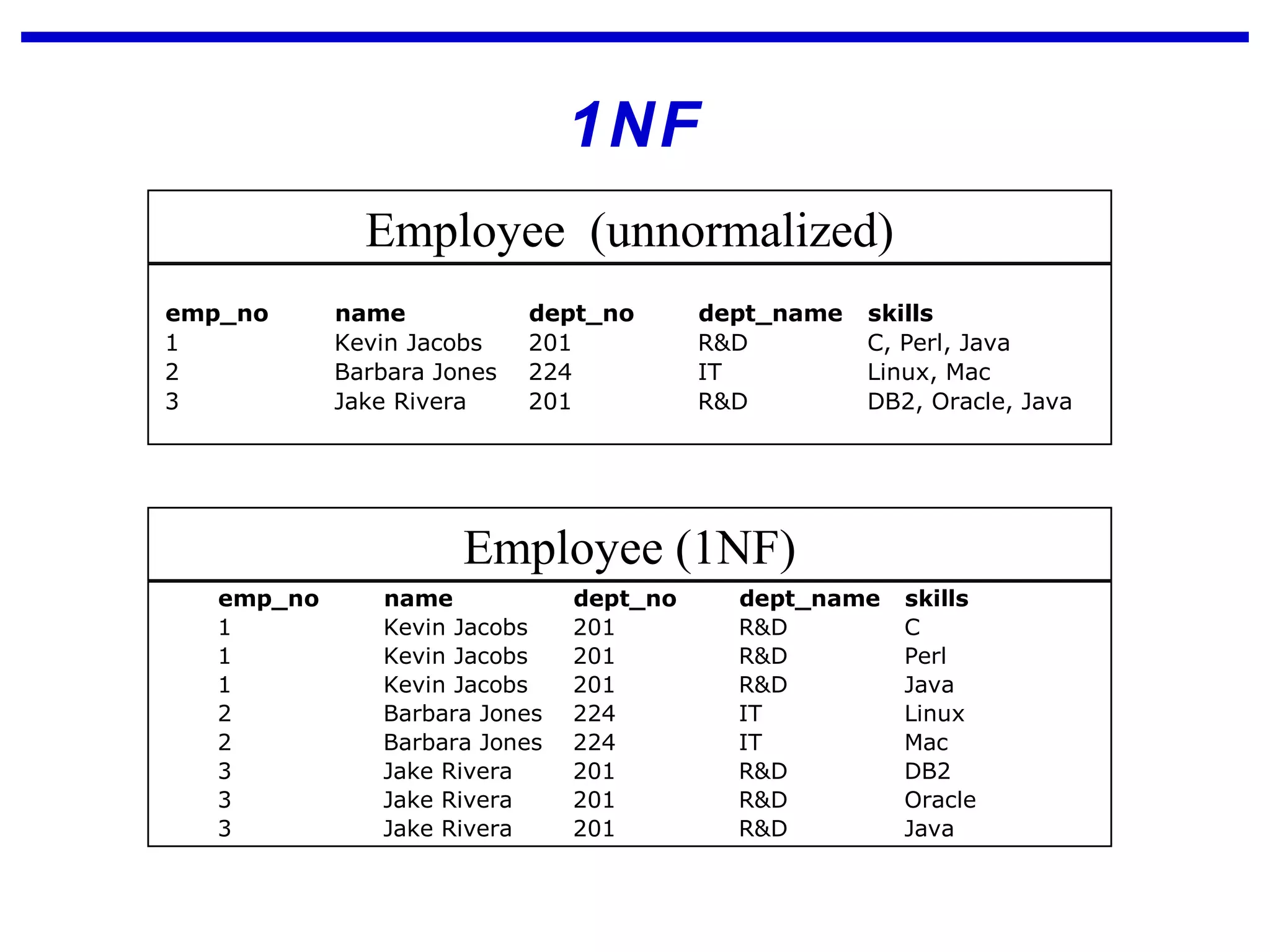
