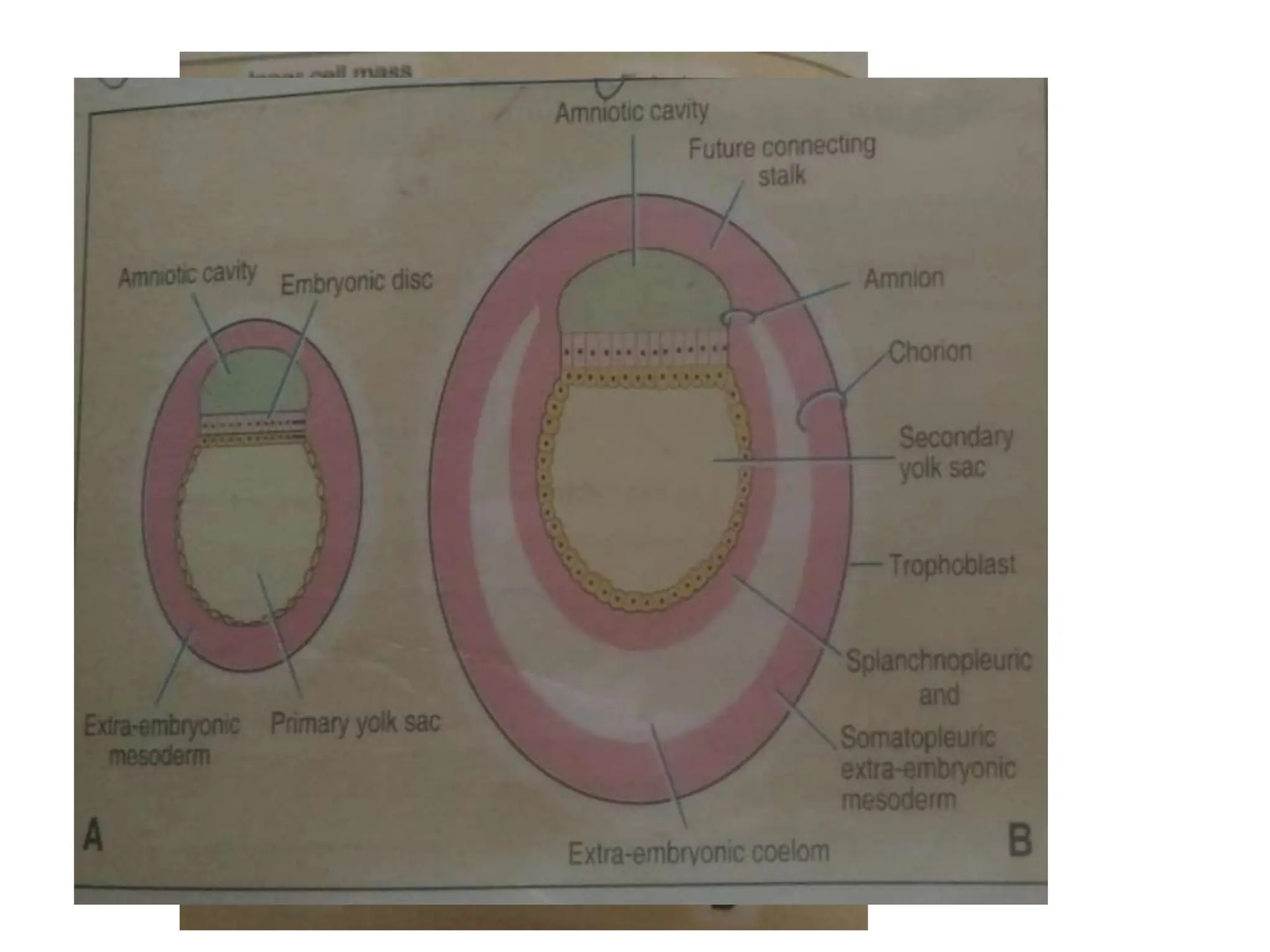
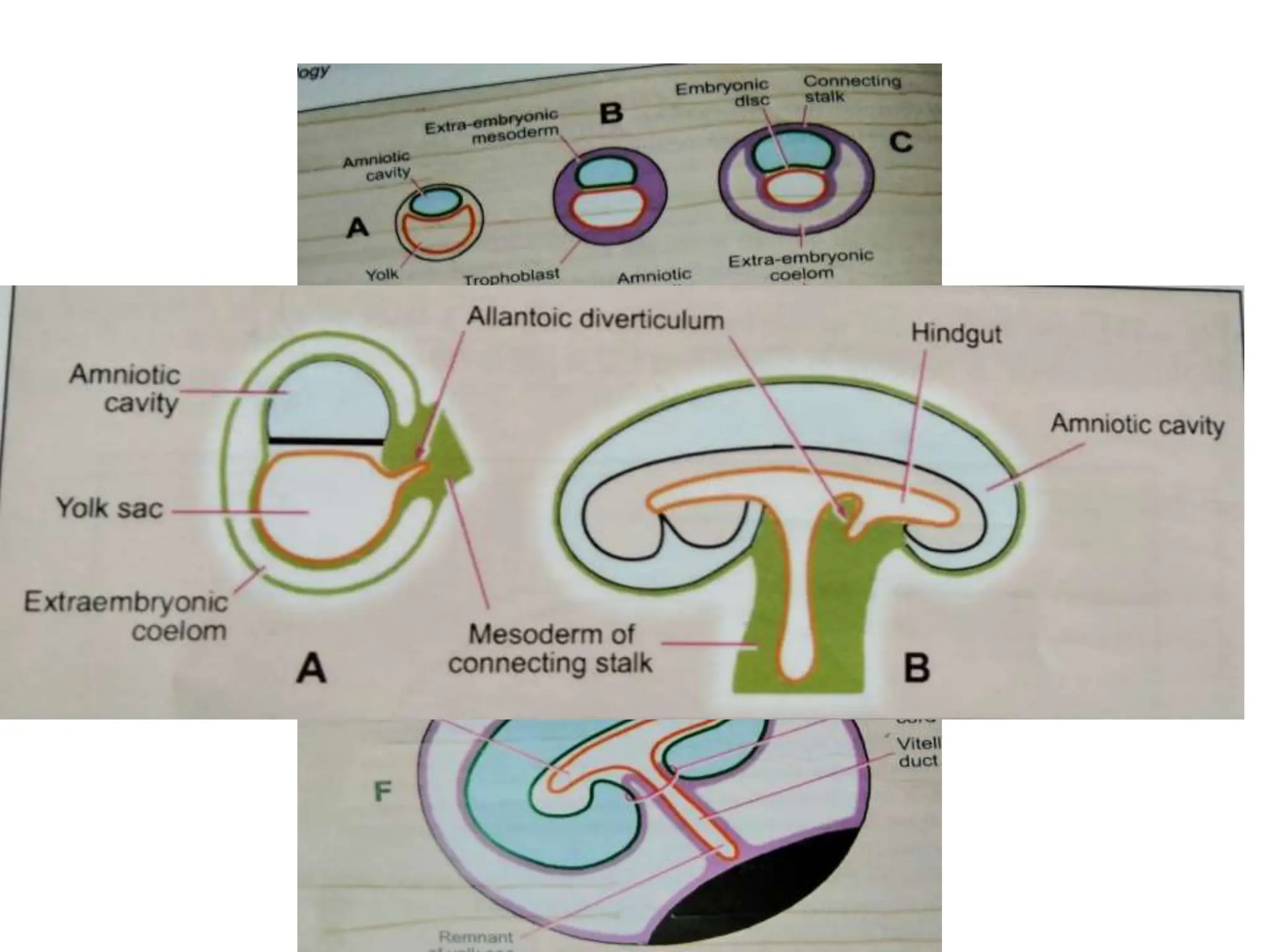
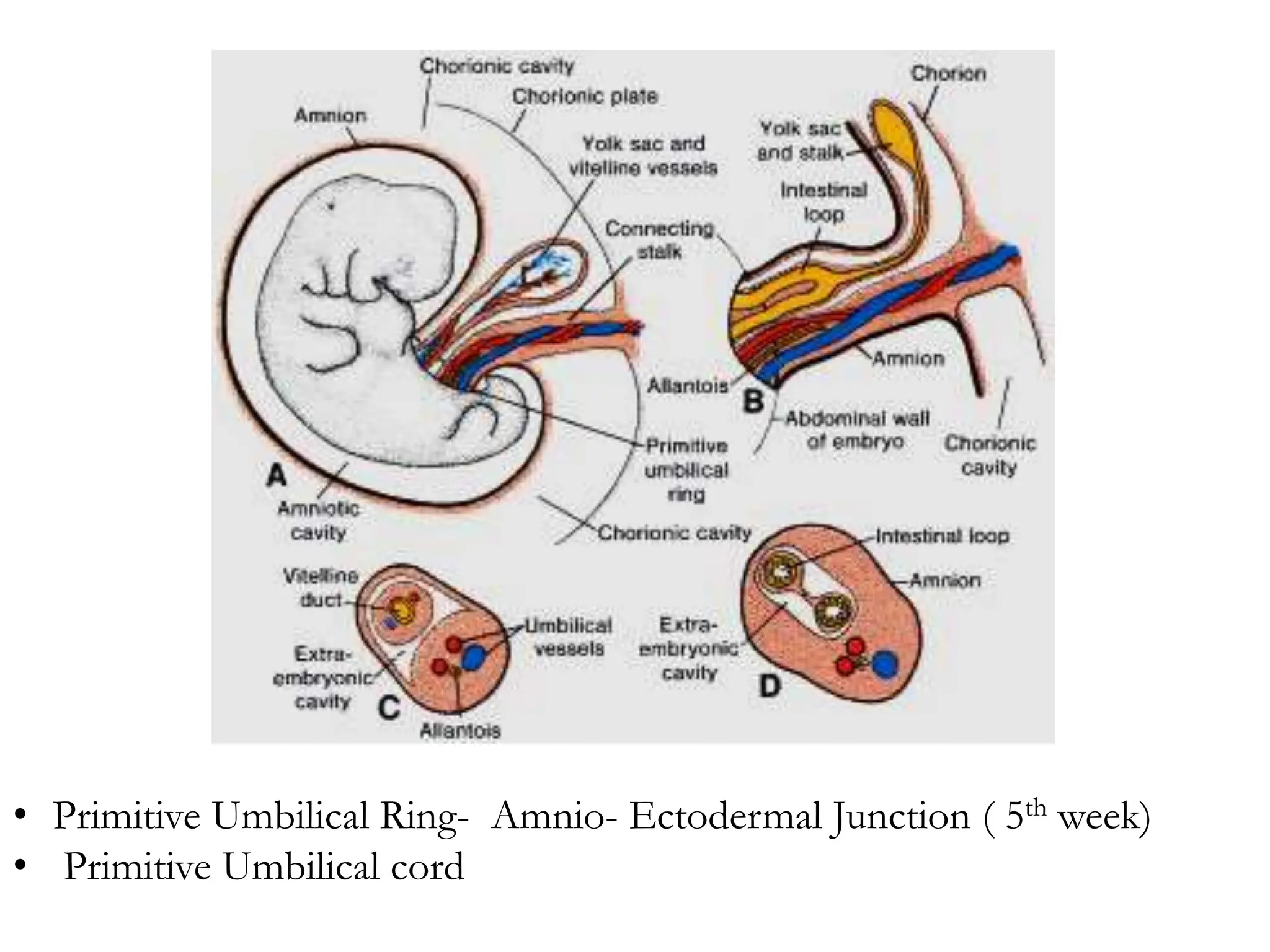
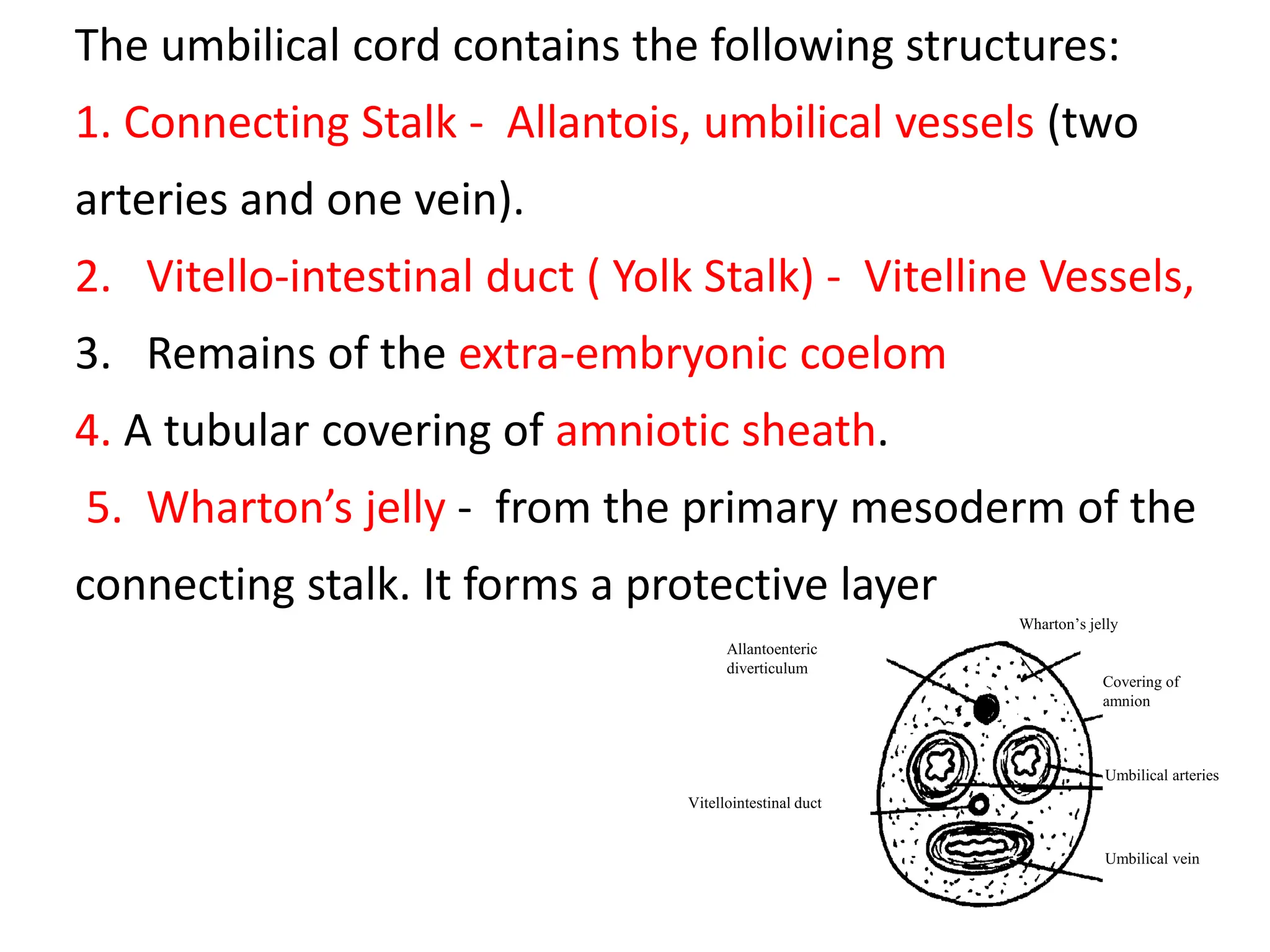
