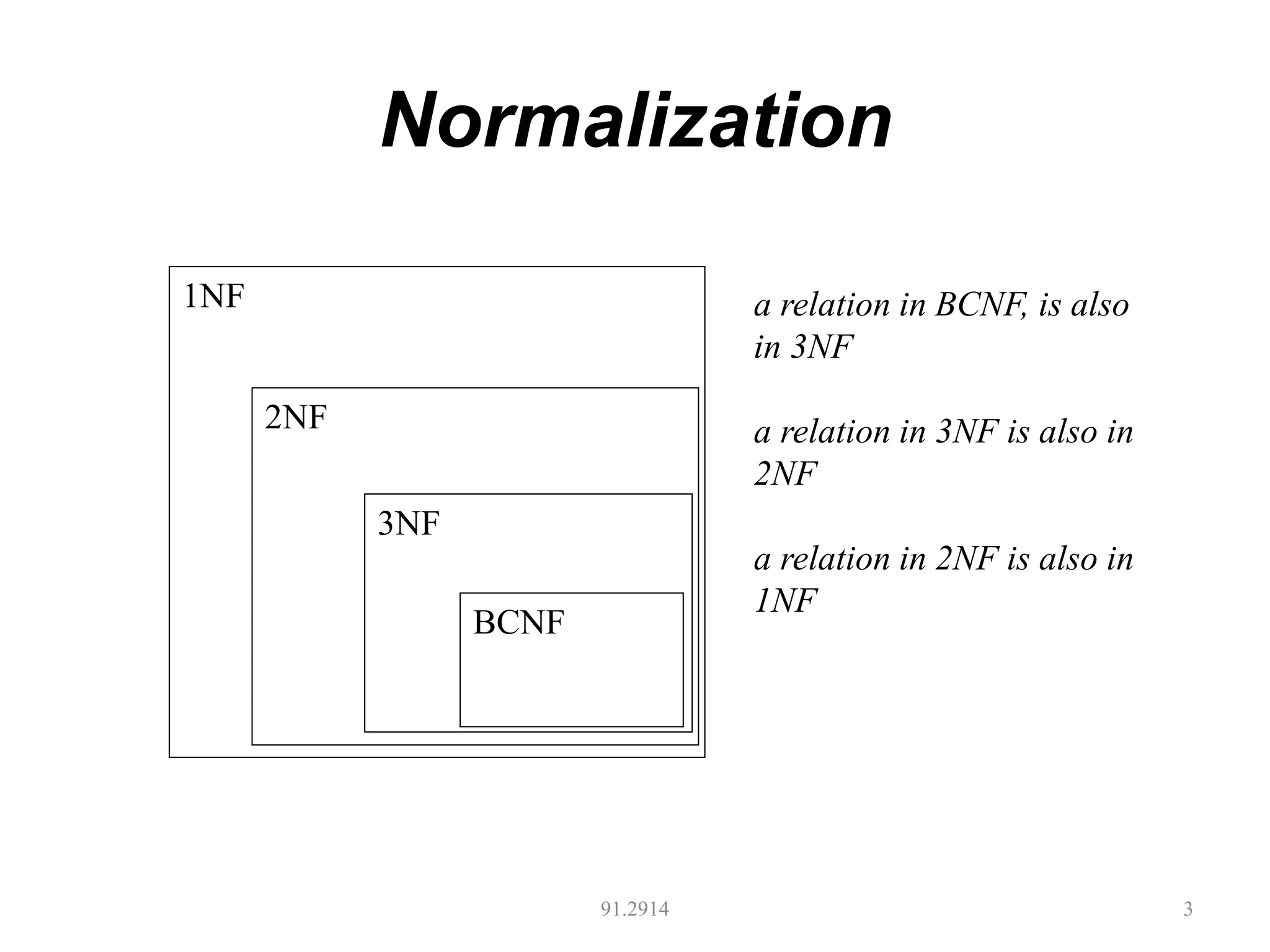
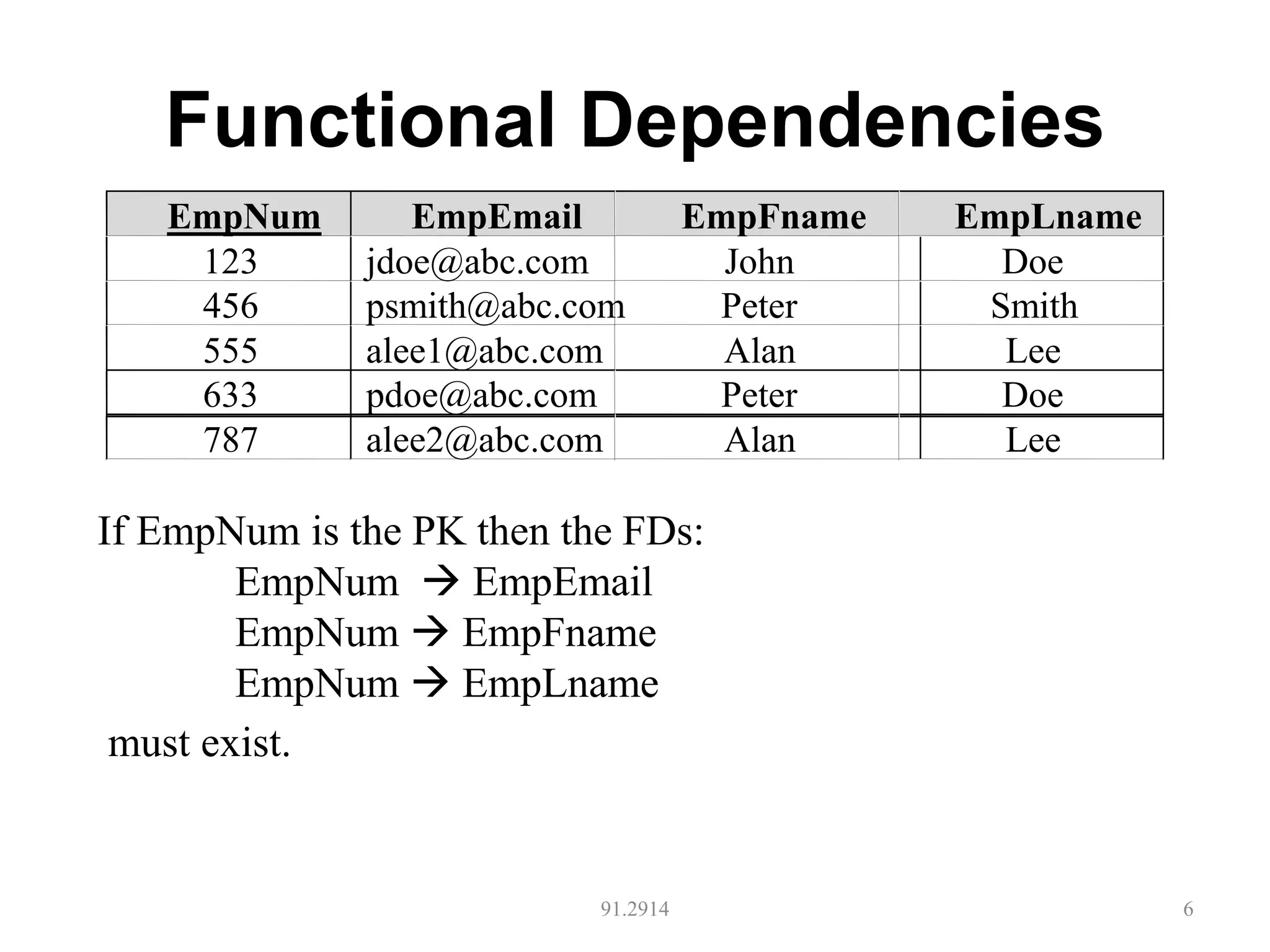
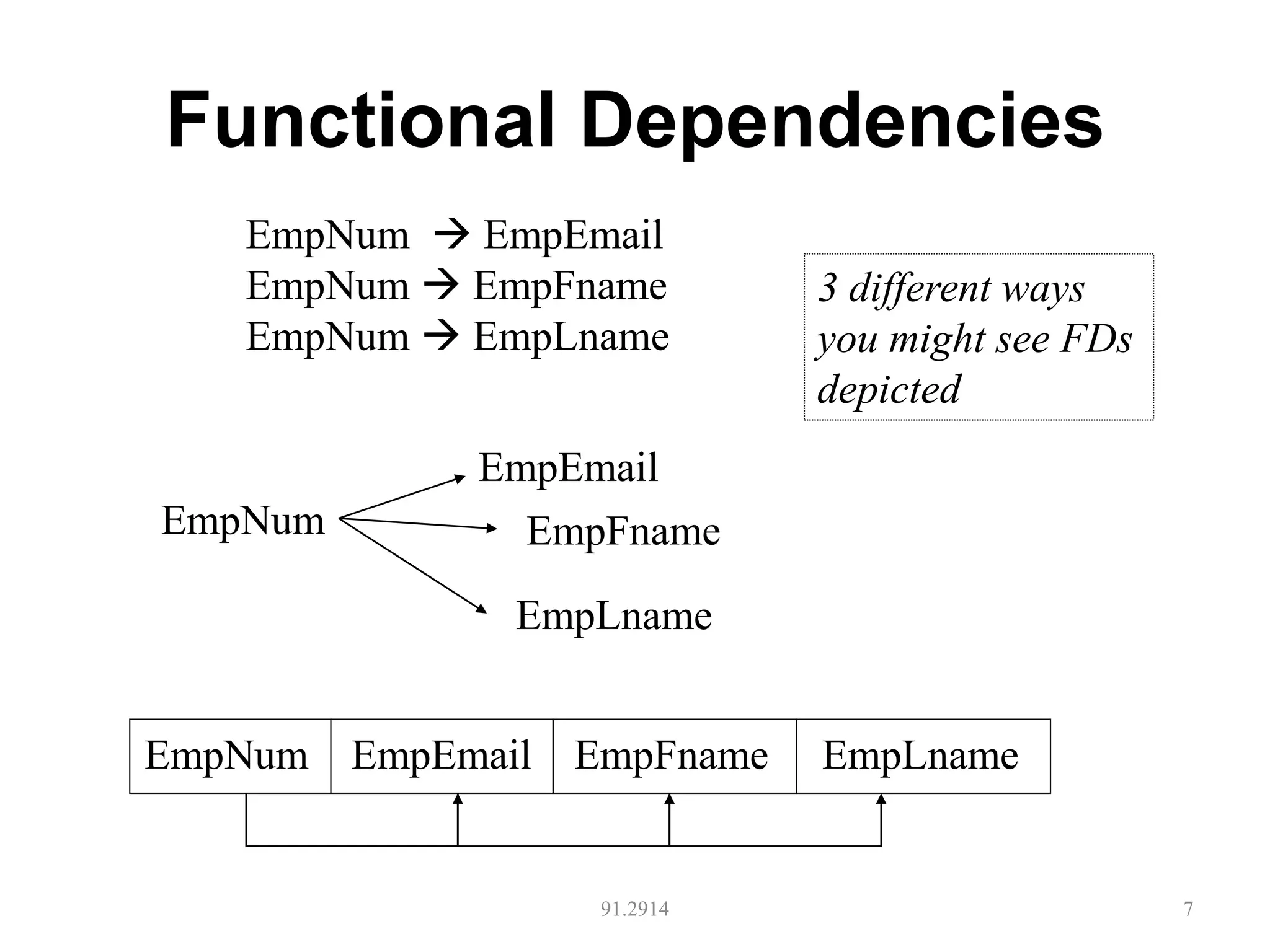
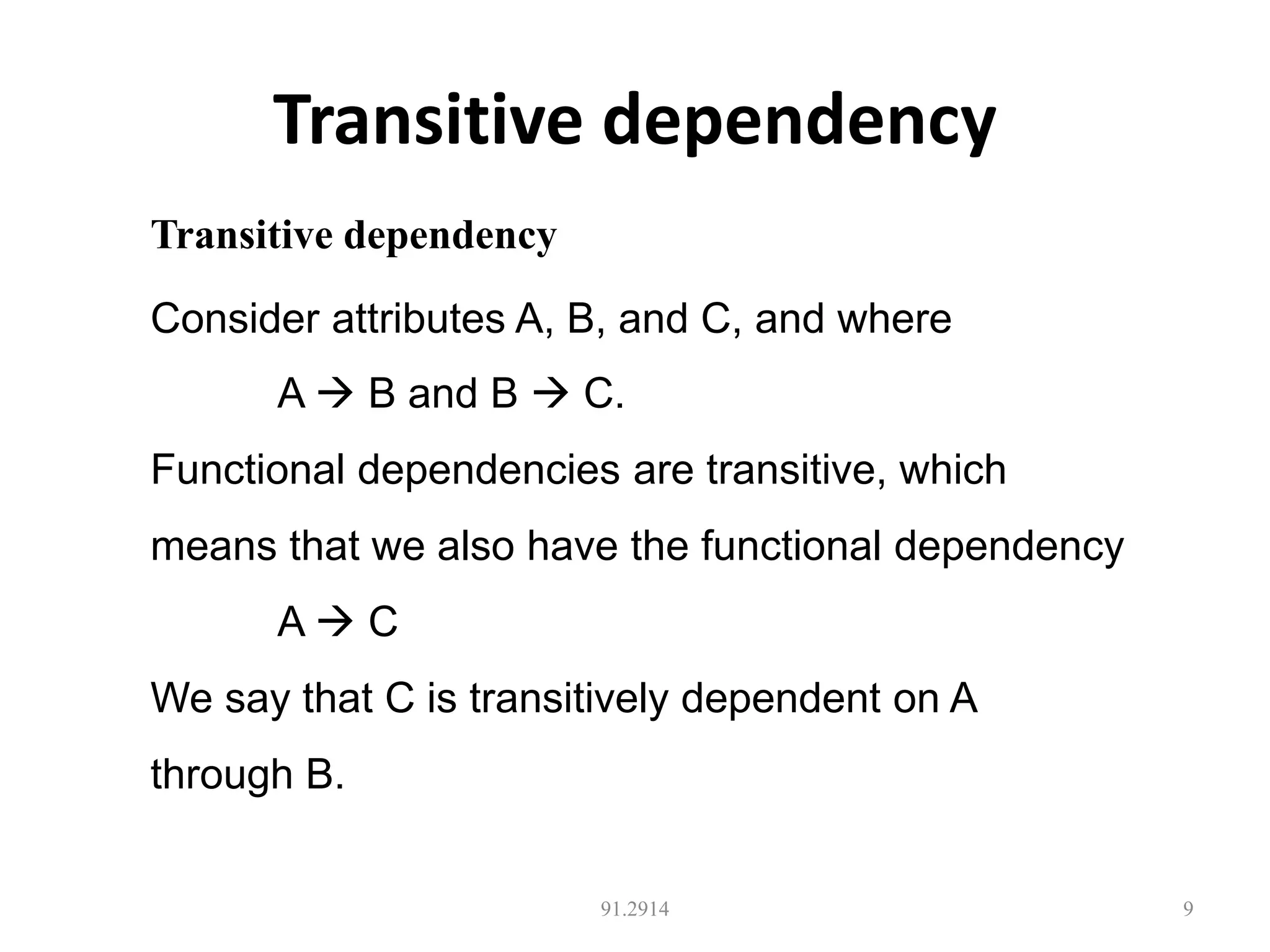
