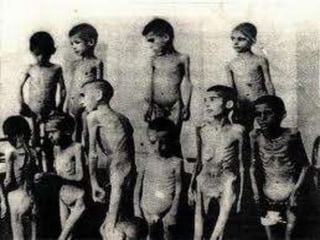
The document provides information on how Hitler and the Nazis utilized various aspects of society and government to consolidate power and propagate their racist ideology. It discusses how Hitler assigned economic recovery to Hjalmar Schacht and aimed for full production and employment through public works programs, resulting in infrastructure projects. It also describes how the Nazis reorganized education, youth groups, women's roles, language and the media to indoctrinate the populace, especially children, with Nazi ideals of Aryan supremacy and anti-Semitism. All dissent was purged and society was tightly controlled and mobilized for Hitler's goals of war and racial conquest in Europe.