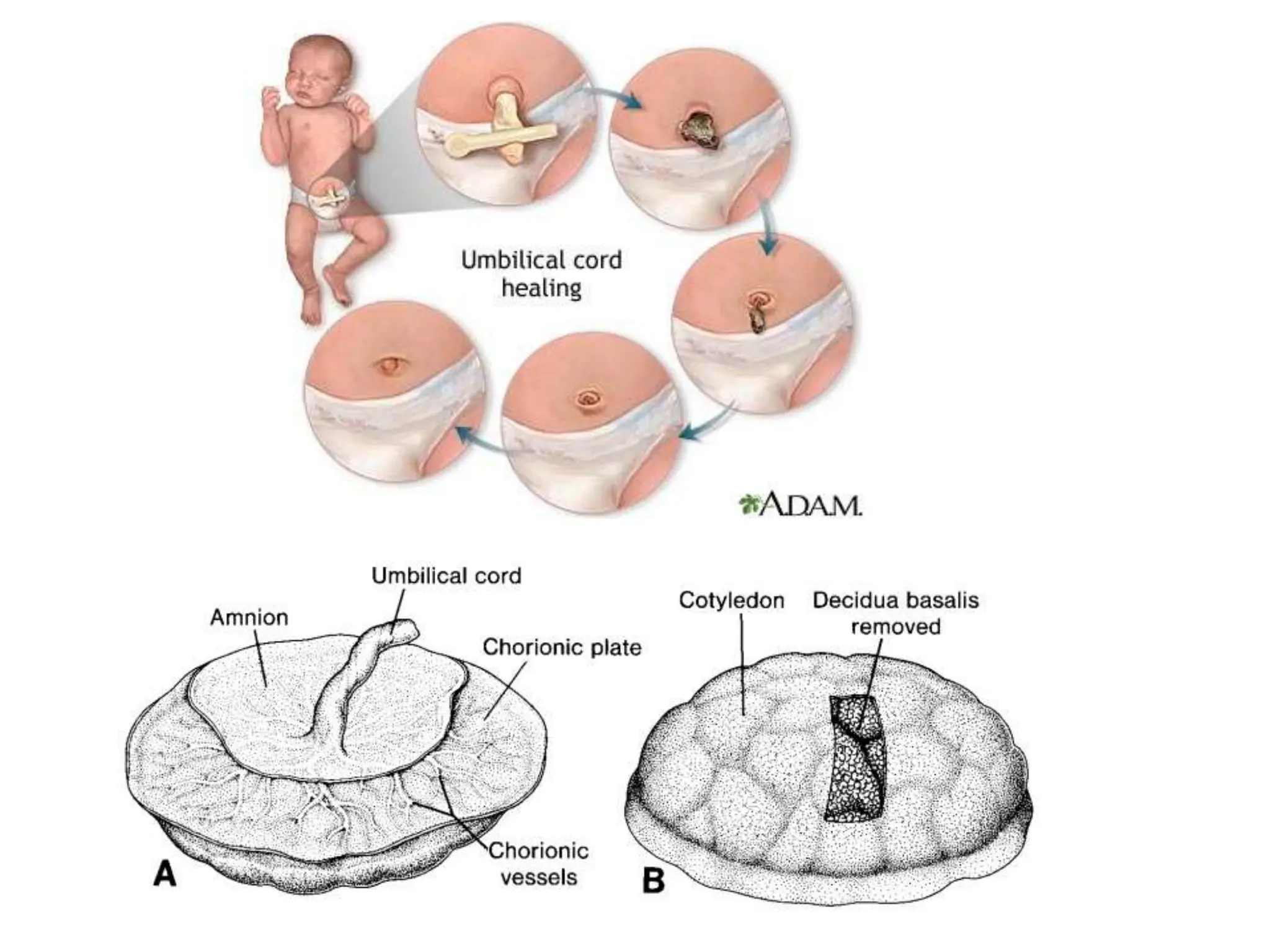
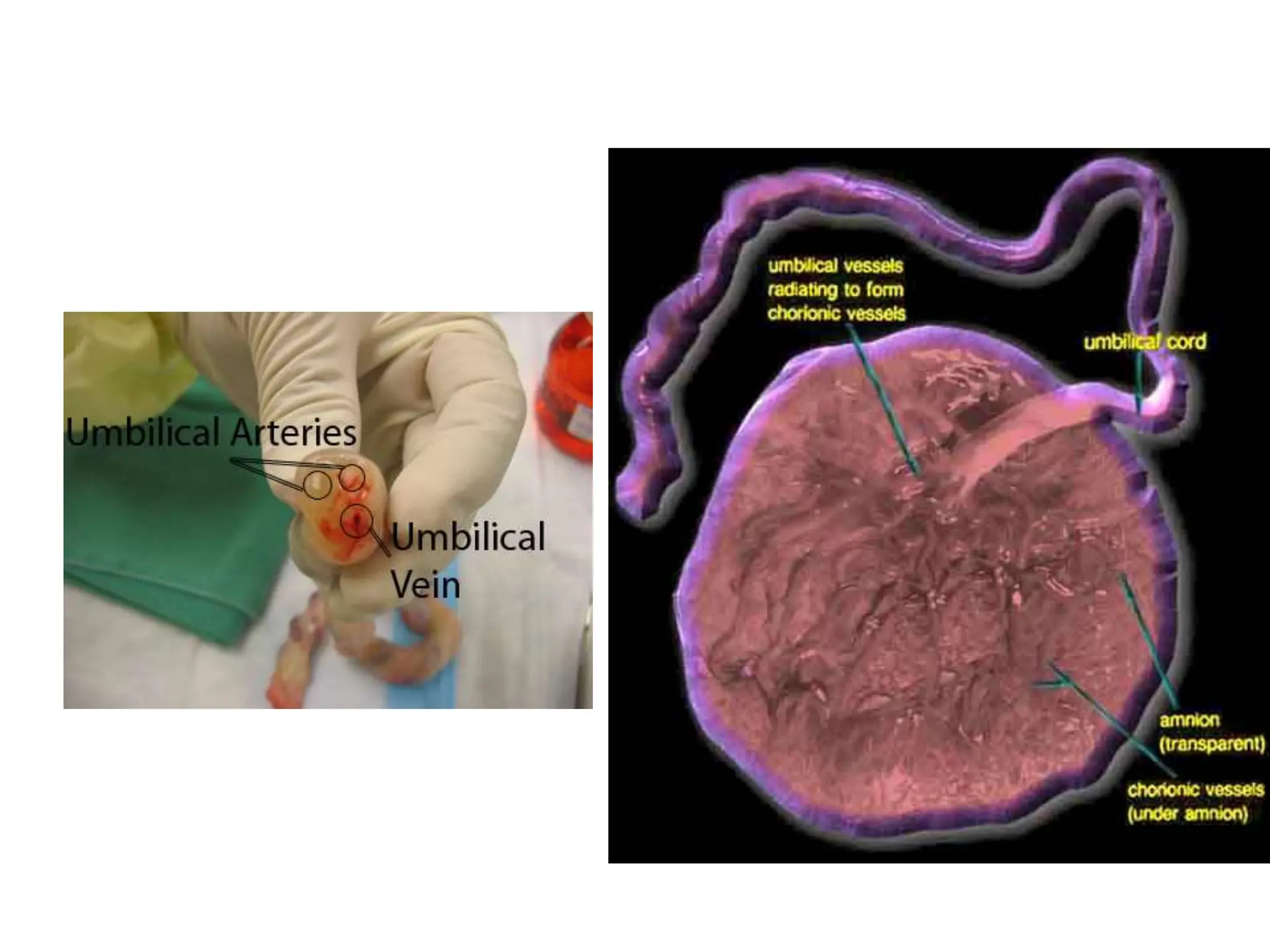
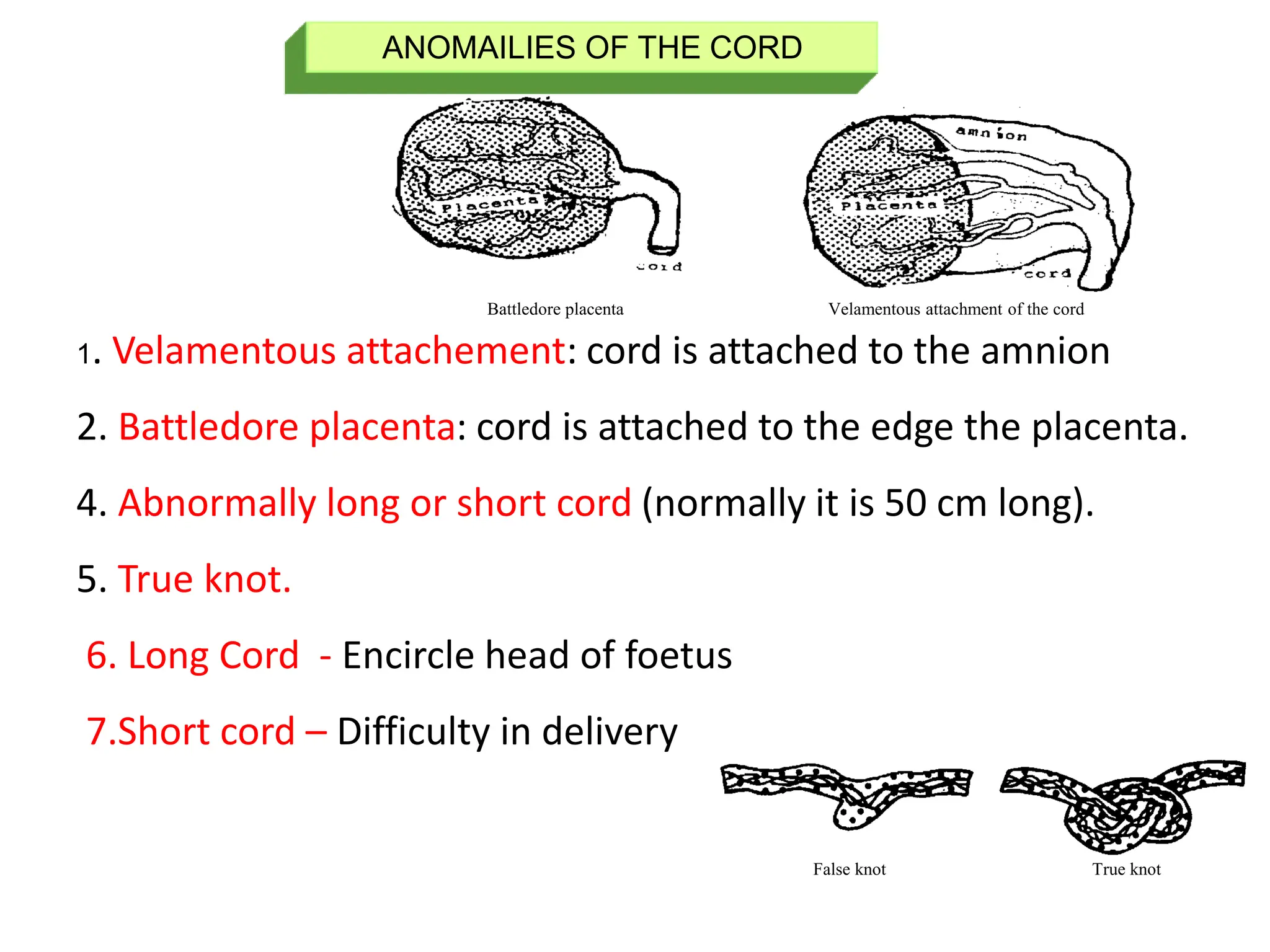
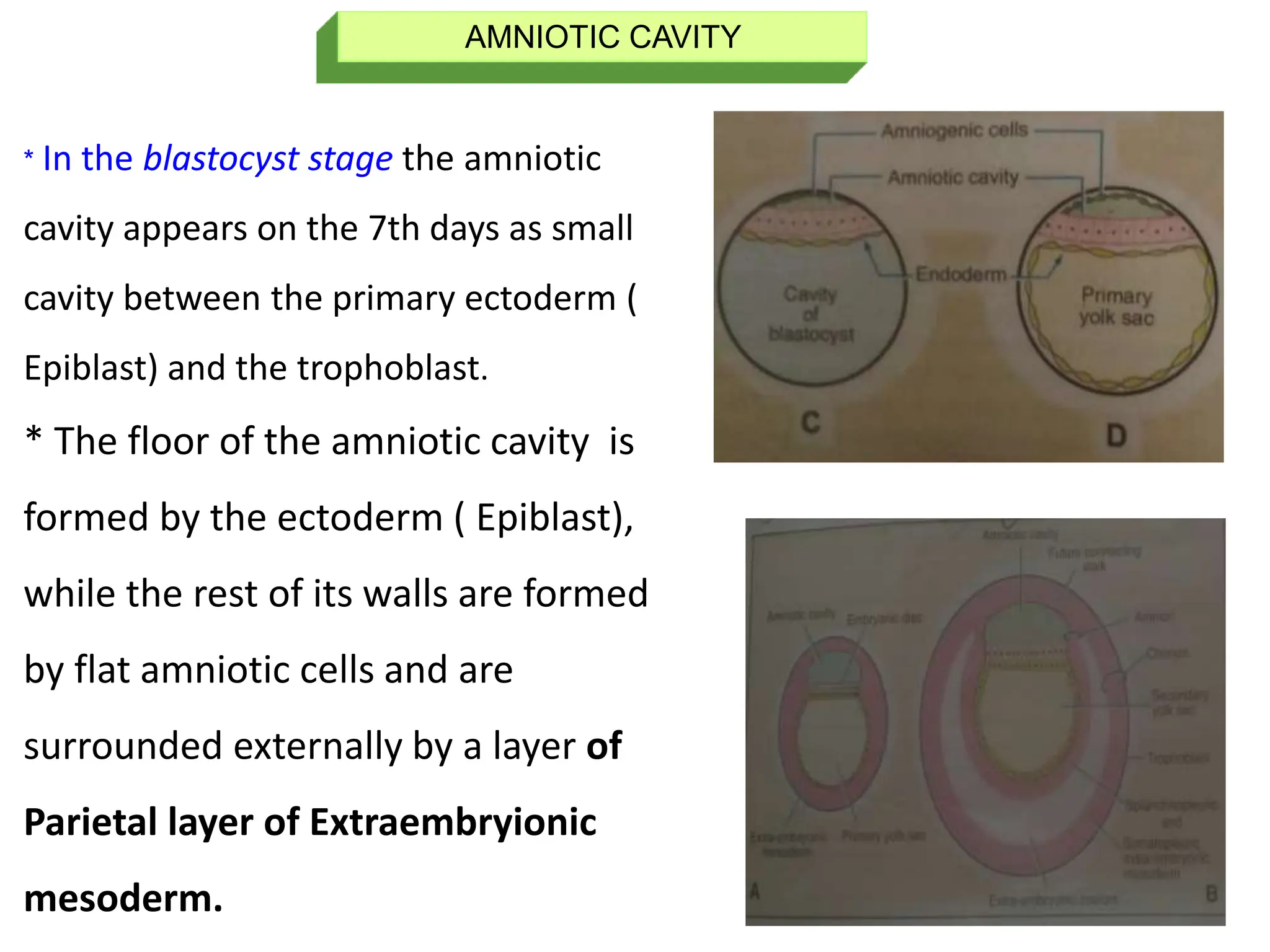
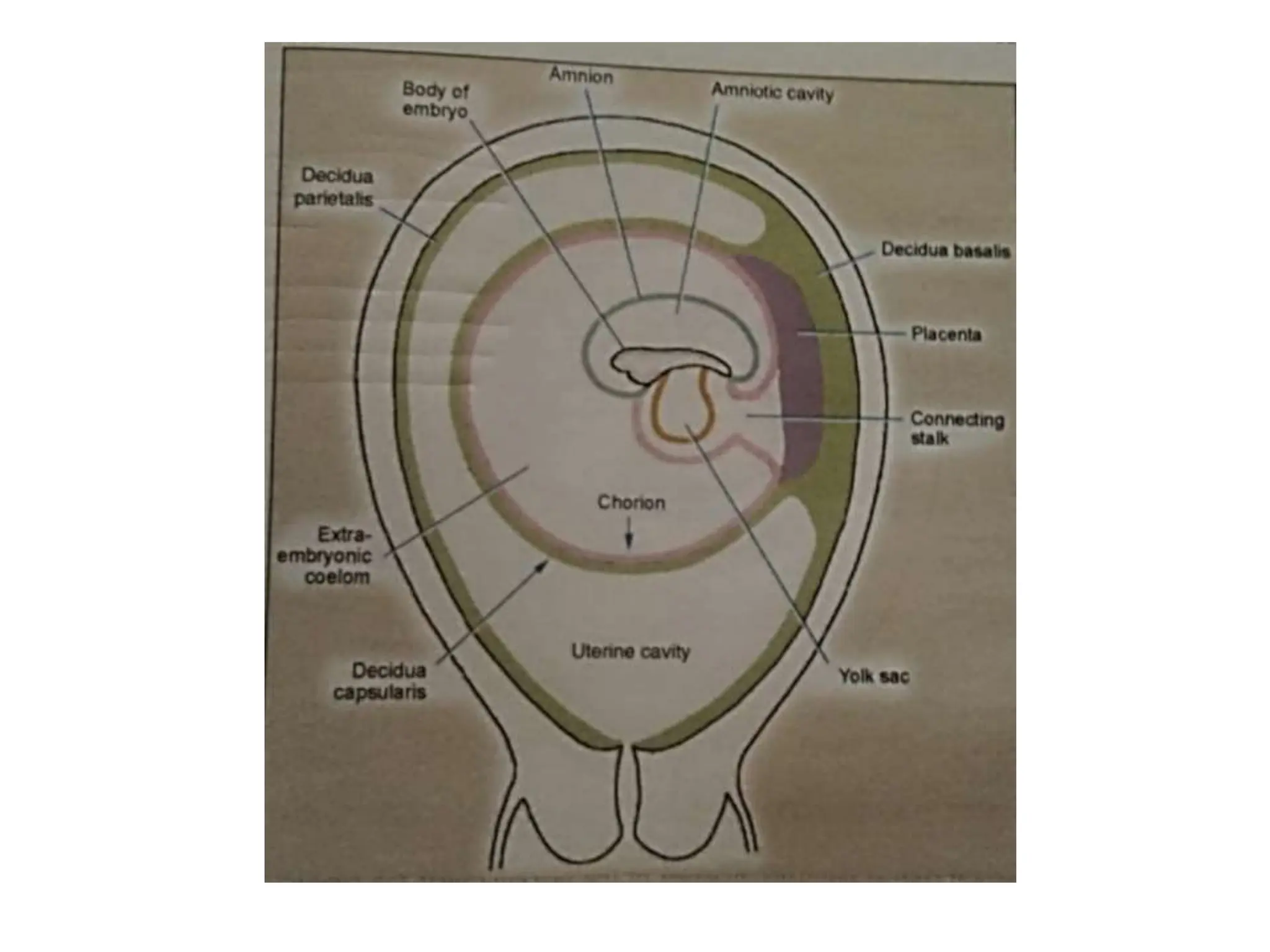