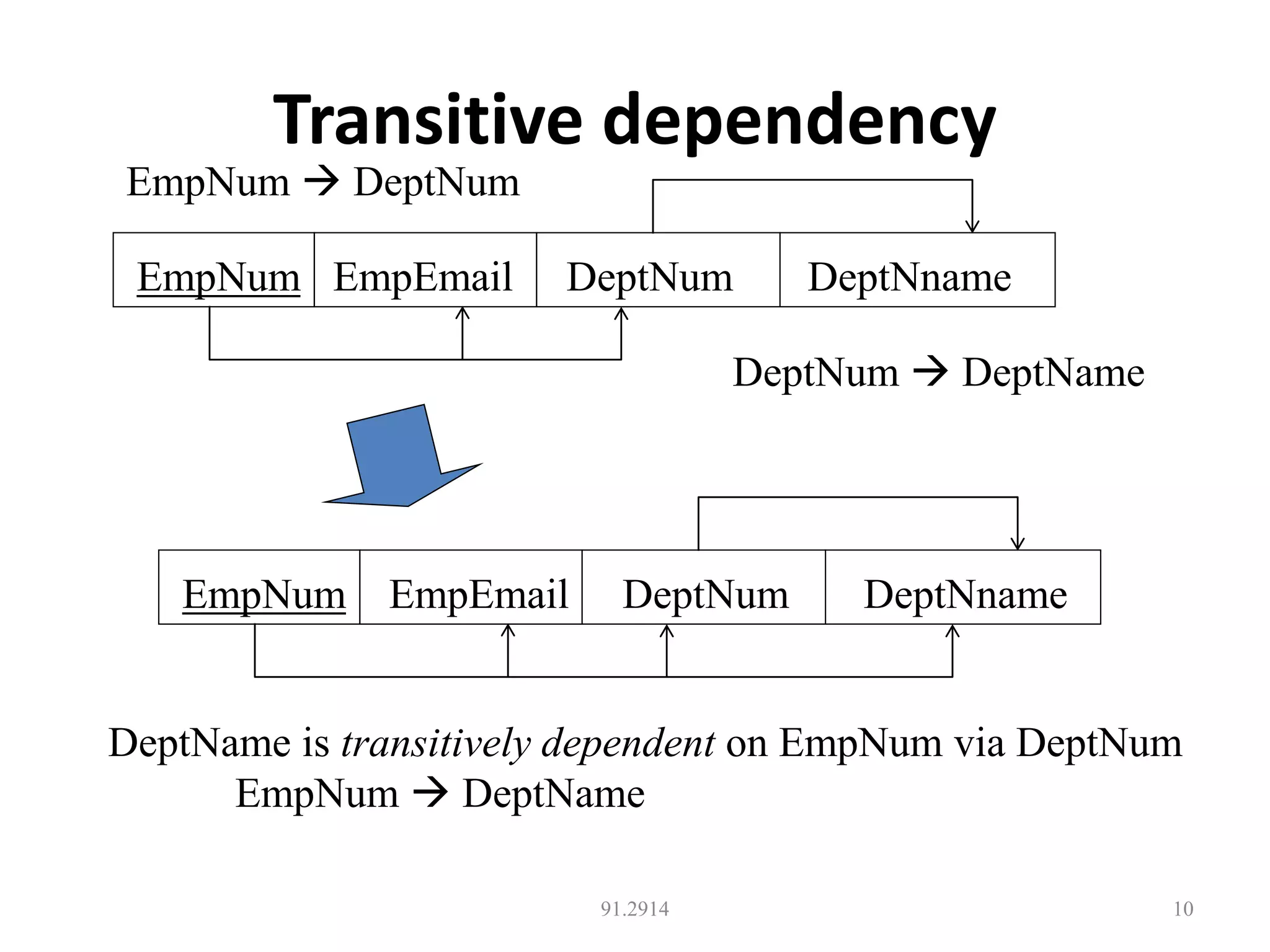
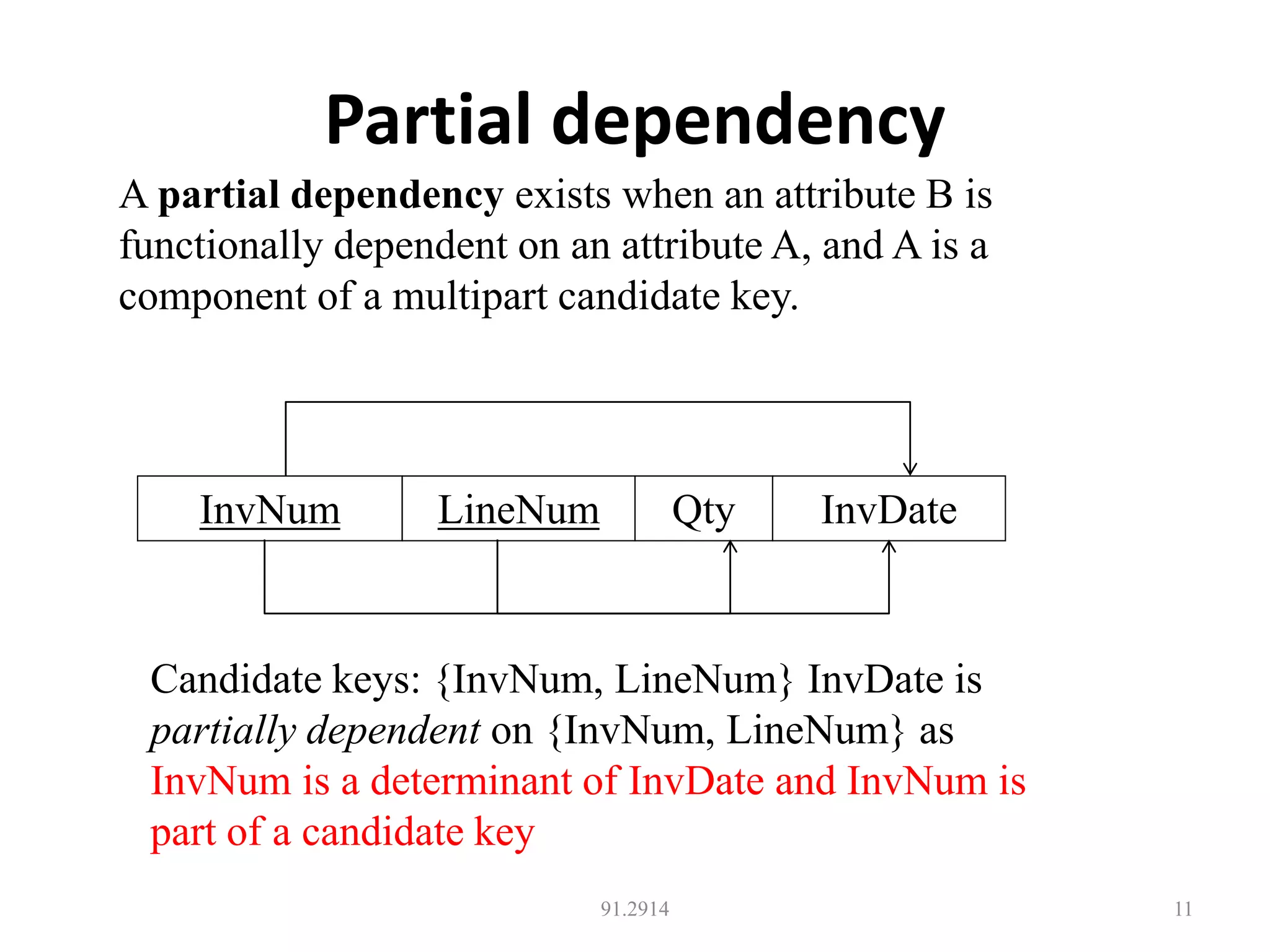
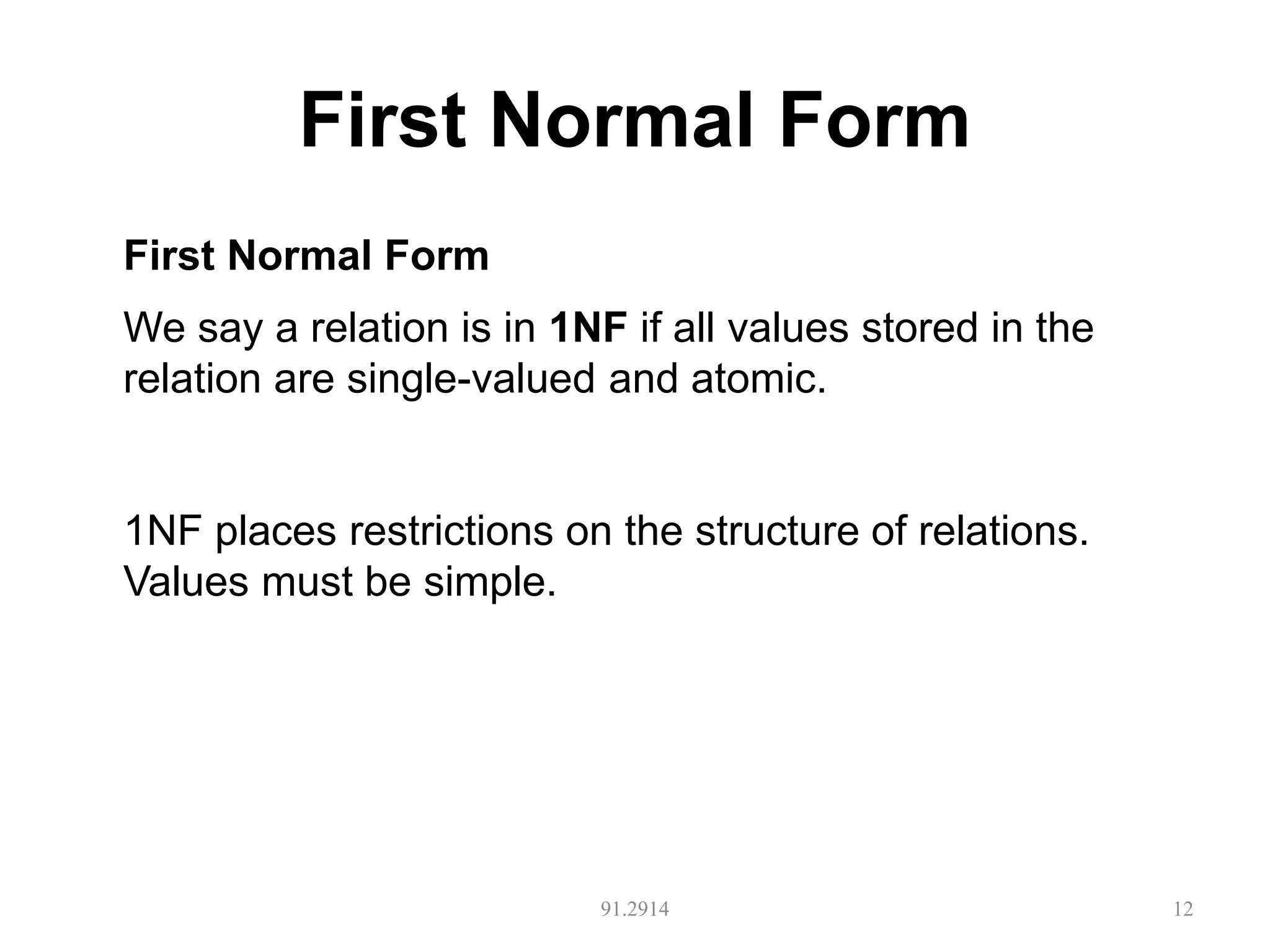
