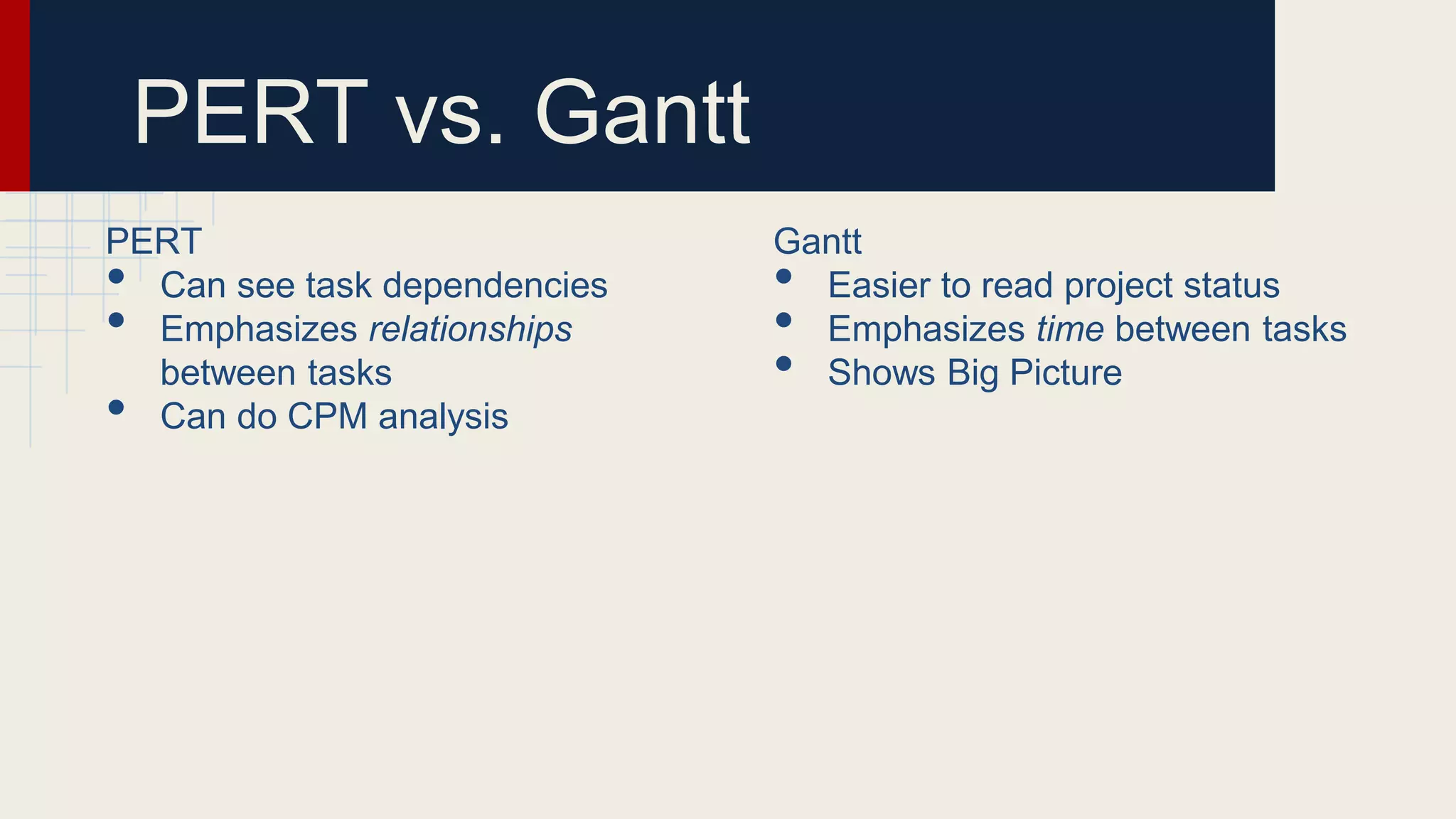
Project management involves applying knowledge, skills, and techniques to execute projects effectively through processes including initiating, planning, and closing. A project manager is responsible for all aspects of project management, ensuring tasks are completed and evaluated. The document outlines a workshop's purpose and includes key components of project planning and execution, such as defining scope and creating Gantt or PERT charts.