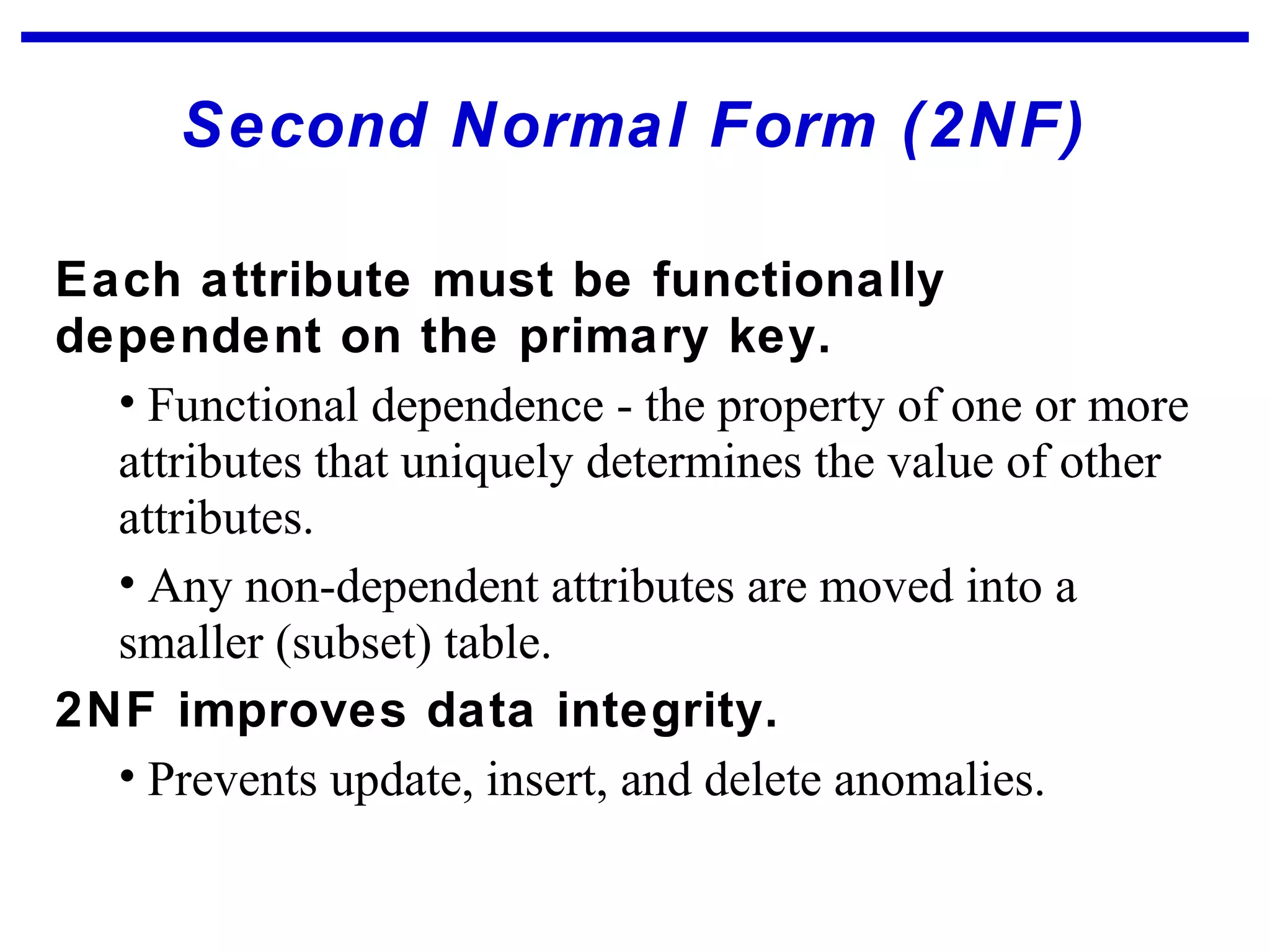