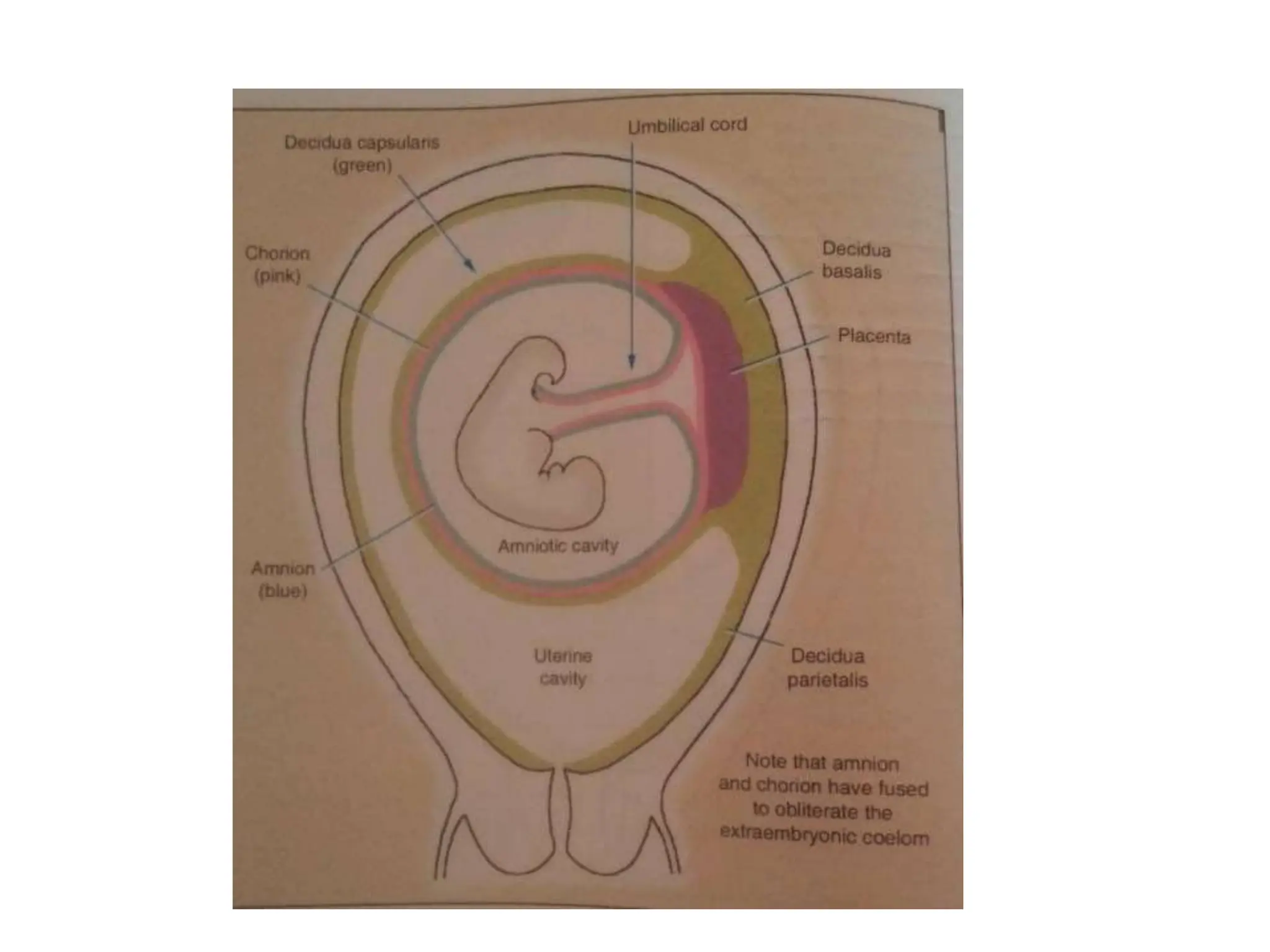
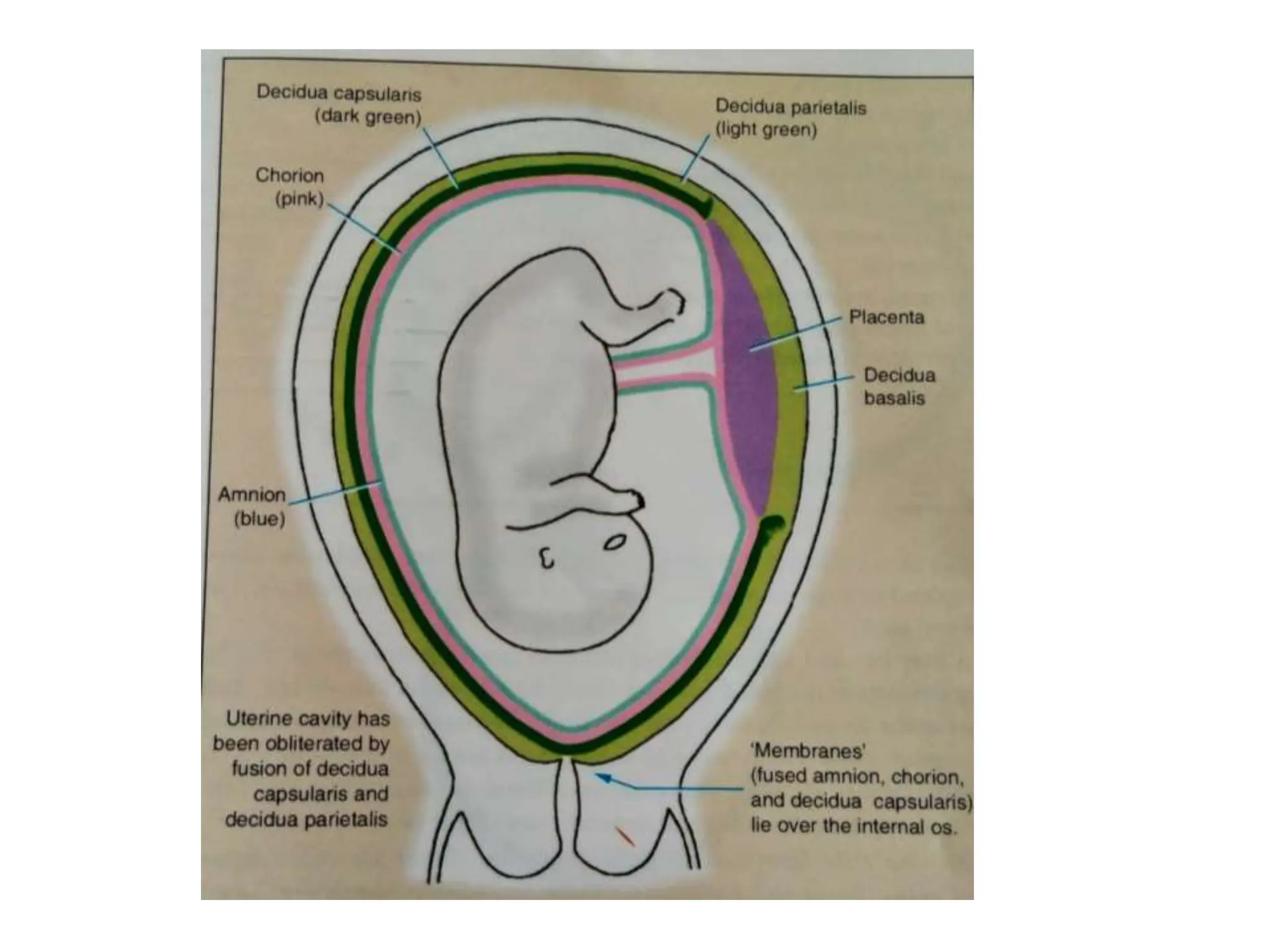
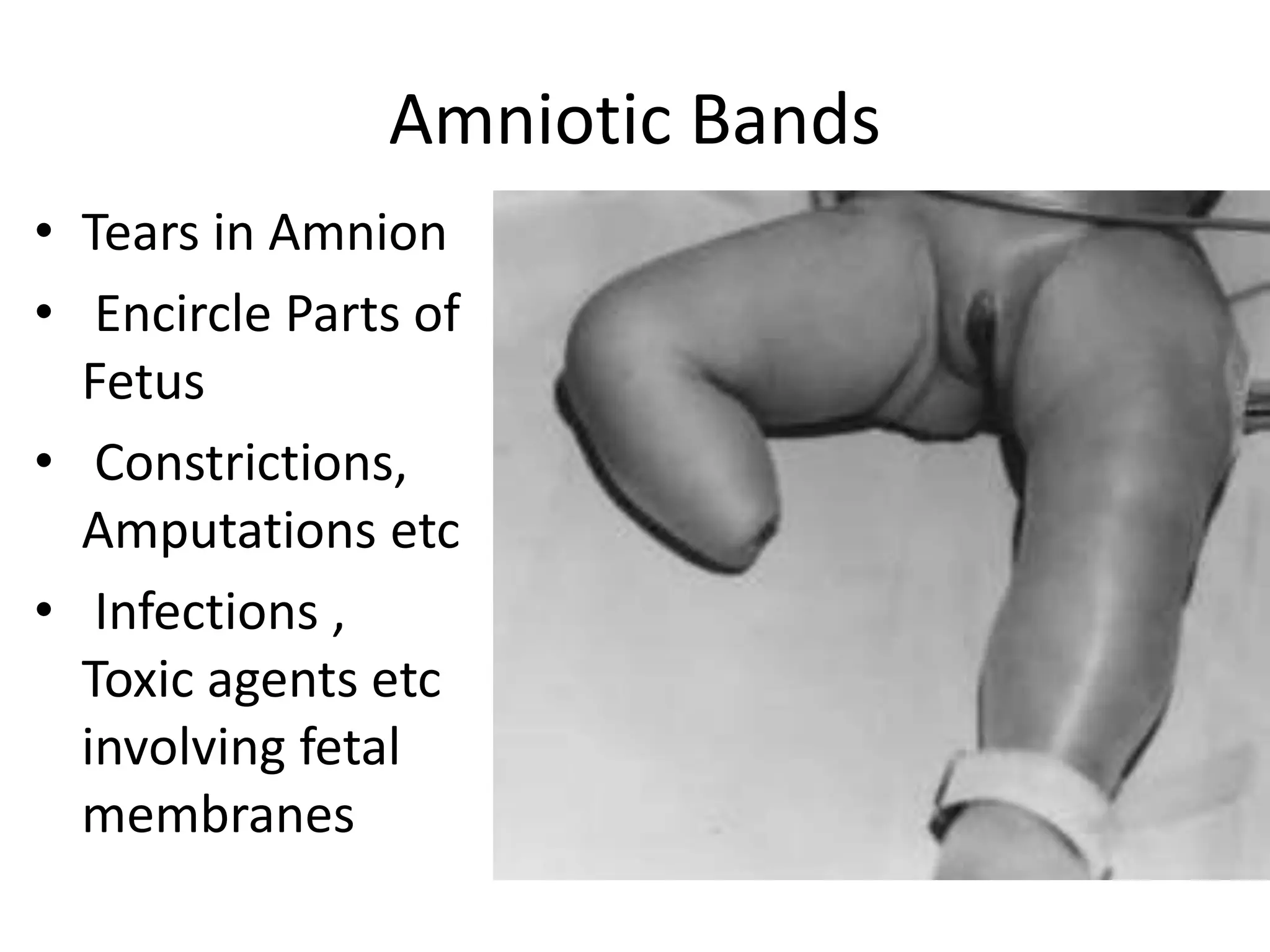
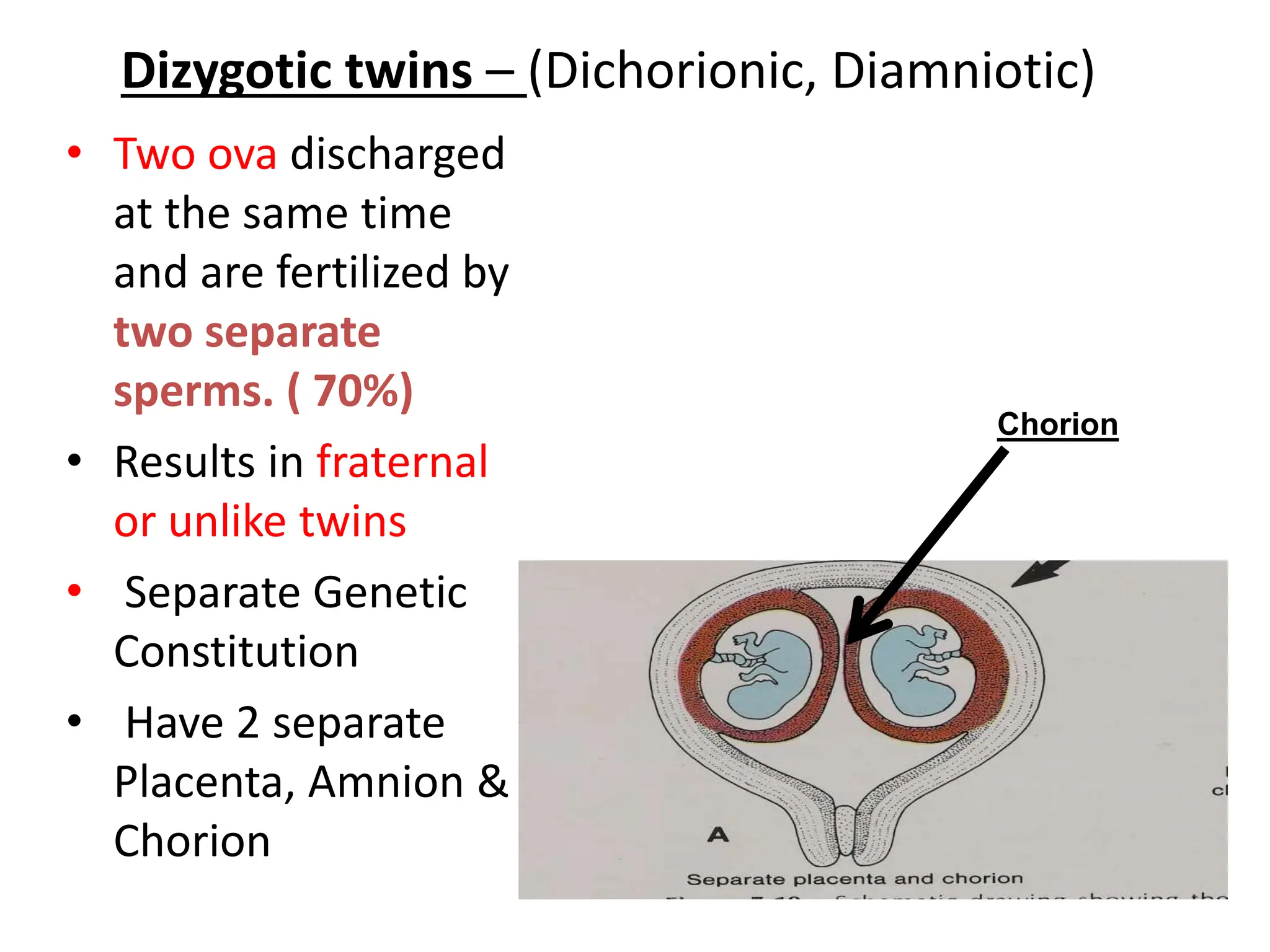
