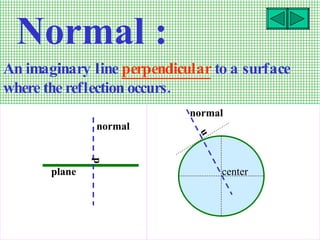
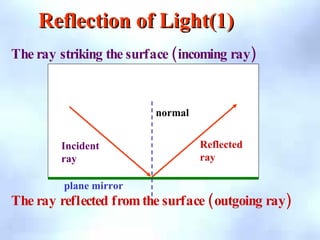
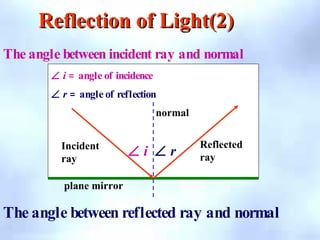
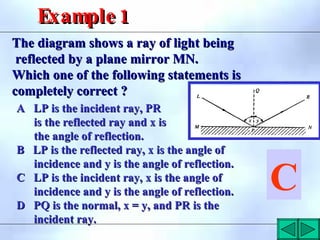
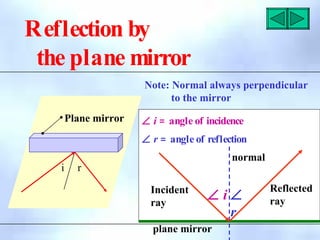
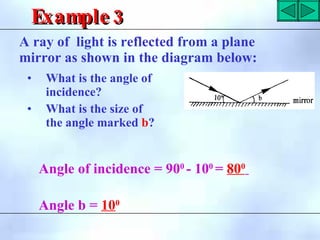
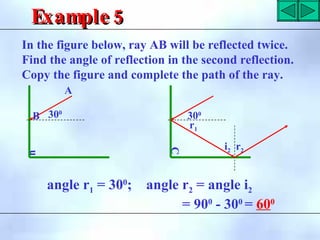
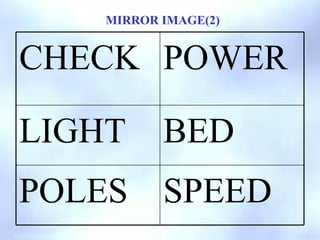
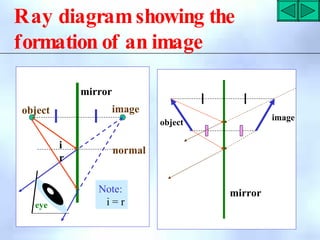
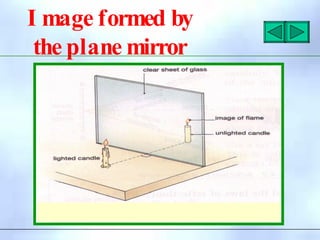
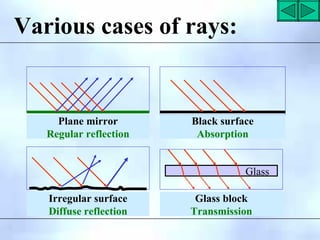
This document defines key terms related to reflection of light, including normal, angle of incidence, and angle of reflection. It states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, and provides examples of using this principle in construction, measurements, and calculations. It also describes the nature of light, light rays, beams of light, reflection, laws of reflection, and image formation using plane mirrors. Examples are provided to illustrate reflection geometry and calculating angles of incidence and reflection.



















![Pe
ris
c
o
p
e
:[Co
nt.]
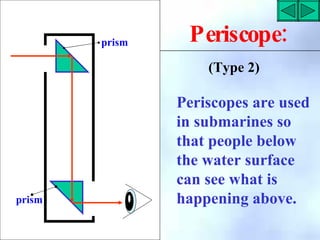
• The periscope consists of two parallel plane
mirrors (or prism) .
• Could you guess at what angle should each
mirror (or prism) be placed ?
• Why ?
• Which type of periscope is better ? Mirror or
prism ? Why ?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reflectionoflight-100829070425-phpapp021-230328235728-139856cc/85/reflectionoflight-100829070425-phpapp02-1-pdf-34-320.jpg)



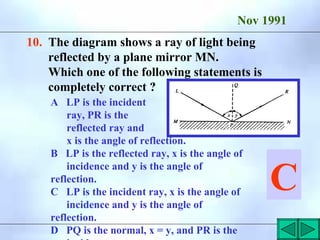
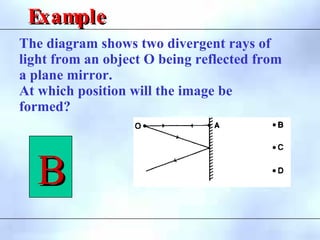
![4. The diagram below shows the position I of the image
formed by a plane mirror of an object O.
(a) Continue the two rays drawn leaving O to show
how they would be reflected at the mirror. [2]
GCE ‘O’ LEVEL Nov 1995
I O](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reflectionoflight-100829070425-phpapp021-230328235728-139856cc/85/reflectionoflight-100829070425-phpapp02-1-pdf-39-320.jpg)
![4.(b) I is a virtual image. Explain the meaning of
this. [2]
(Cont. …) Q. 4 Nov 1995
Since the image, I, is produced by the reflection
of light and cannot project on a screen, there-
fore it is a virtual image.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reflectionoflight-100829070425-phpapp021-230328235728-139856cc/85/reflectionoflight-100829070425-phpapp02-1-pdf-40-320.jpg)