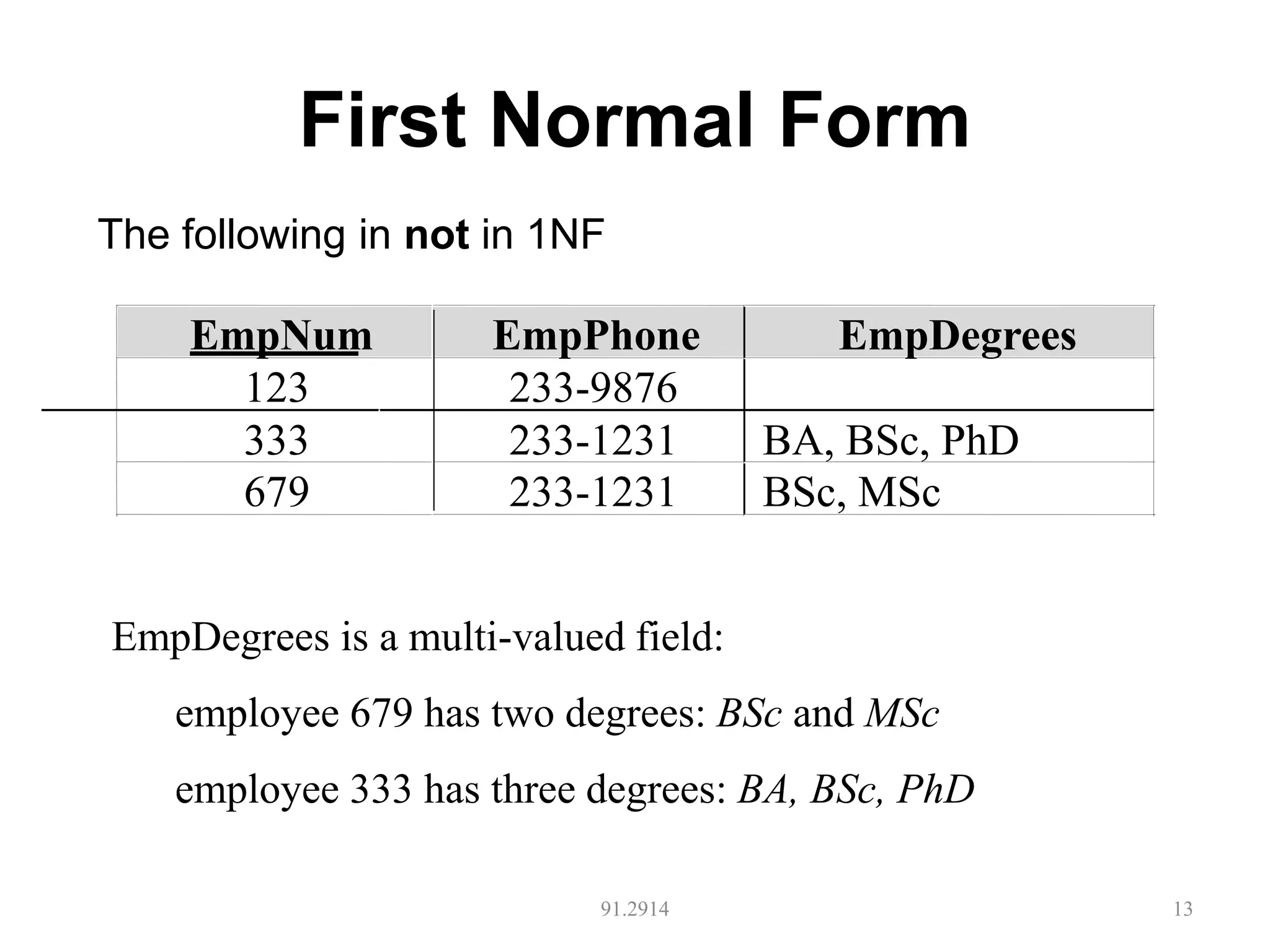
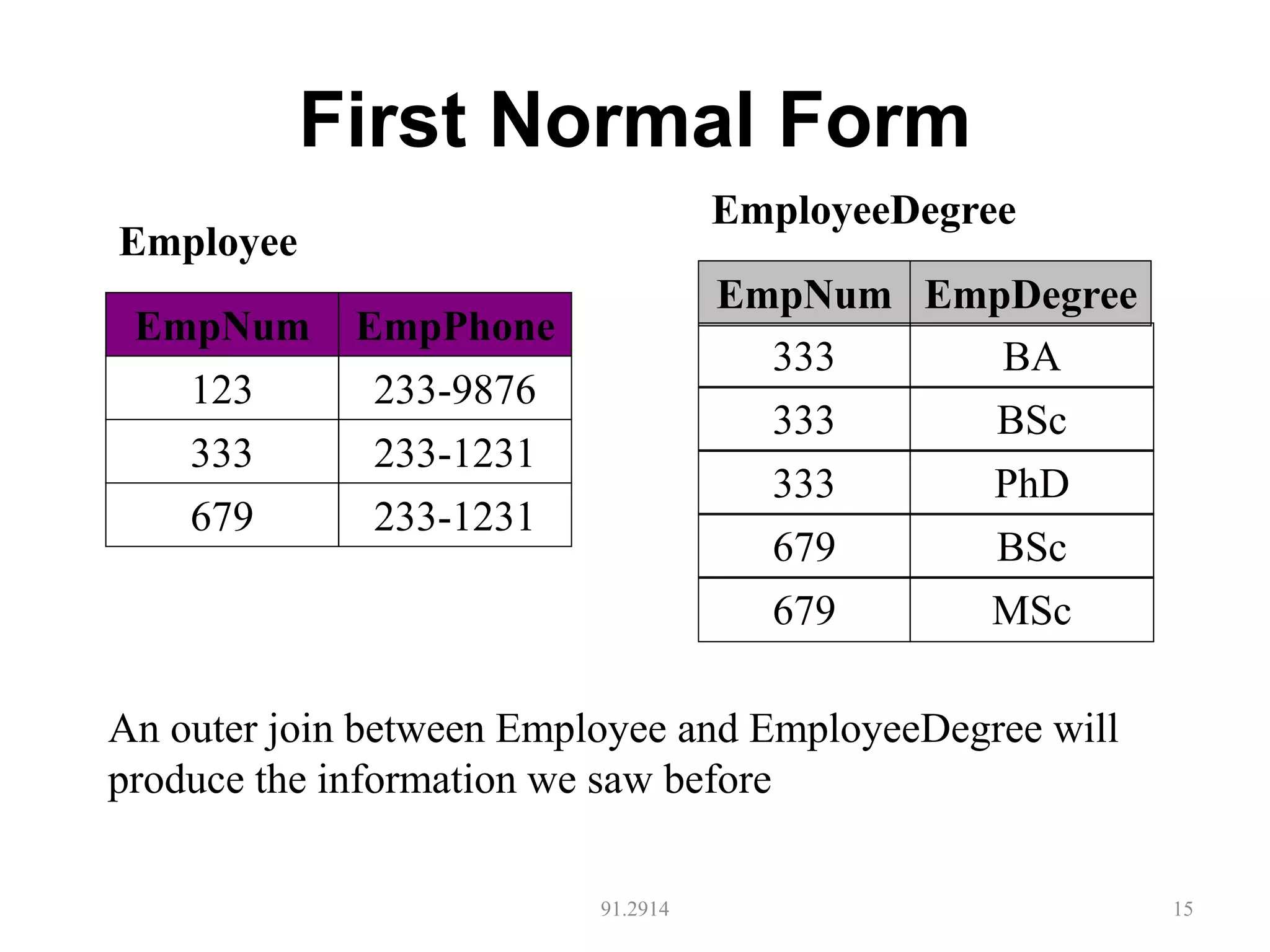
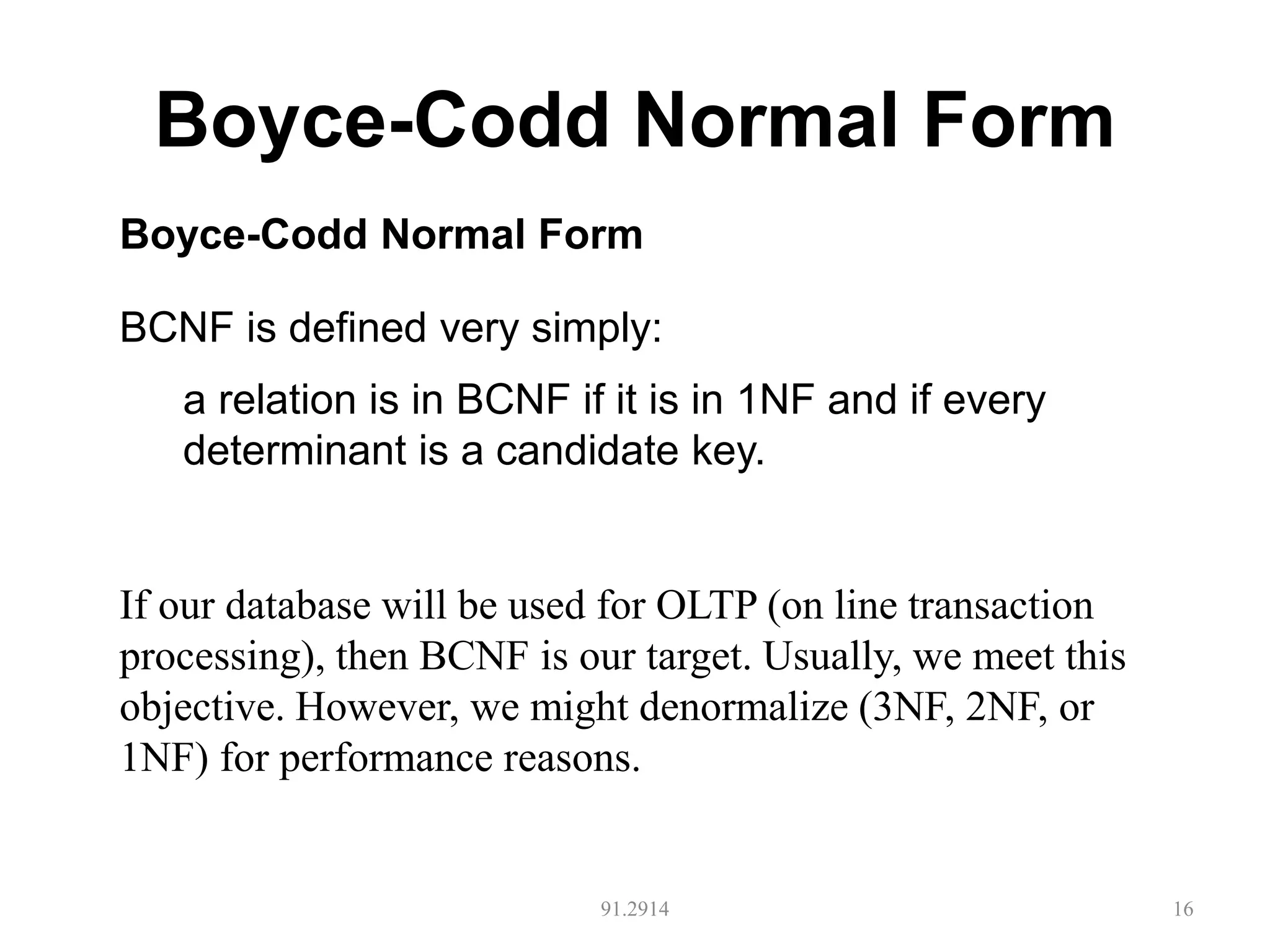
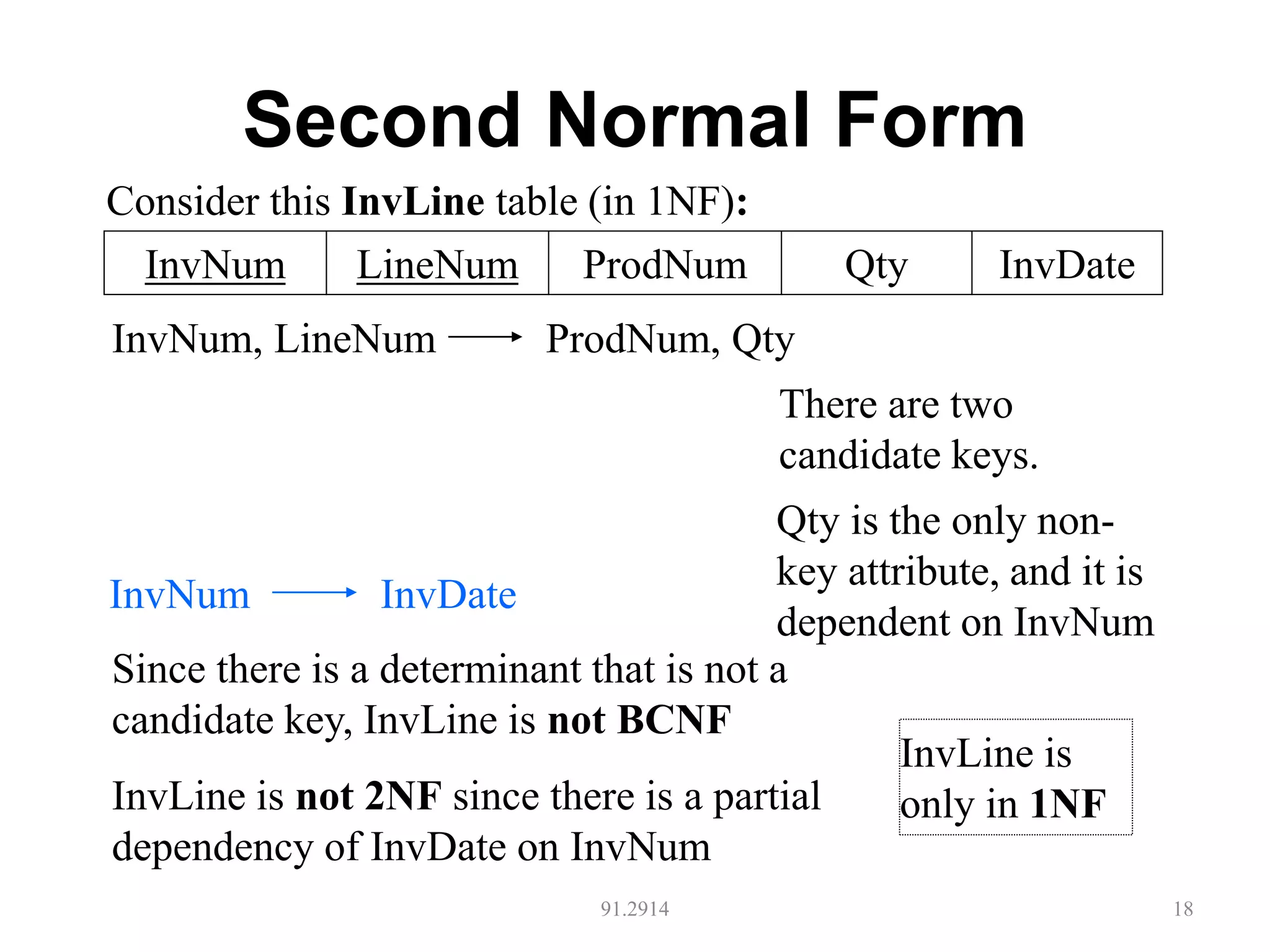
