Embed presentation
Download to read offline
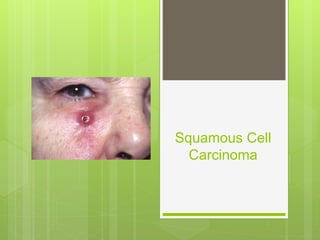






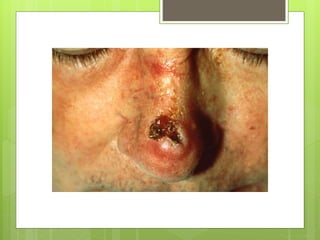


Squamous cell carcinoma affects squamous epithelial tissue that covers areas like the lungs, mouth, and esophagus. It often presents as an ulcer or reddish plaque with hard raised edges and thickened skin around it. Squamous cell carcinoma tends to arise in areas of chronic inflammation or pre-malignant conditions and is associated with sun exposure, immunosuppression, tobacco, and HPV. Treatment options include surgical excision for tumors less than 4cm or other local therapies like photodynamic therapy, topical chemotherapy, or radiotherapy.