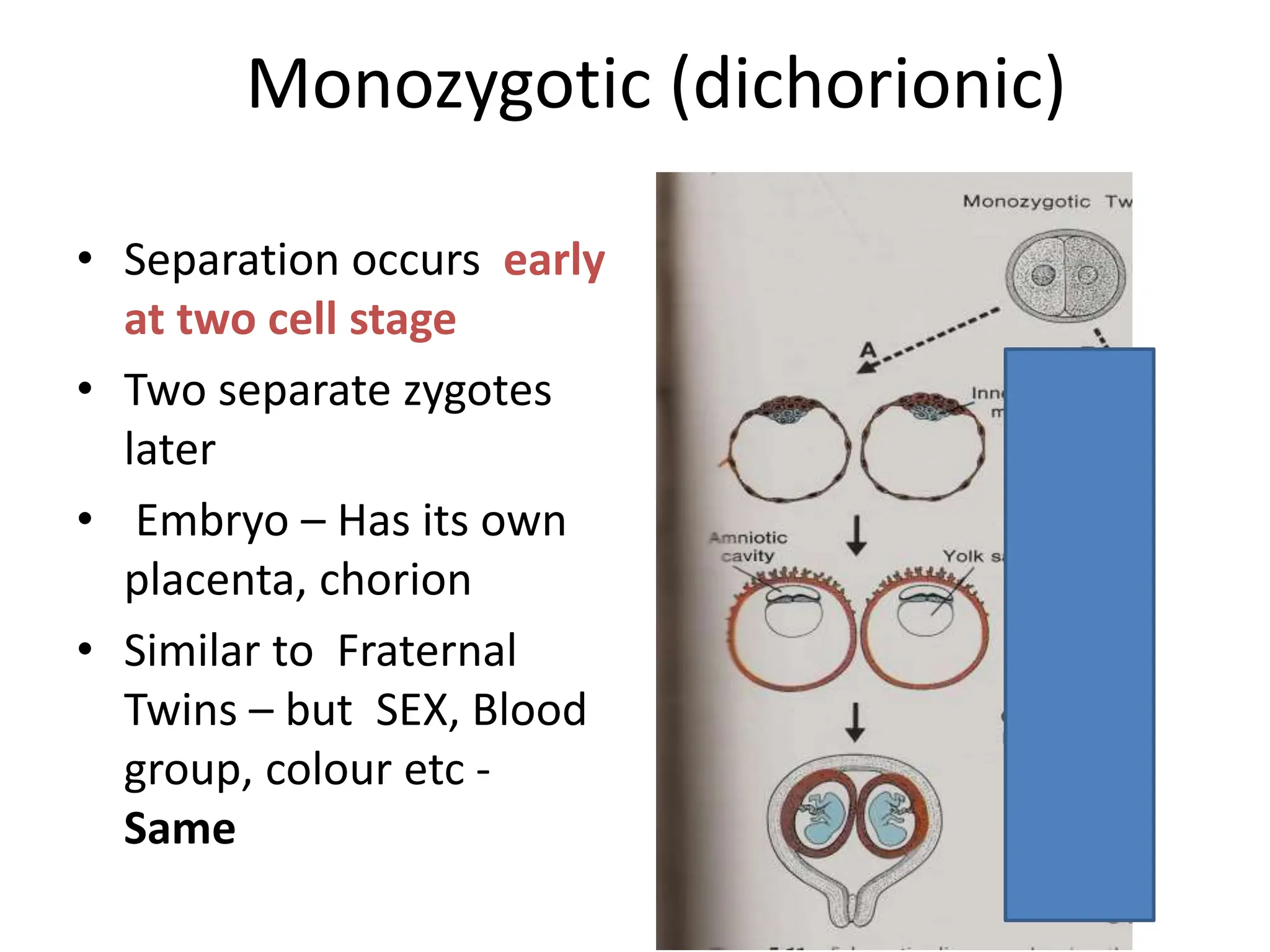
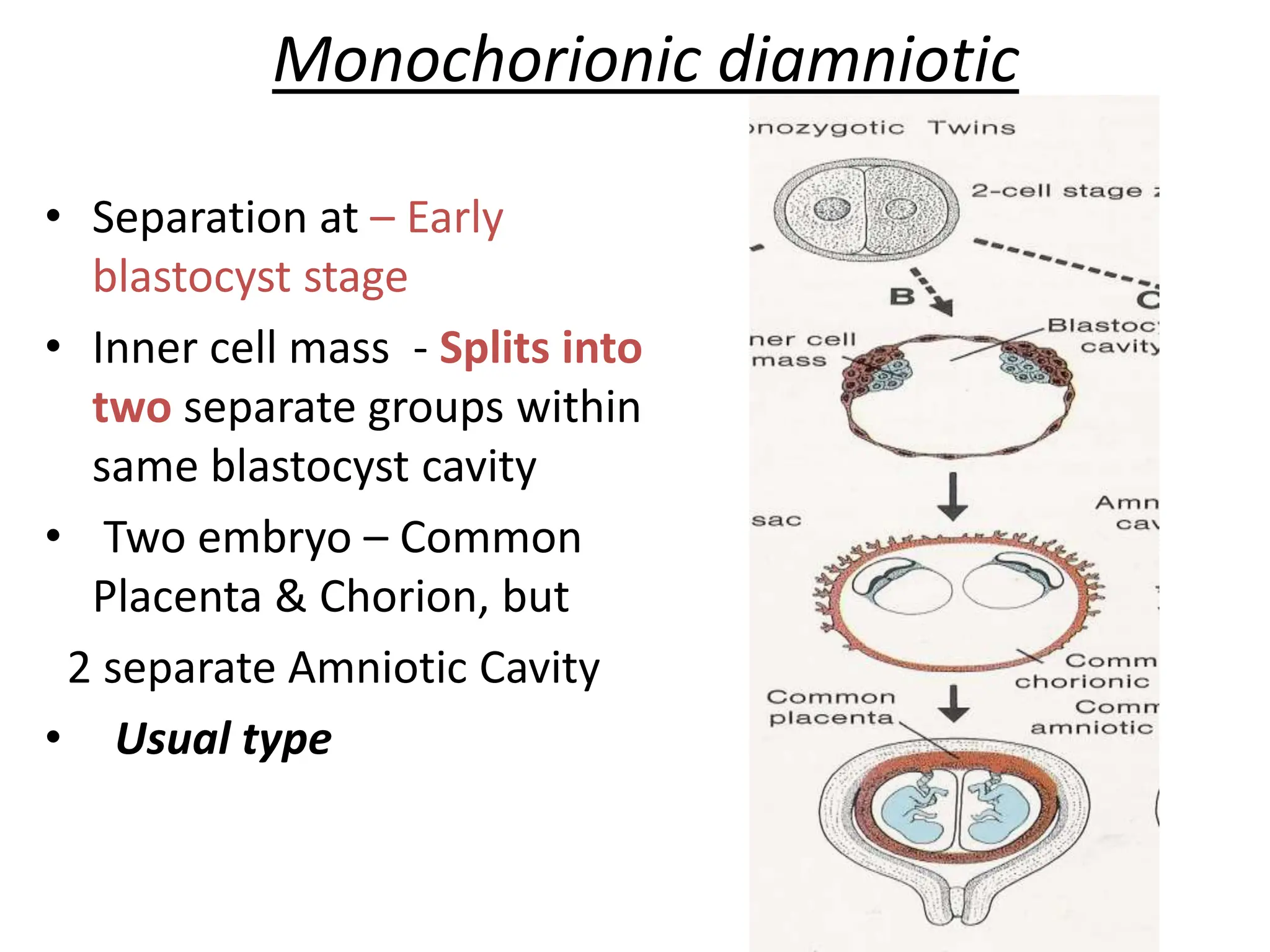
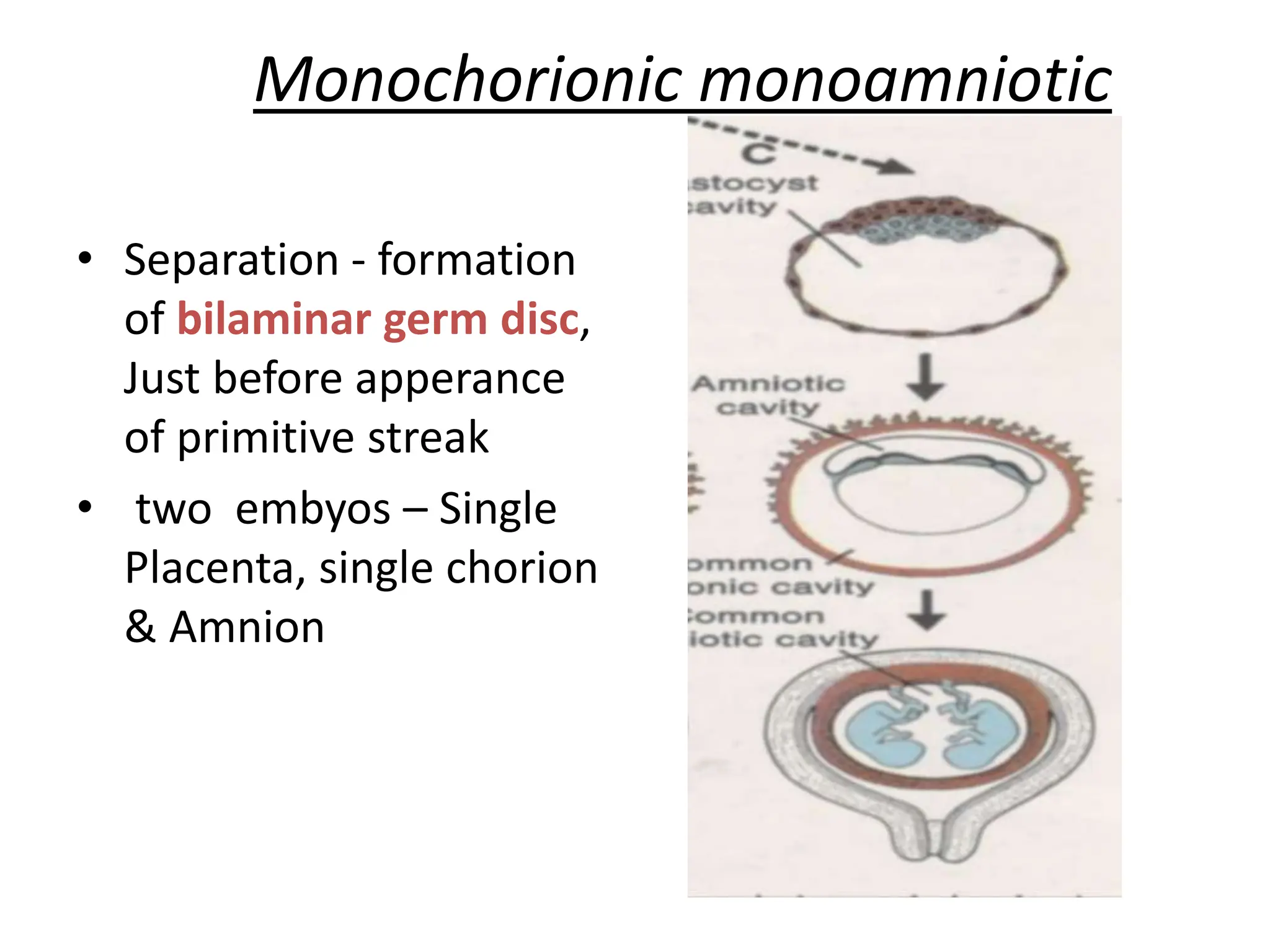
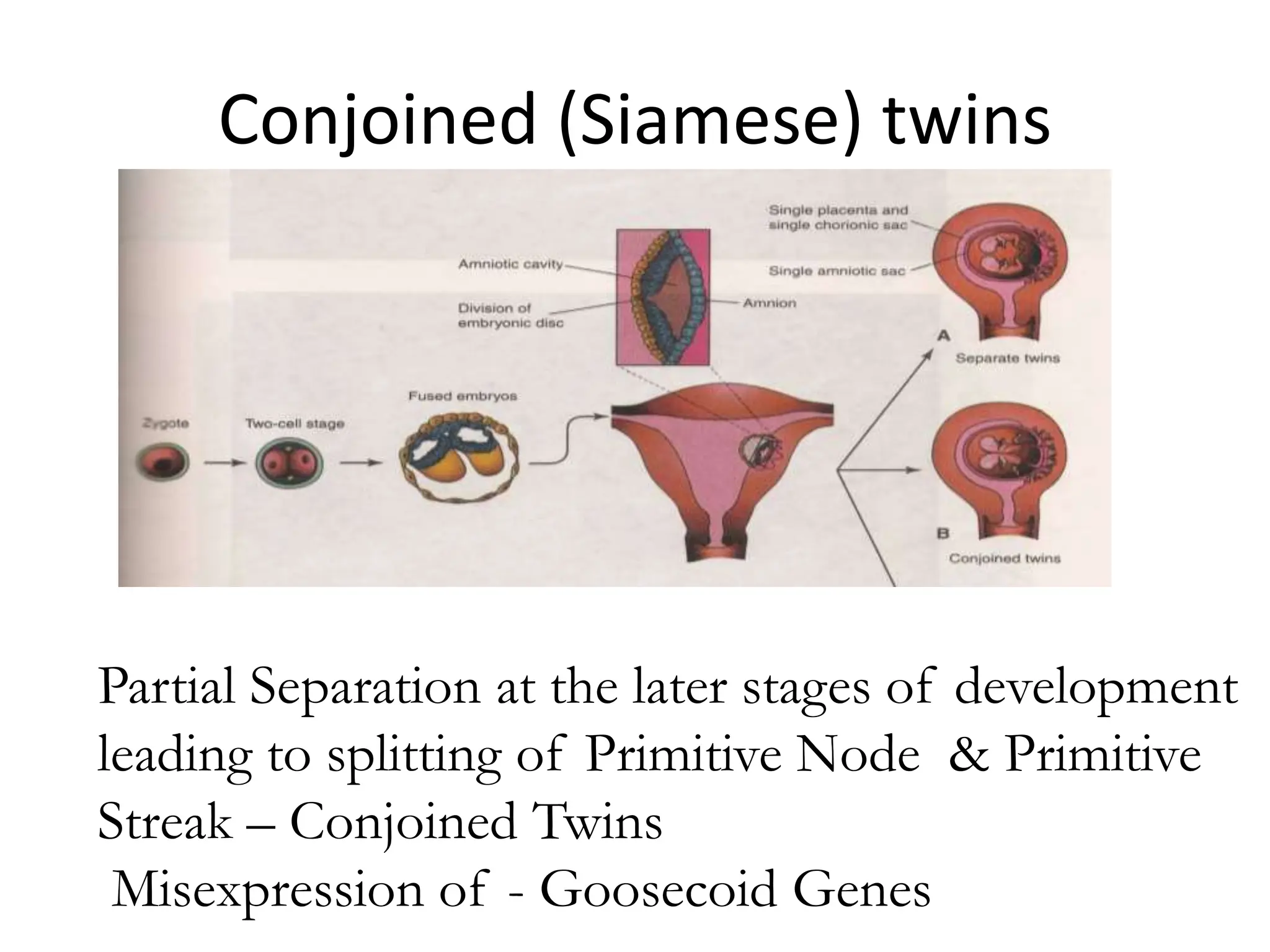
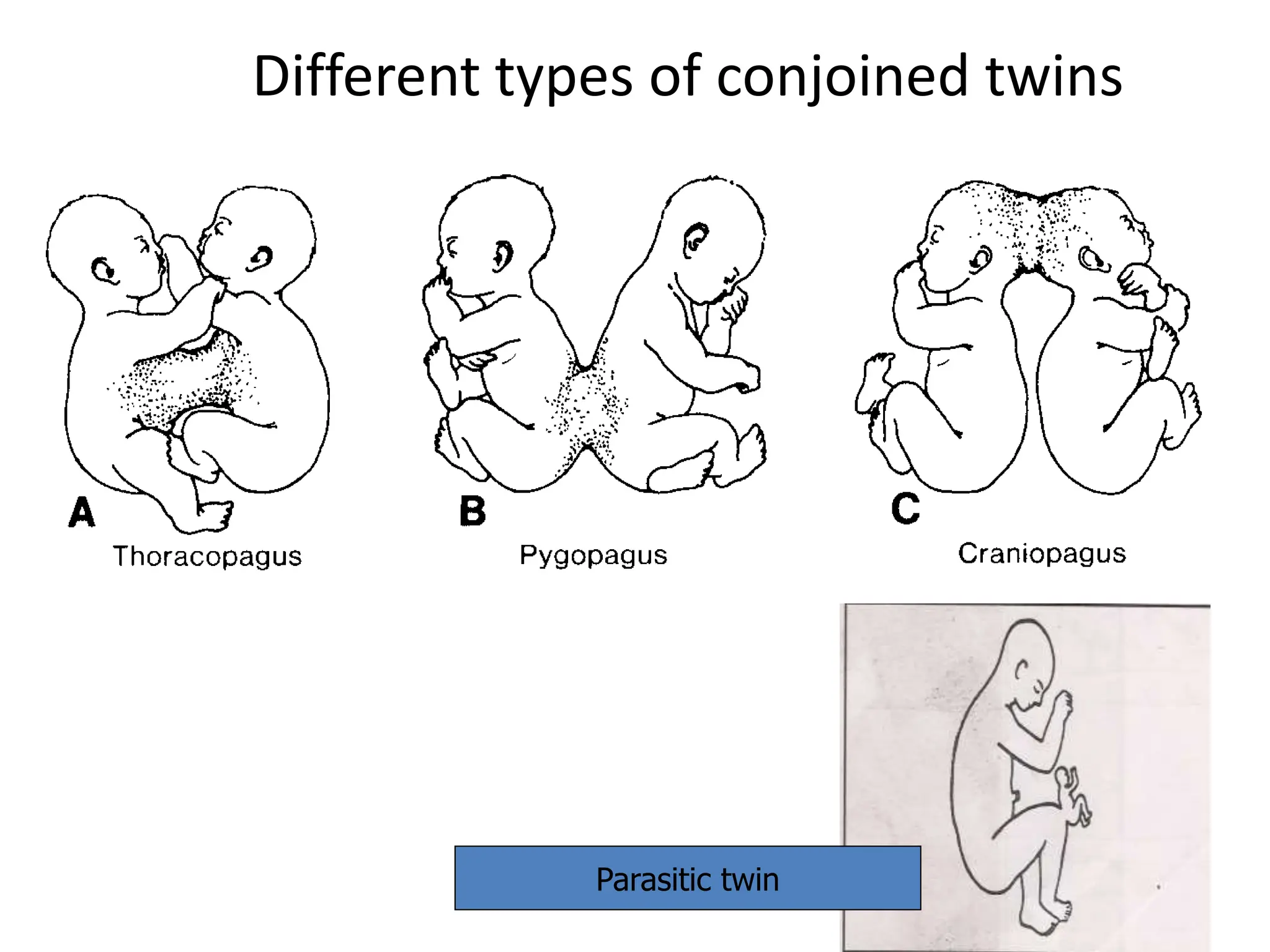