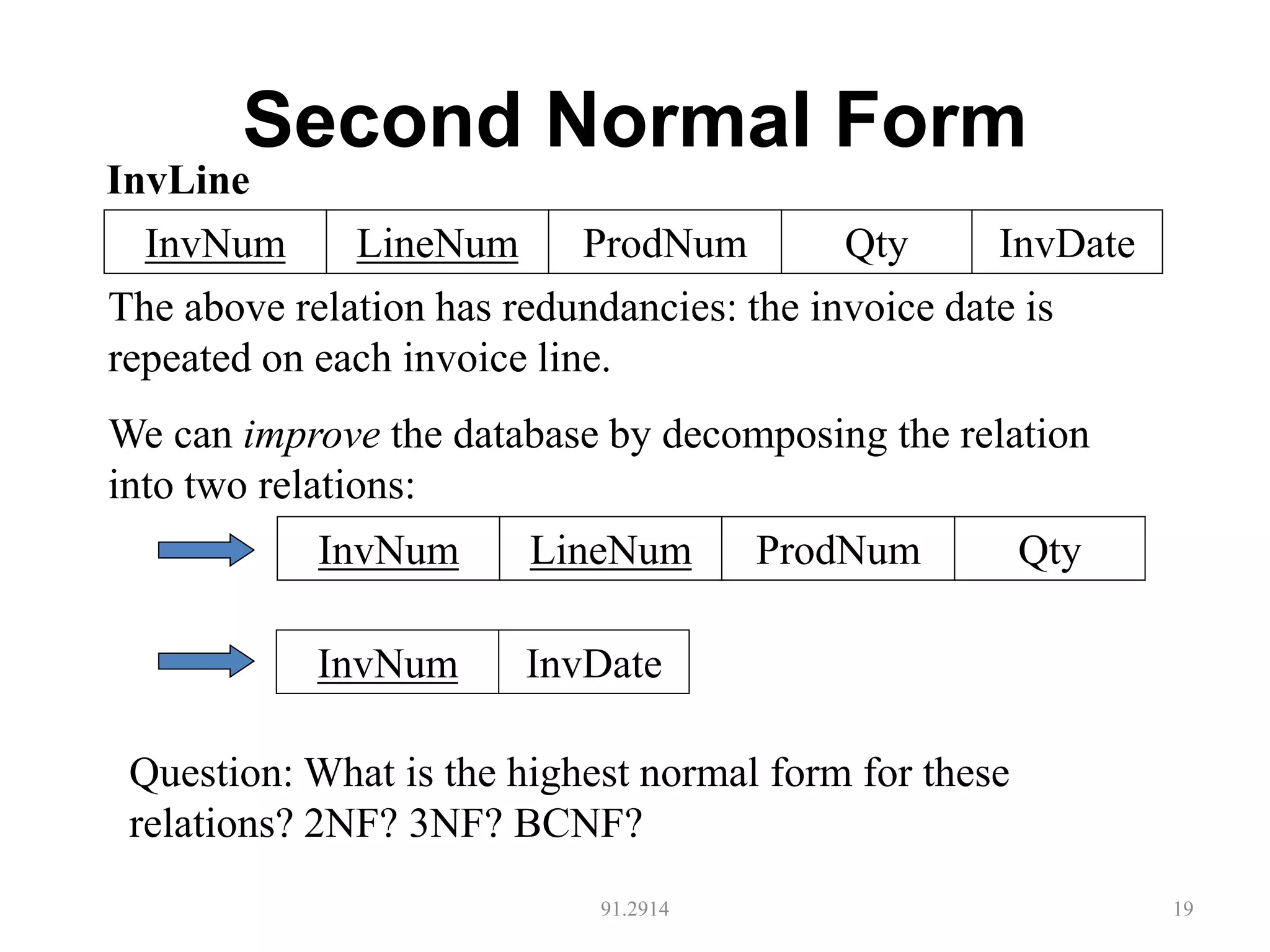
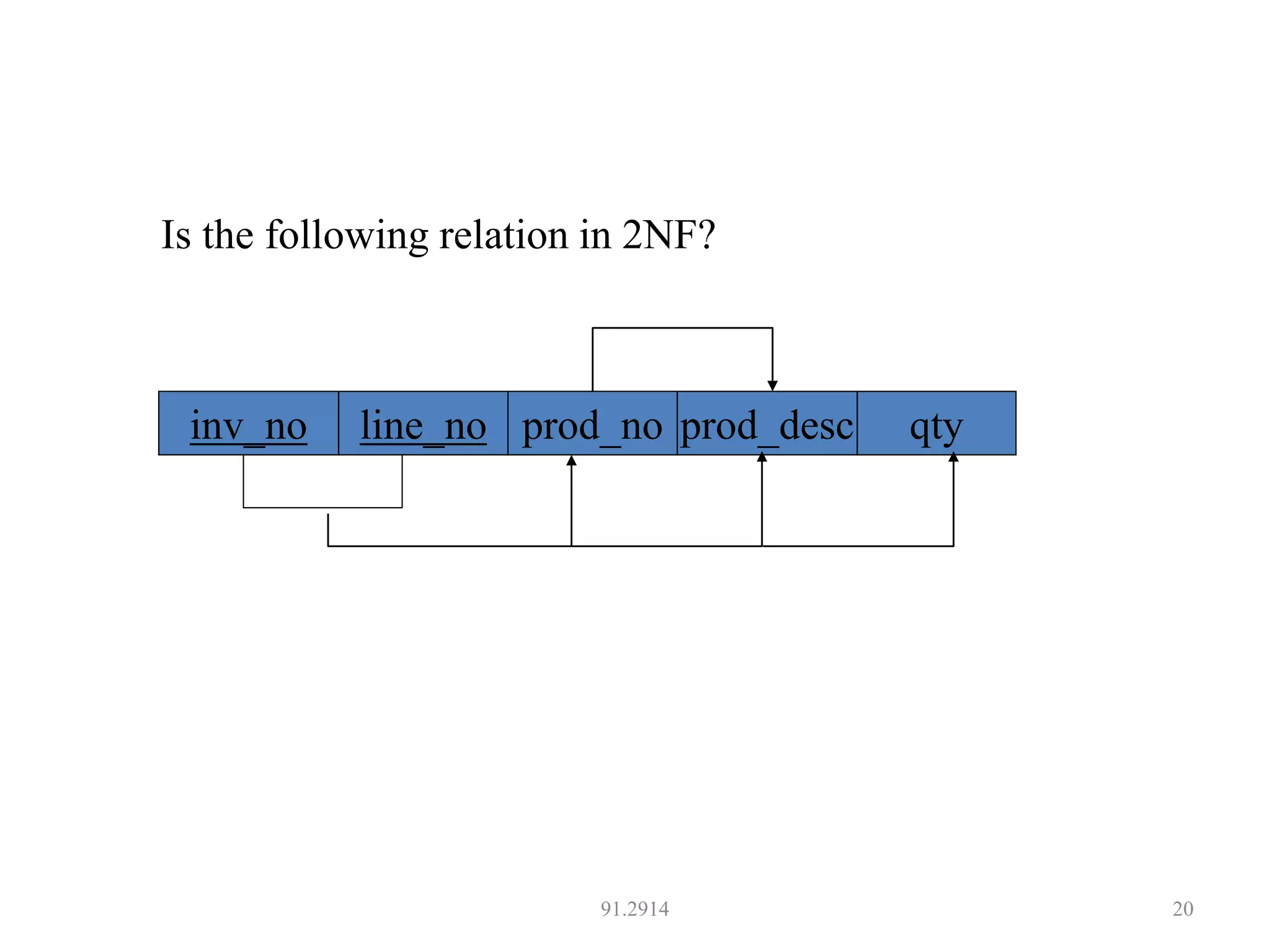
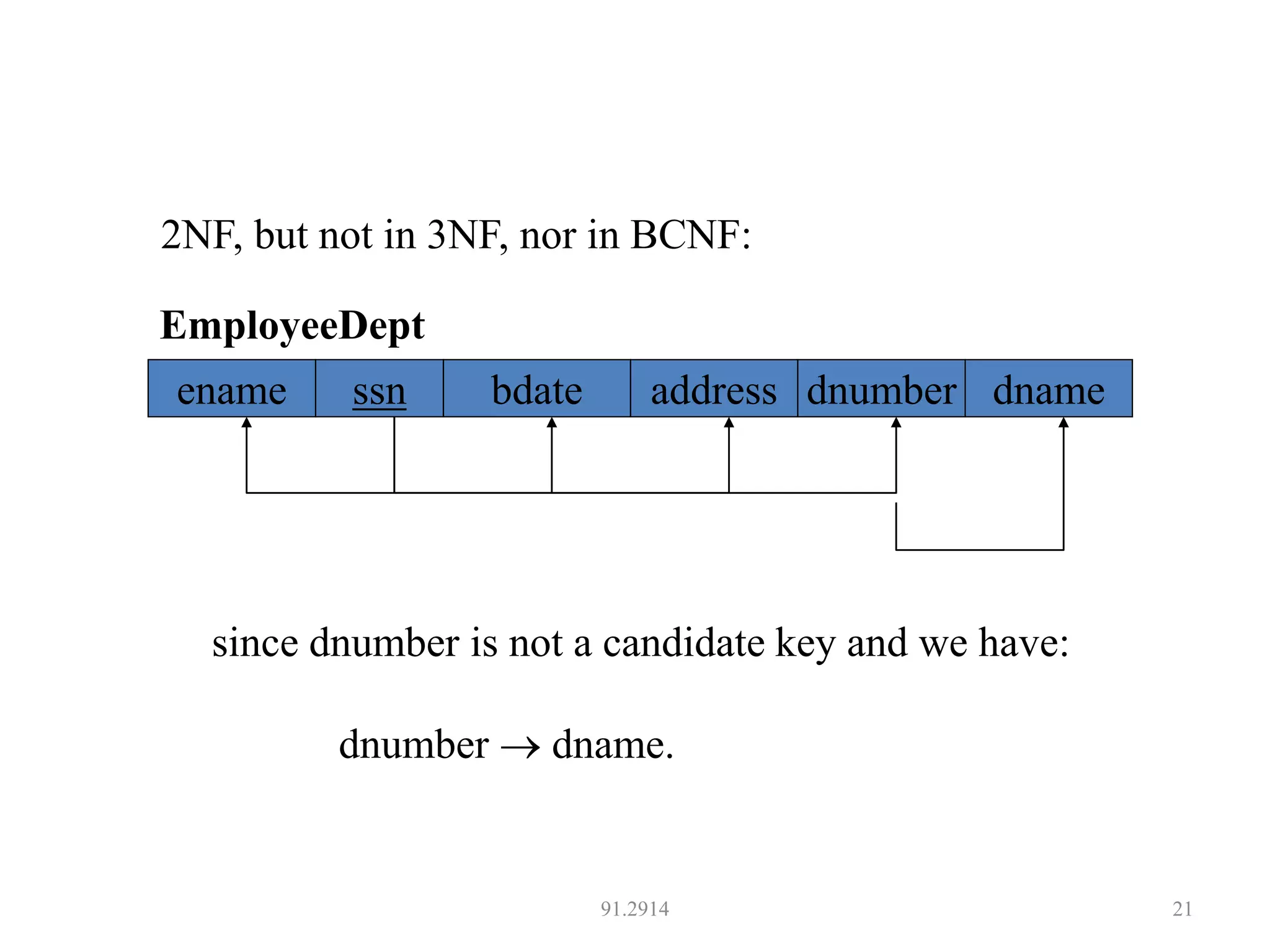
