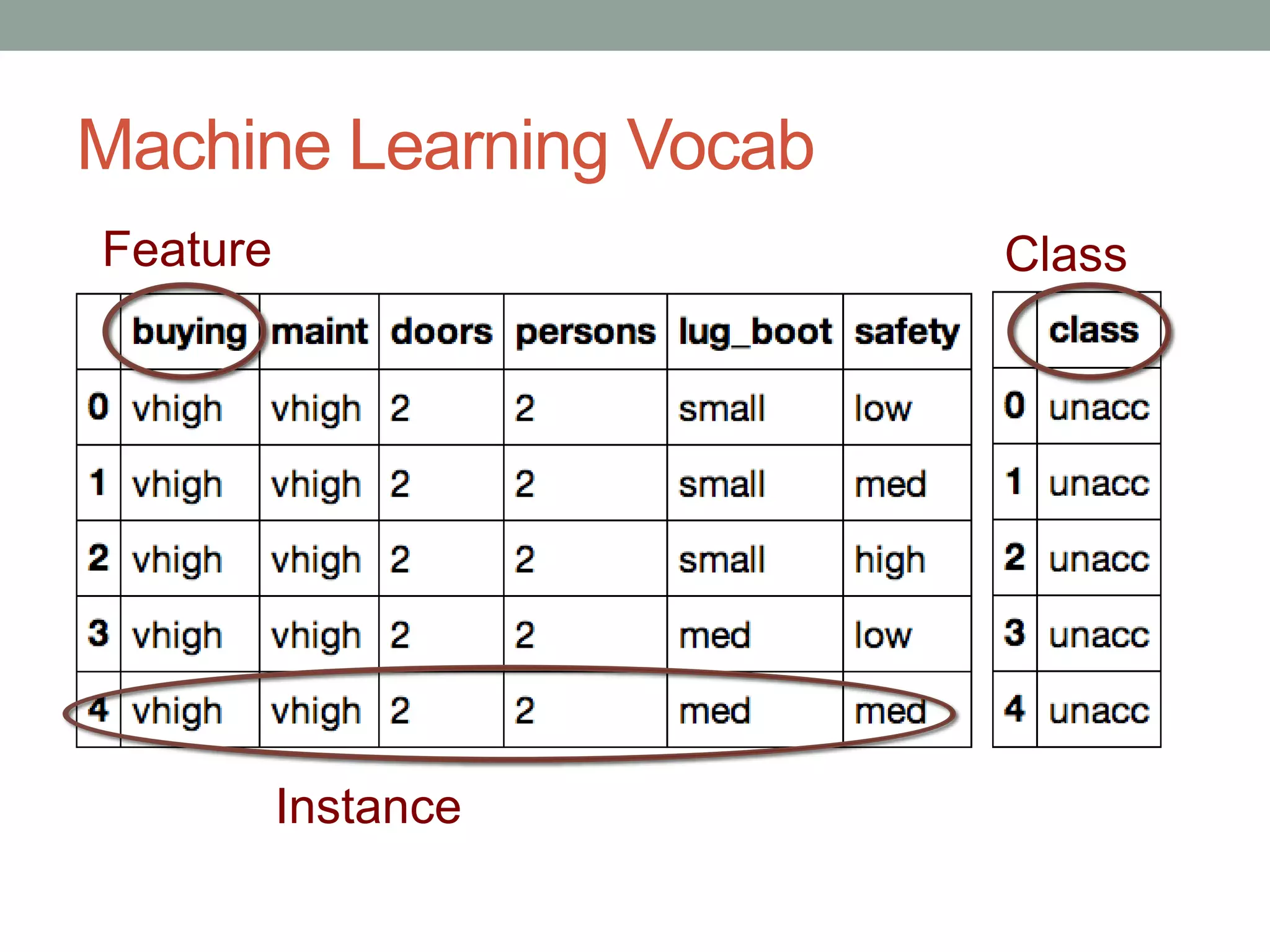
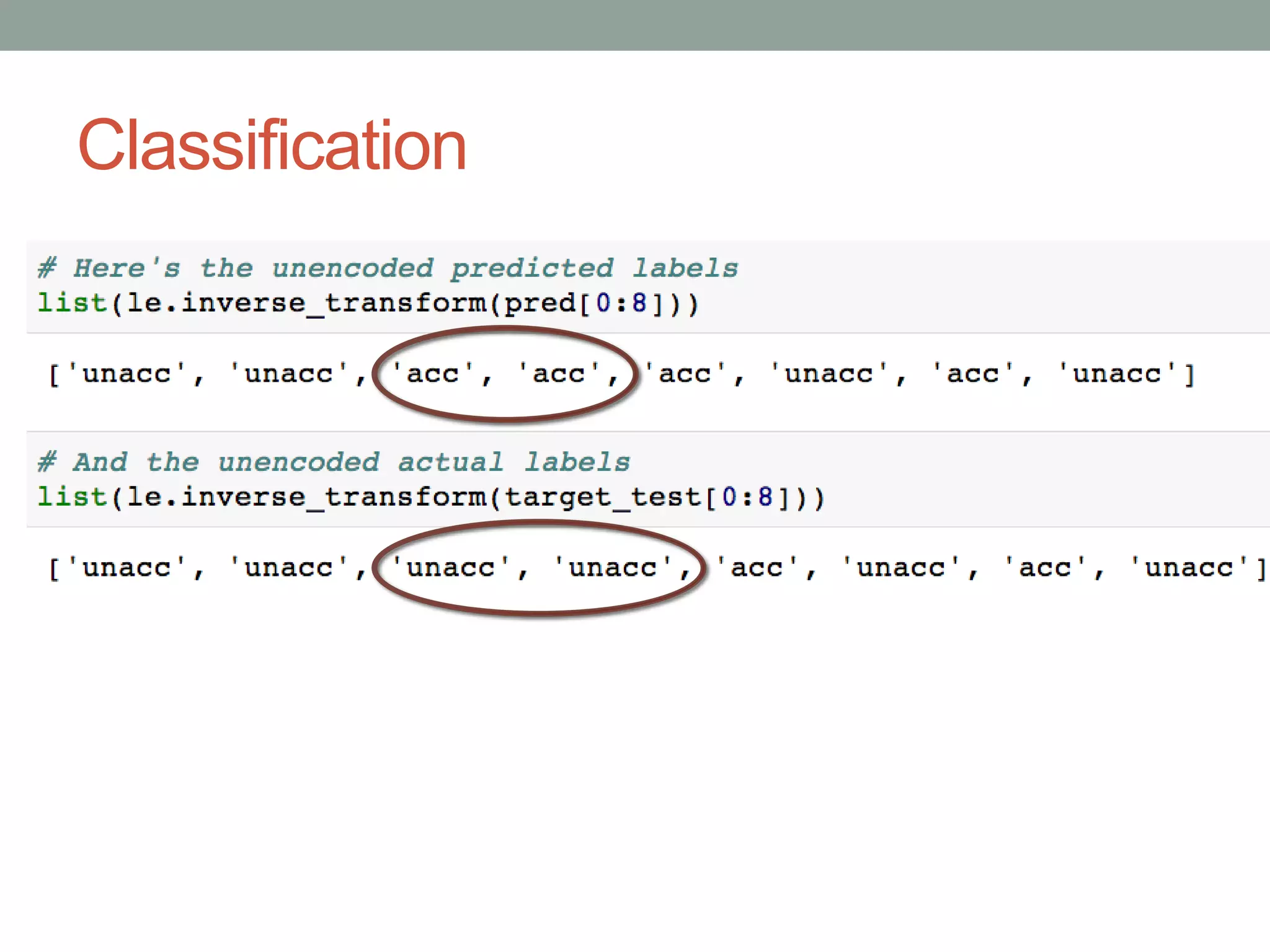
