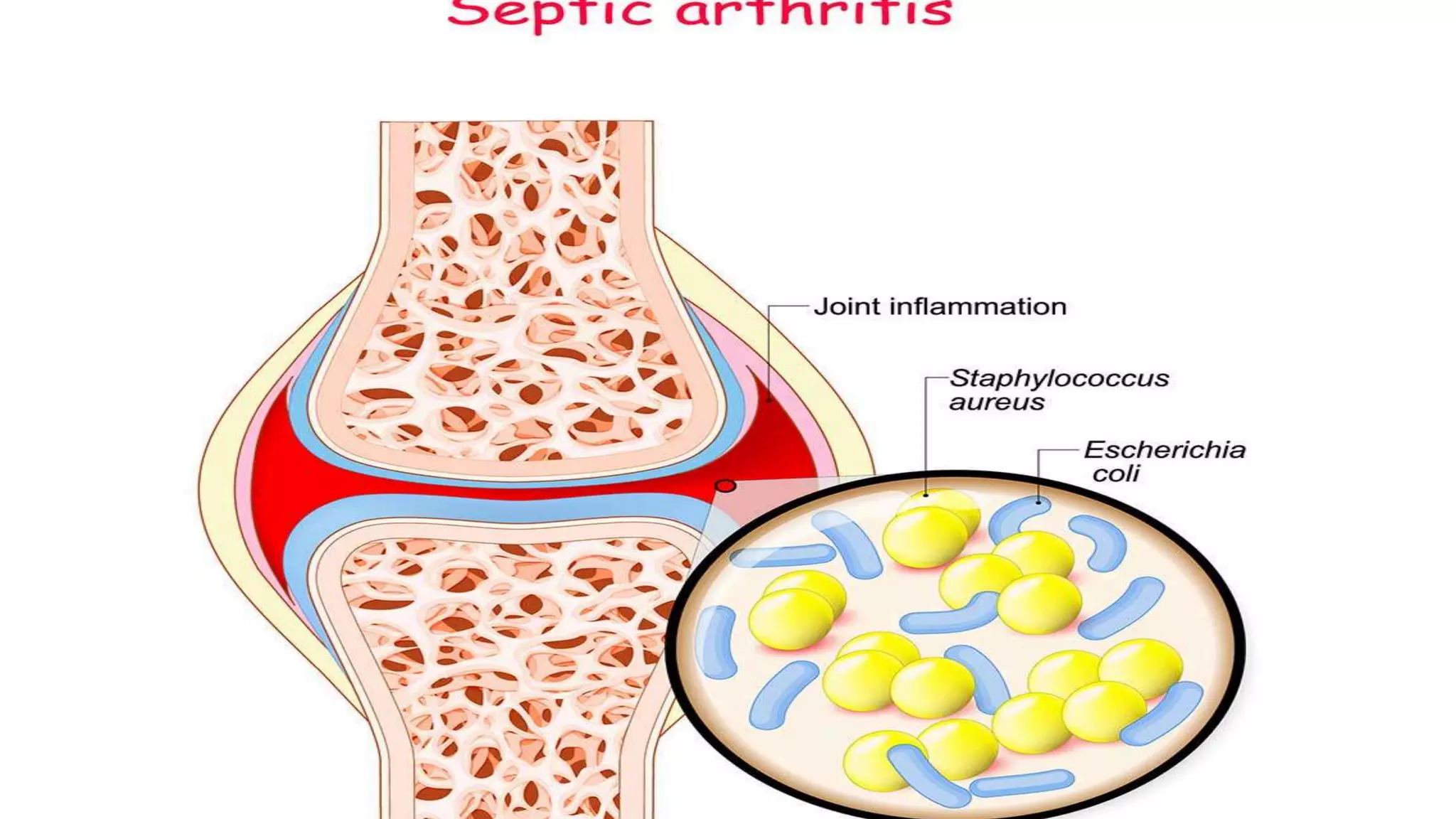
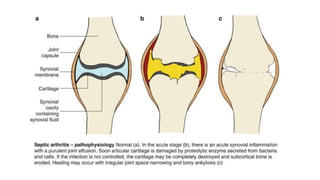
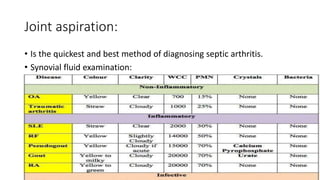
Septic arthritis is a joint infection caused by bacteria or other microorganisms. It most commonly affects children and the knee joint. Patients typically present with severe pain, swelling, redness, fever and inability to move the affected joint. Diagnosis involves examination of the inflamed joint as well as imaging, blood tests and joint fluid aspiration. Treatment consists of broad spectrum antibiotics based on fluid culture and sensitivity, immobilizing the joint, and sometimes surgical drainage if pus is present.