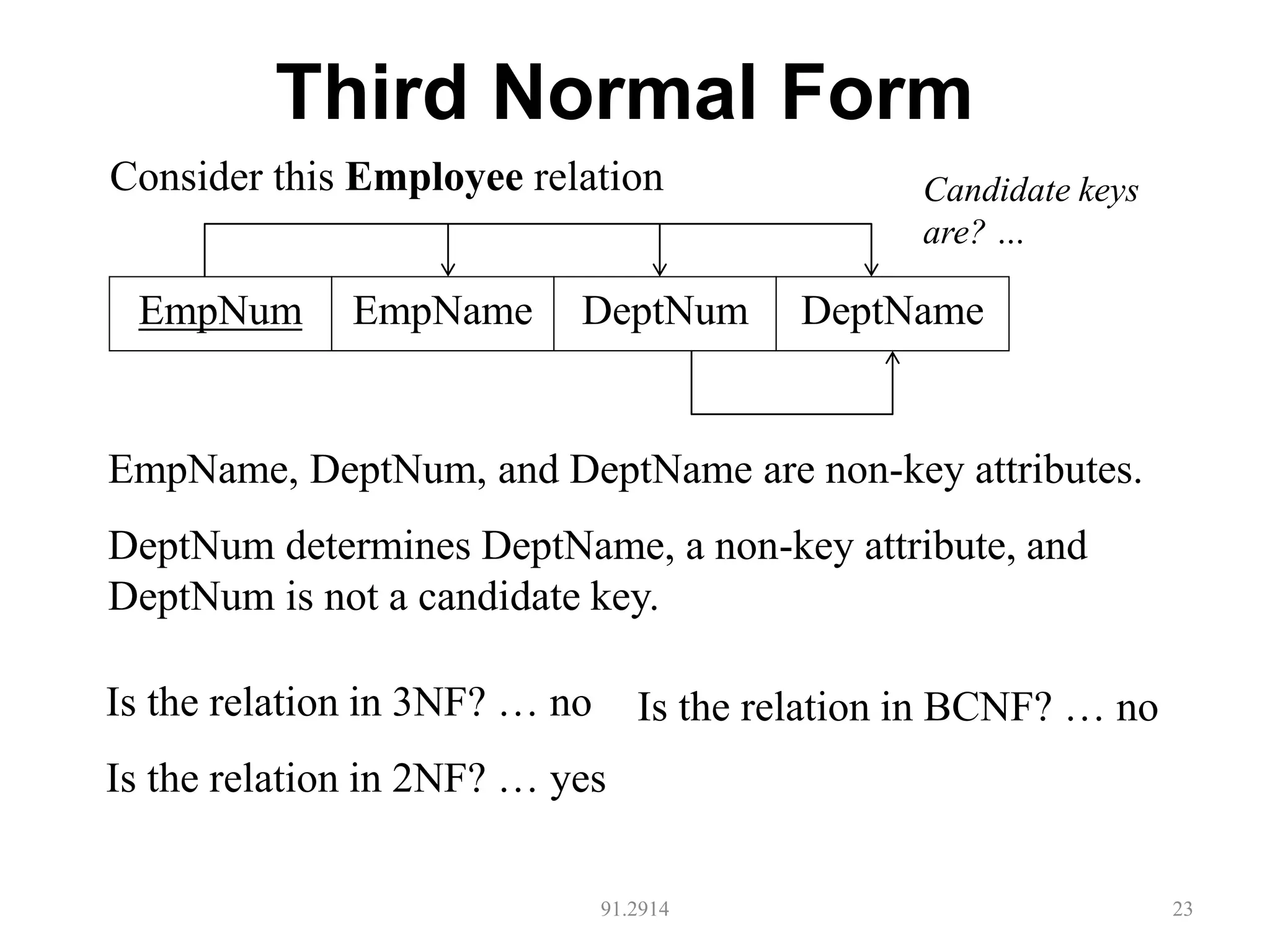
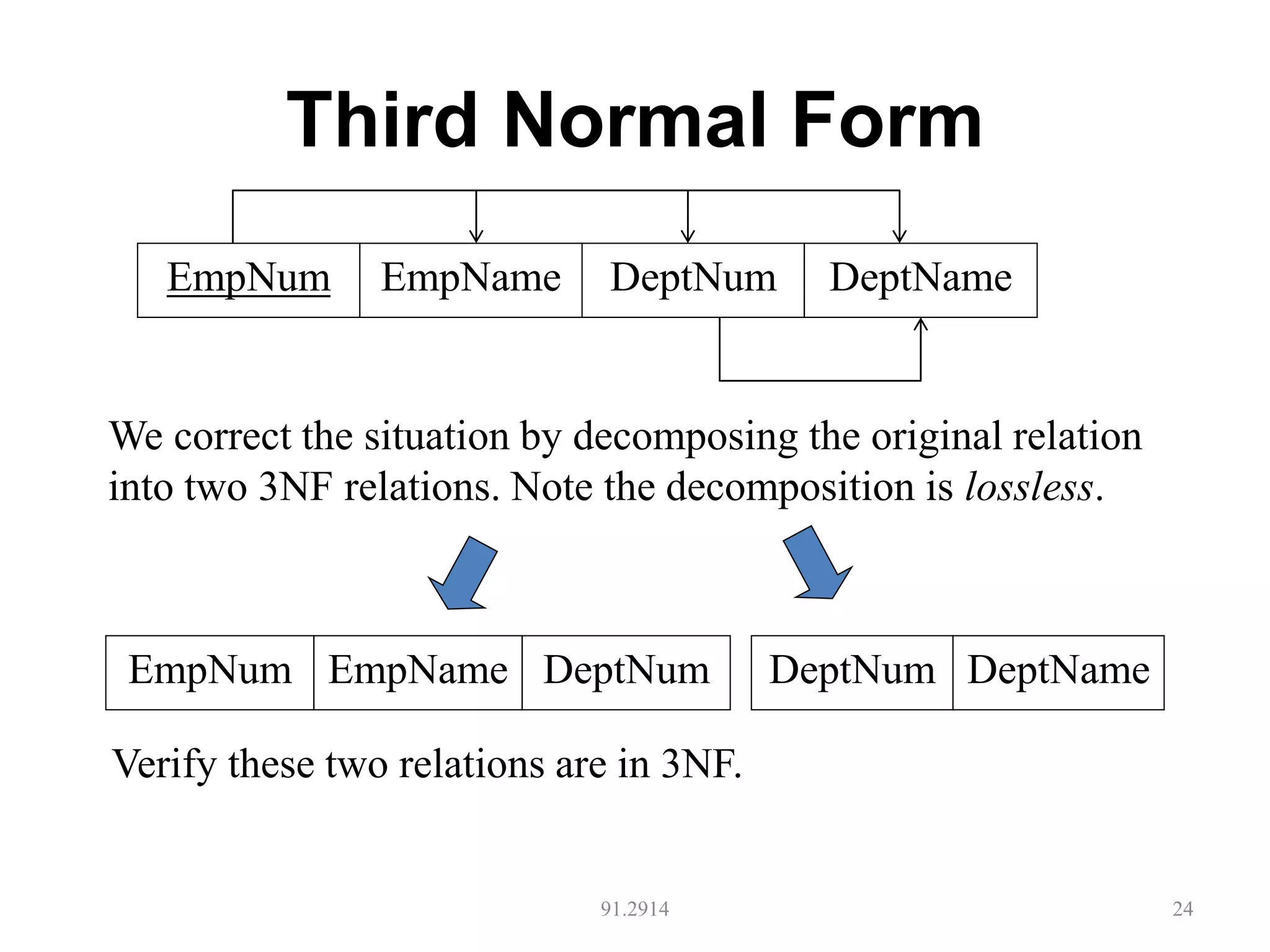
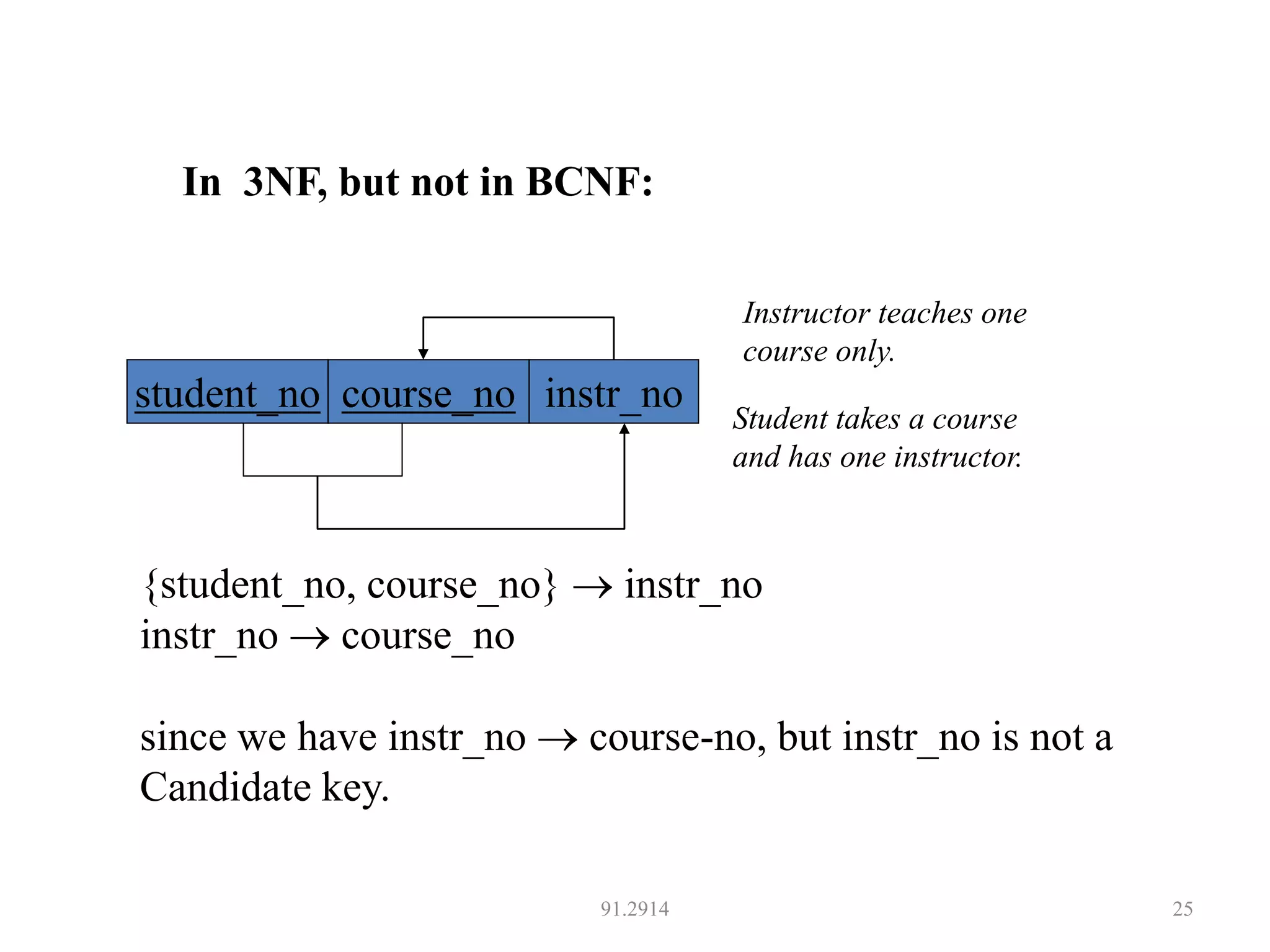
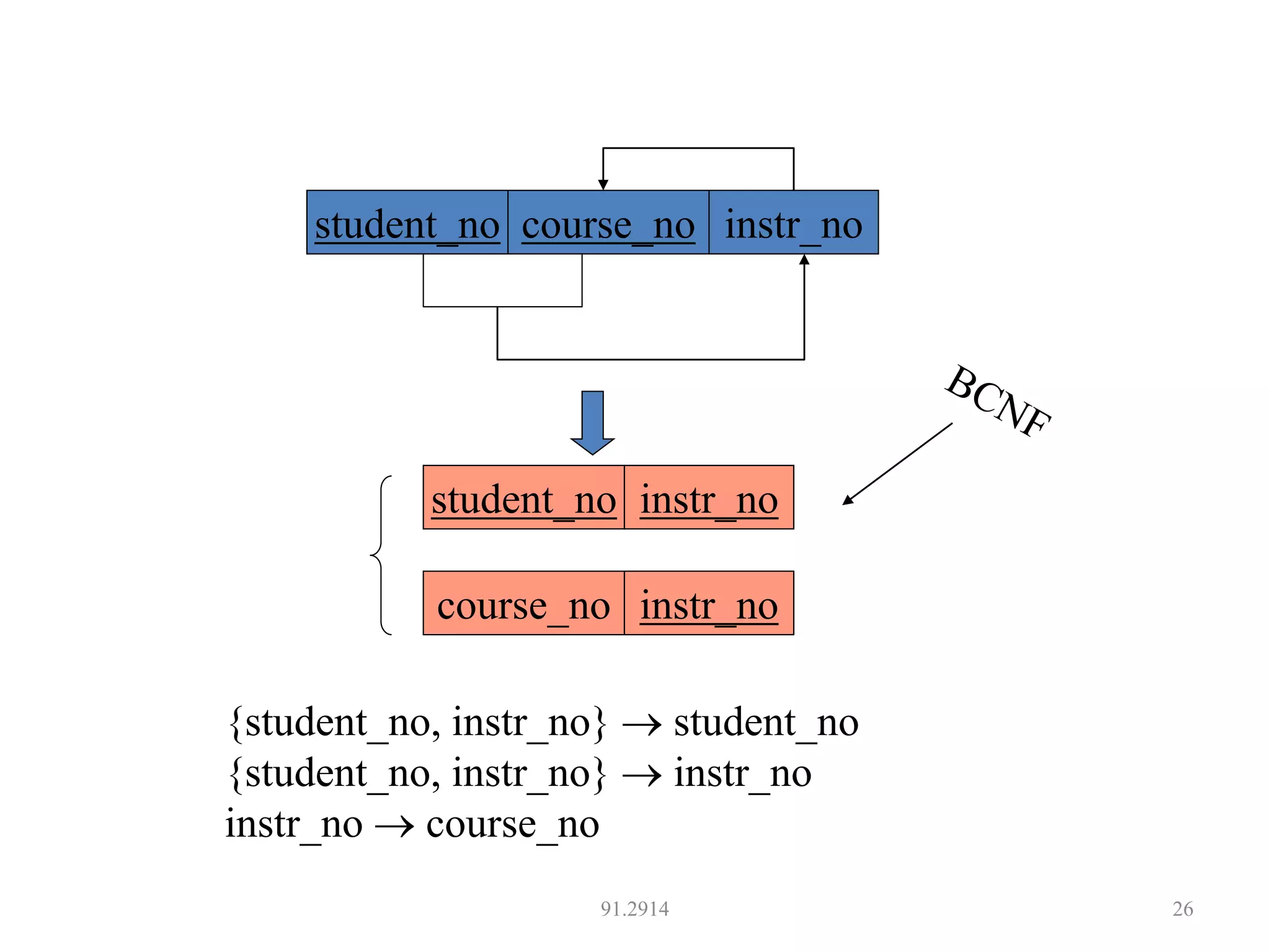
The document discusses database normalization and different normal forms including 1NF, 2NF, 3NF, and BCNF. It explains that normalization aims to reduce data redundancy and improve data integrity by creating tables where attributes depend on the primary key. Higher normal forms like BCNF are stronger than lower forms like 1NF. The concepts of functional dependencies, candidate keys, and normalizing relations are covered.