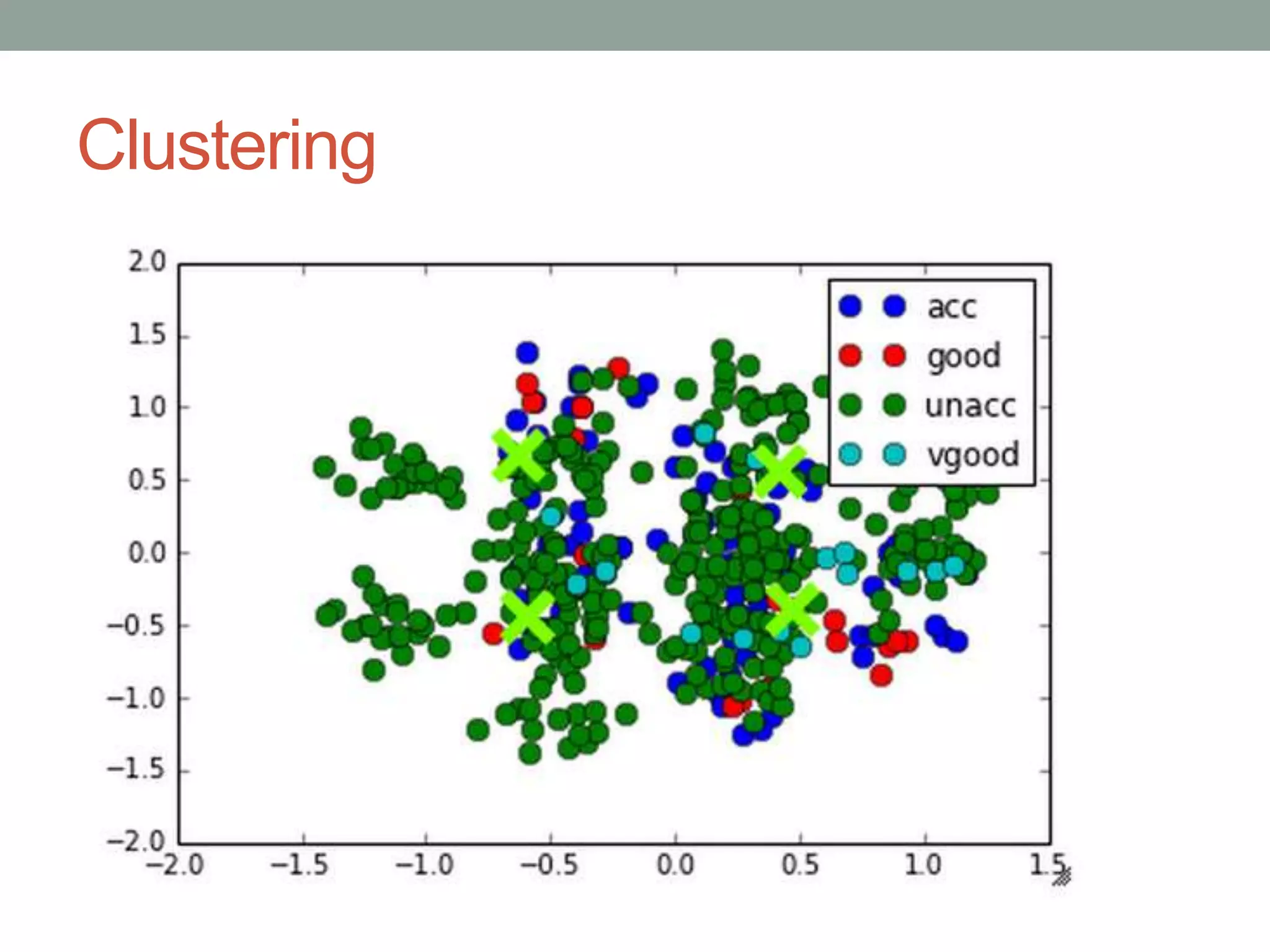
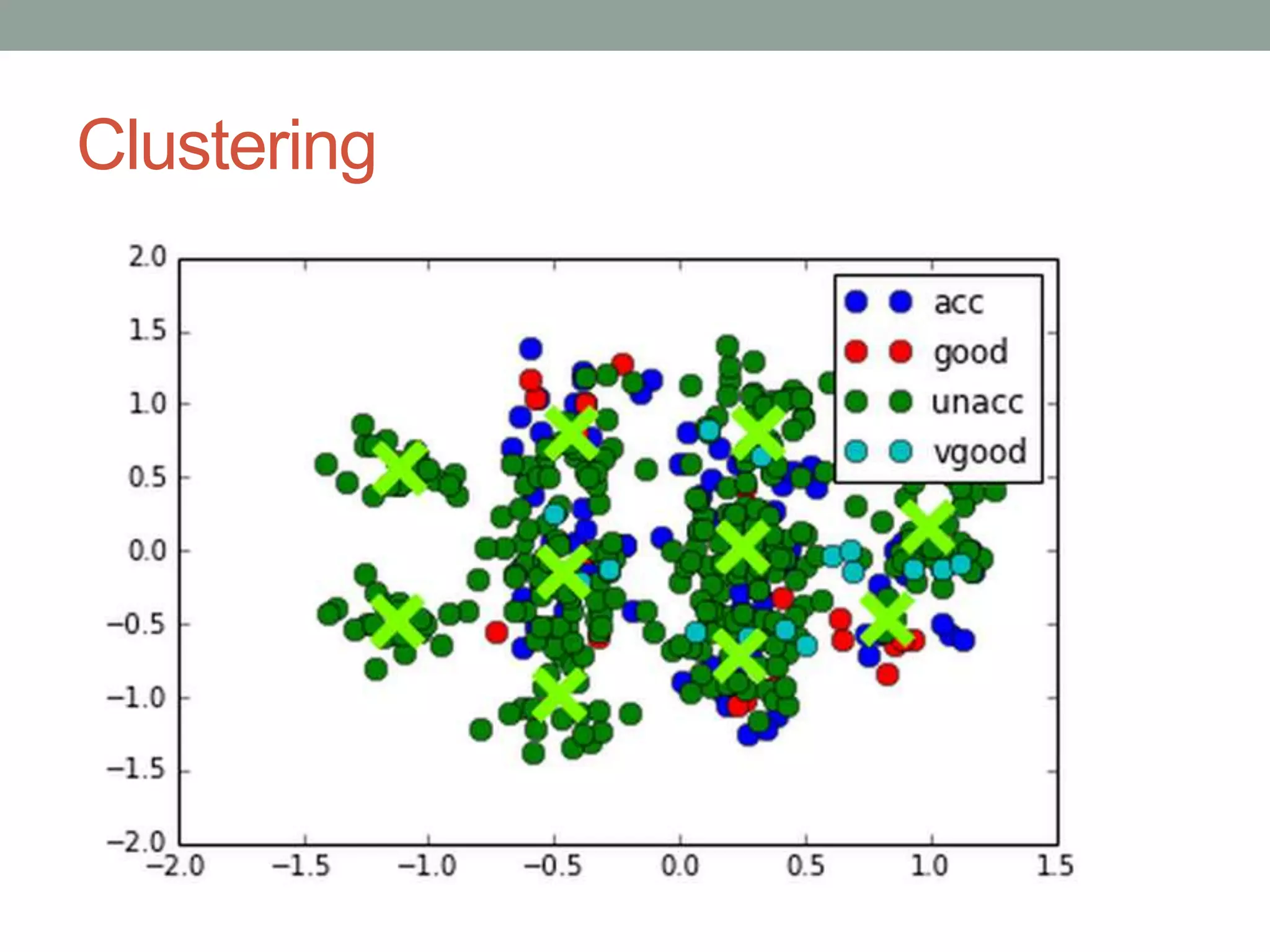
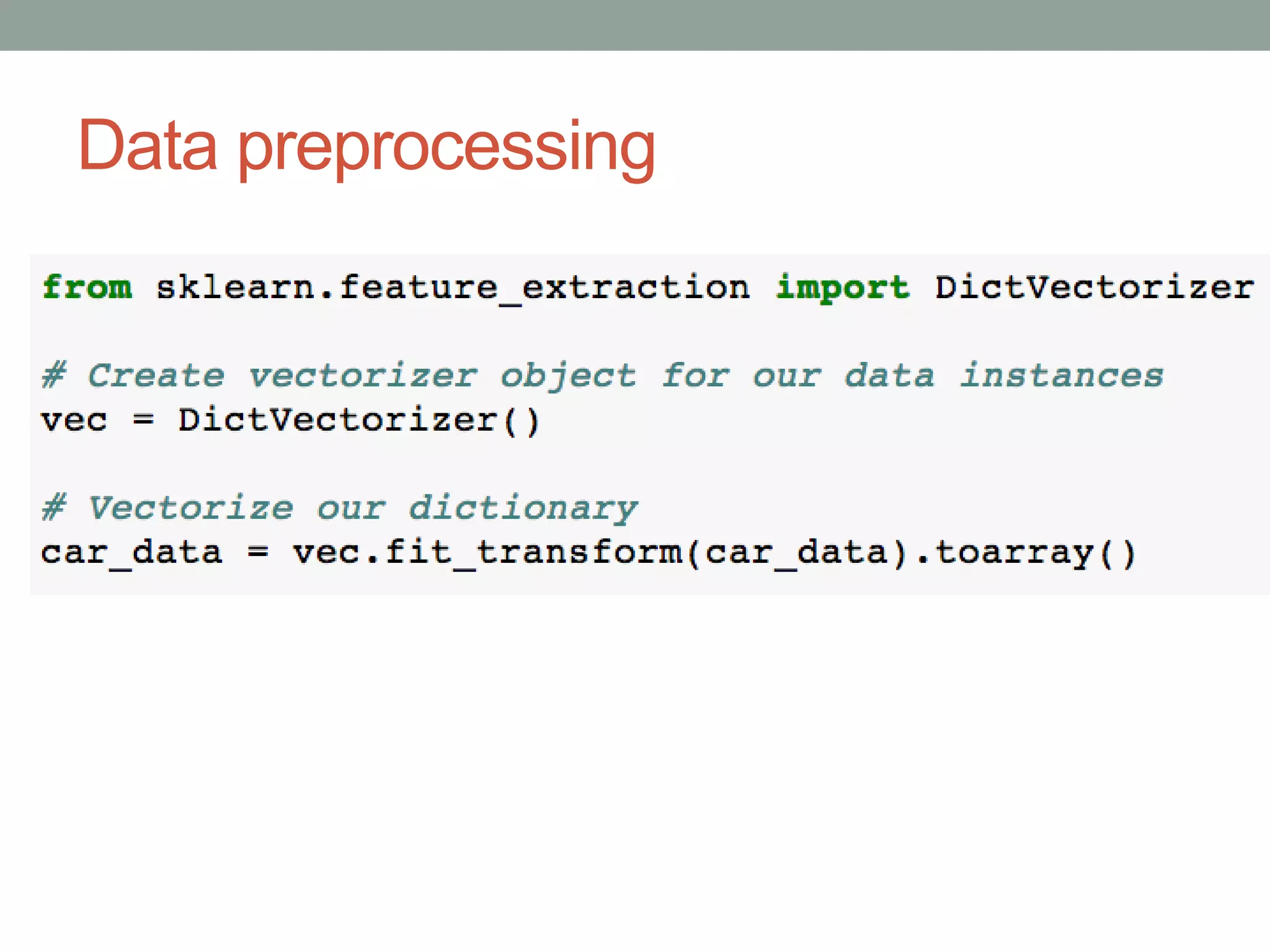