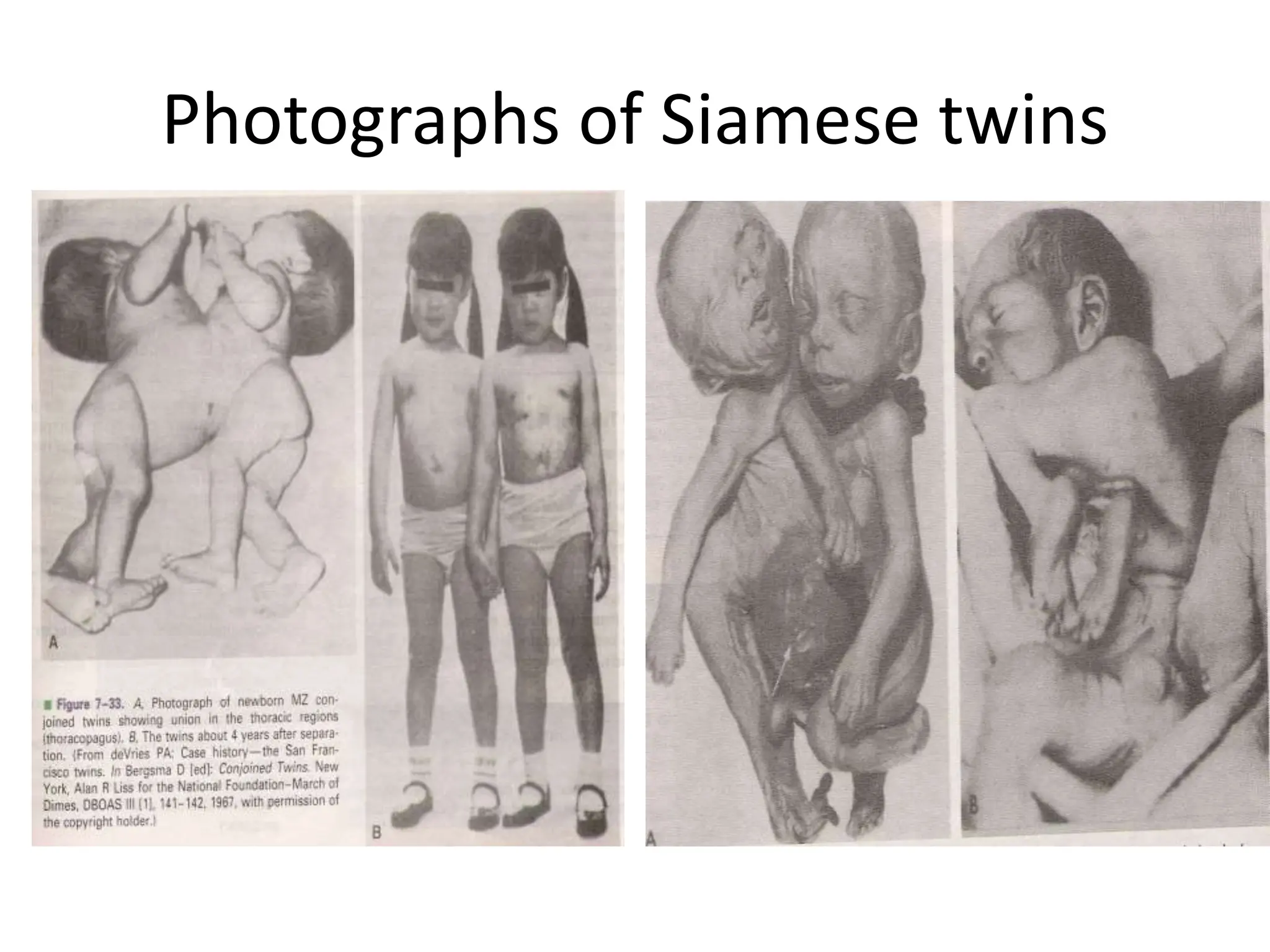
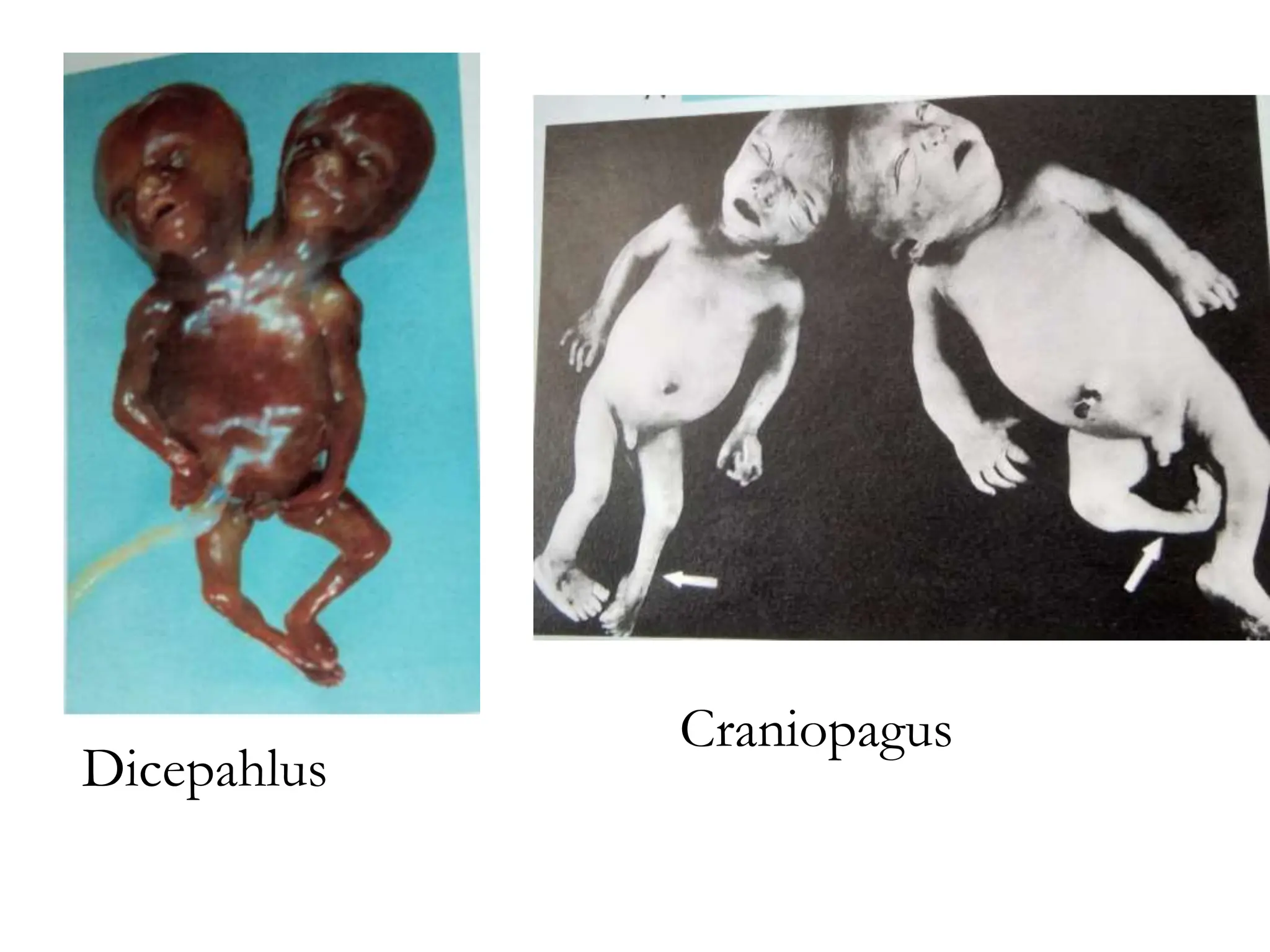
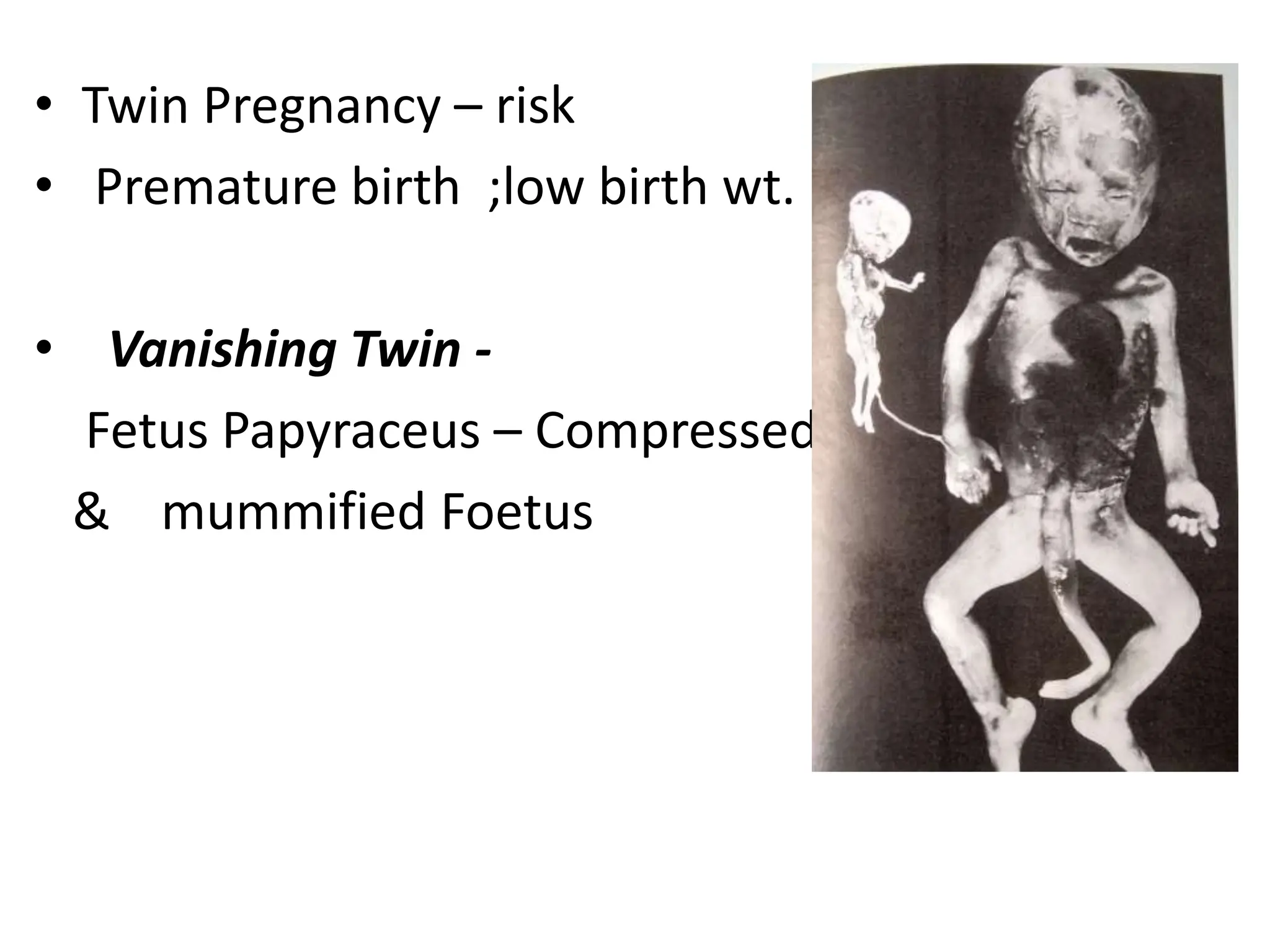
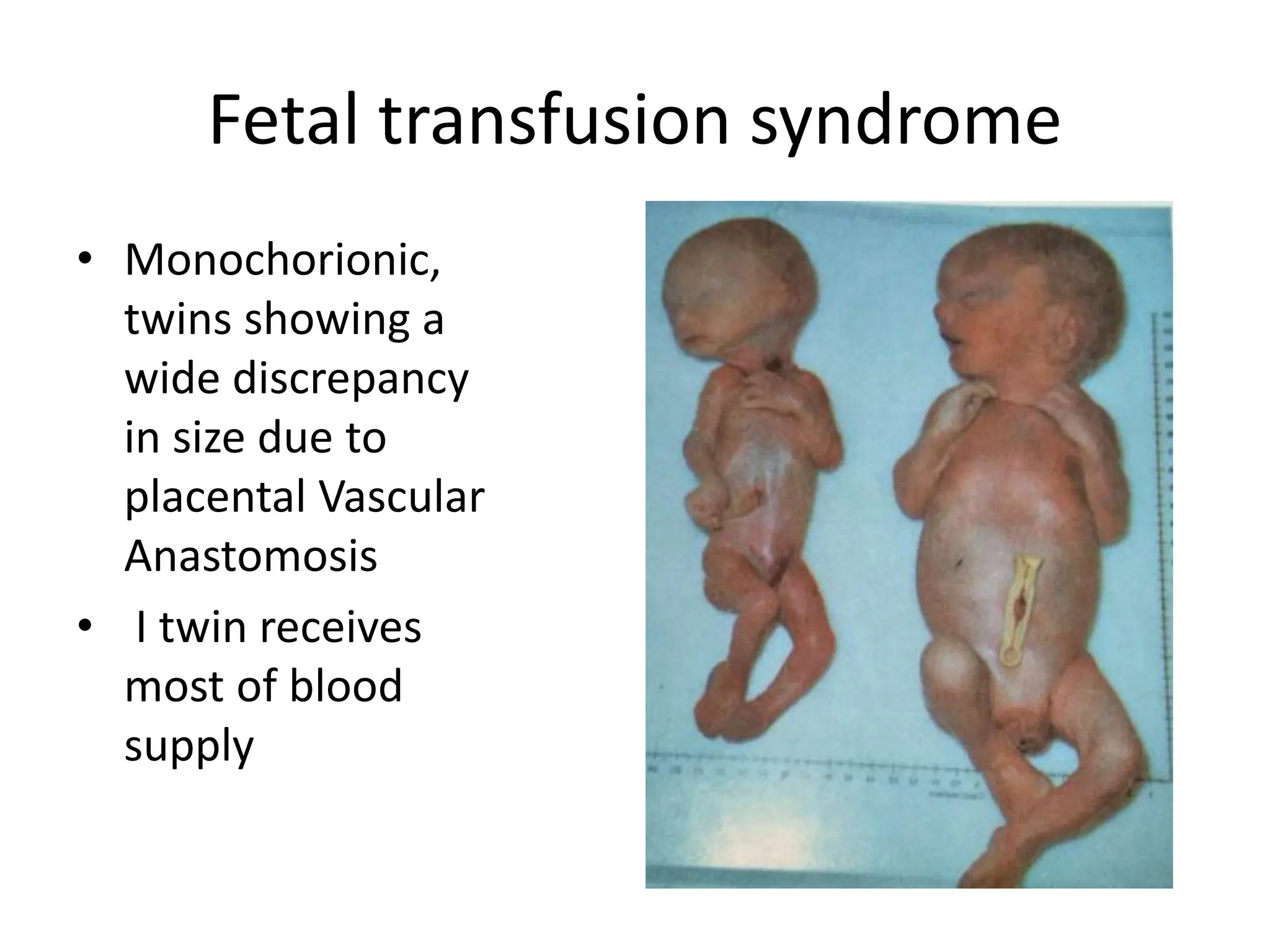
The document discusses the formation and features of the umbilical cord, amniotic fluid, and the embryological basis of twins, detailing structures like the connecting stalk and characteristics of the umbilical cord. It outlines the significance of amniotic fluid, including its average volume, functions, and associated conditions like oligohydramnios and polyhydramnios. The document further explains the types of twinning, including dizygotic and monozygotic twins, along with their anatomical configurations and potential complications during pregnancy.