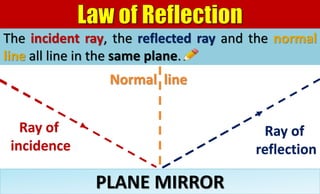
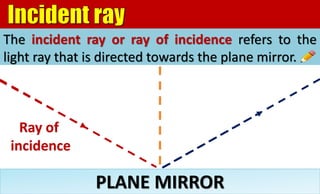
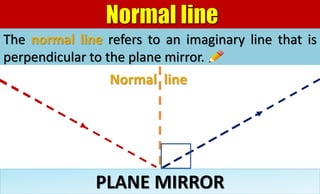
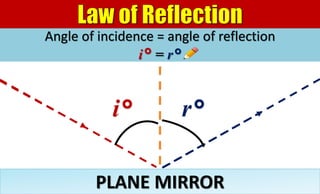
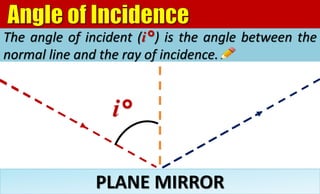
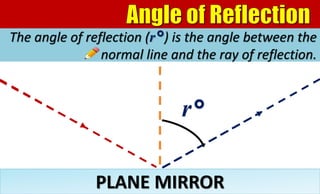
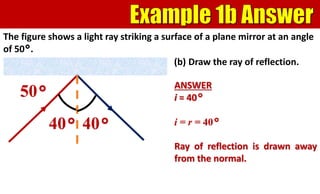
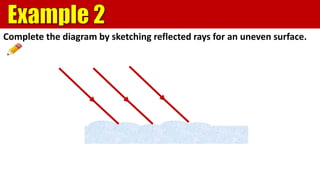
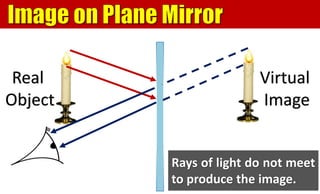
The document explains the behavior of light rays when they interact with a plane mirror, detailing the concepts of incident ray, normal line, and reflected ray, as well as the laws of reflection where the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. It distinguishes between specular reflection on smooth surfaces and diffuse reflection on rough surfaces. Additionally, it describes the characteristics of the virtual images formed by plane mirrors, including their size, orientation, and location relative to the object.