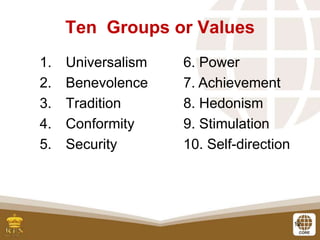
This document discusses values and virtues. It defines values as ideals that create meaning and purpose in a person's life. Examples of universal values from the UN are listed, as well as common workplace values. Ten basic human values are identified from the work of Shalom Schwartz. These values influence and sometimes contradict each other. The document also discusses virtues and provides exercises to identify values behind behaviors.