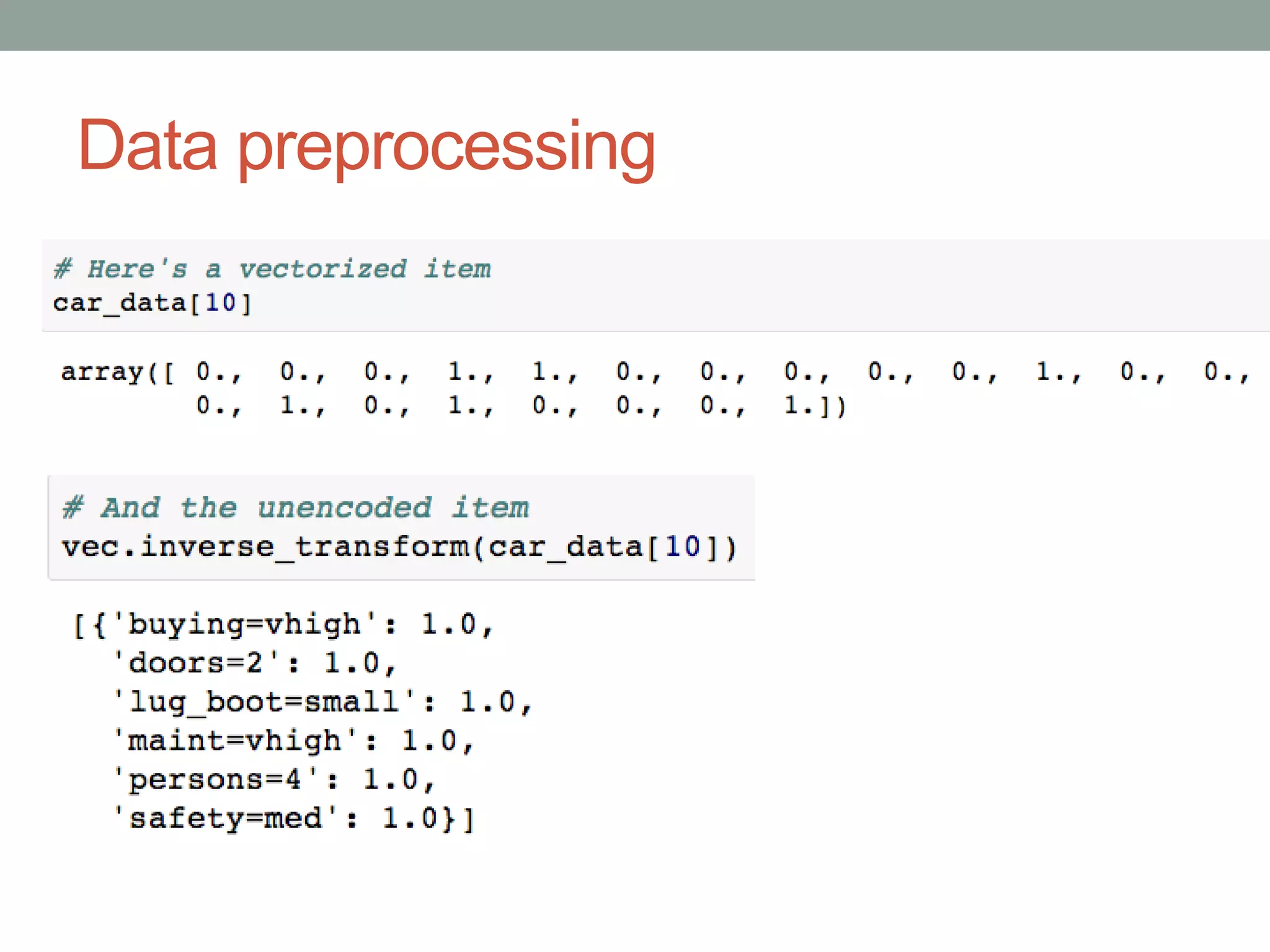
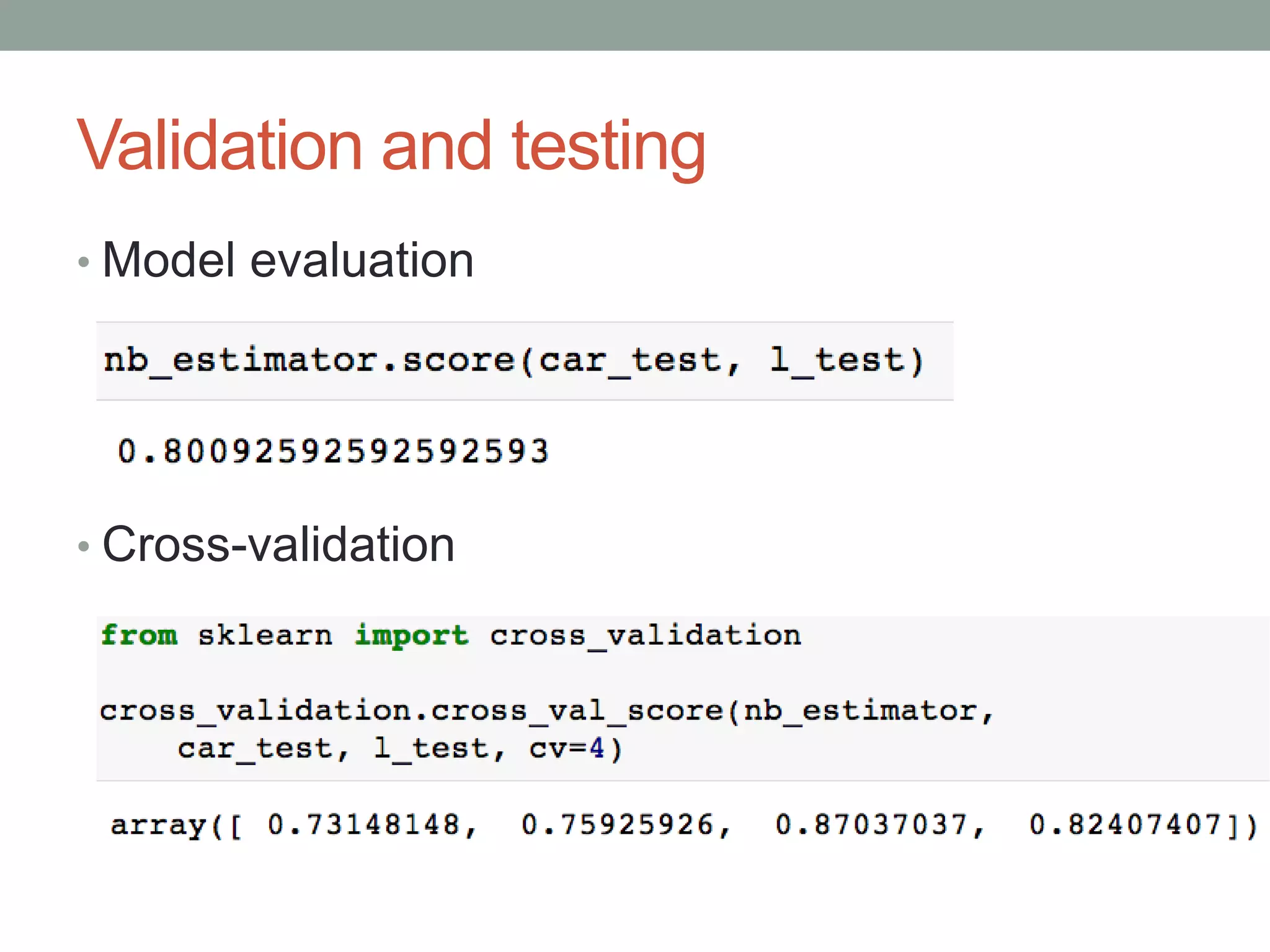
The document is a beginner's guide to machine learning using scikit-learn, covering supervised and unsupervised learning, data preprocessing, and validation strategies. It provides an overview of important machine learning concepts, vocabulary, and practical applications in data analysis. Additionally, it offers resources for learning scikit-learn, including documentation and tutorials.