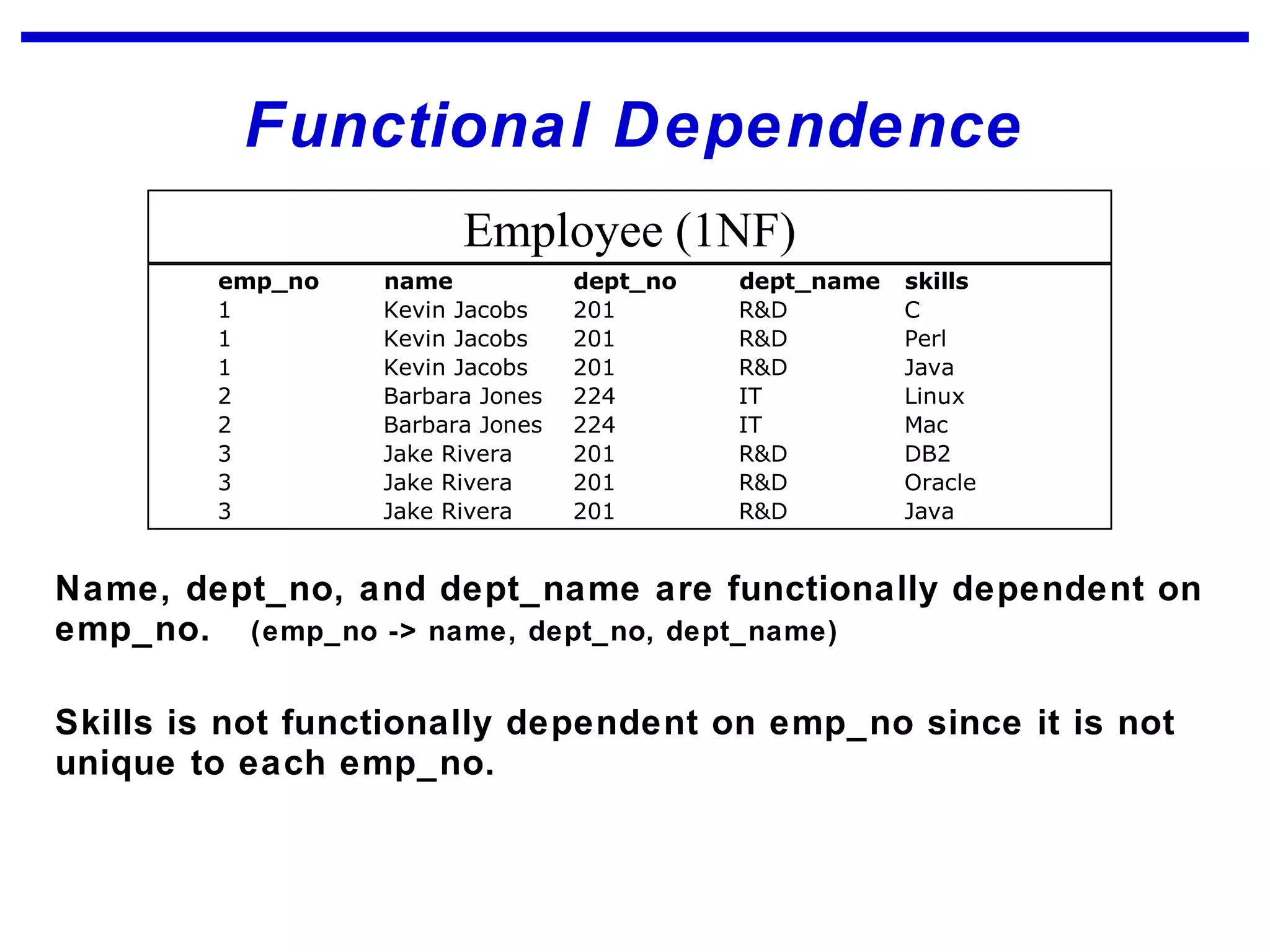
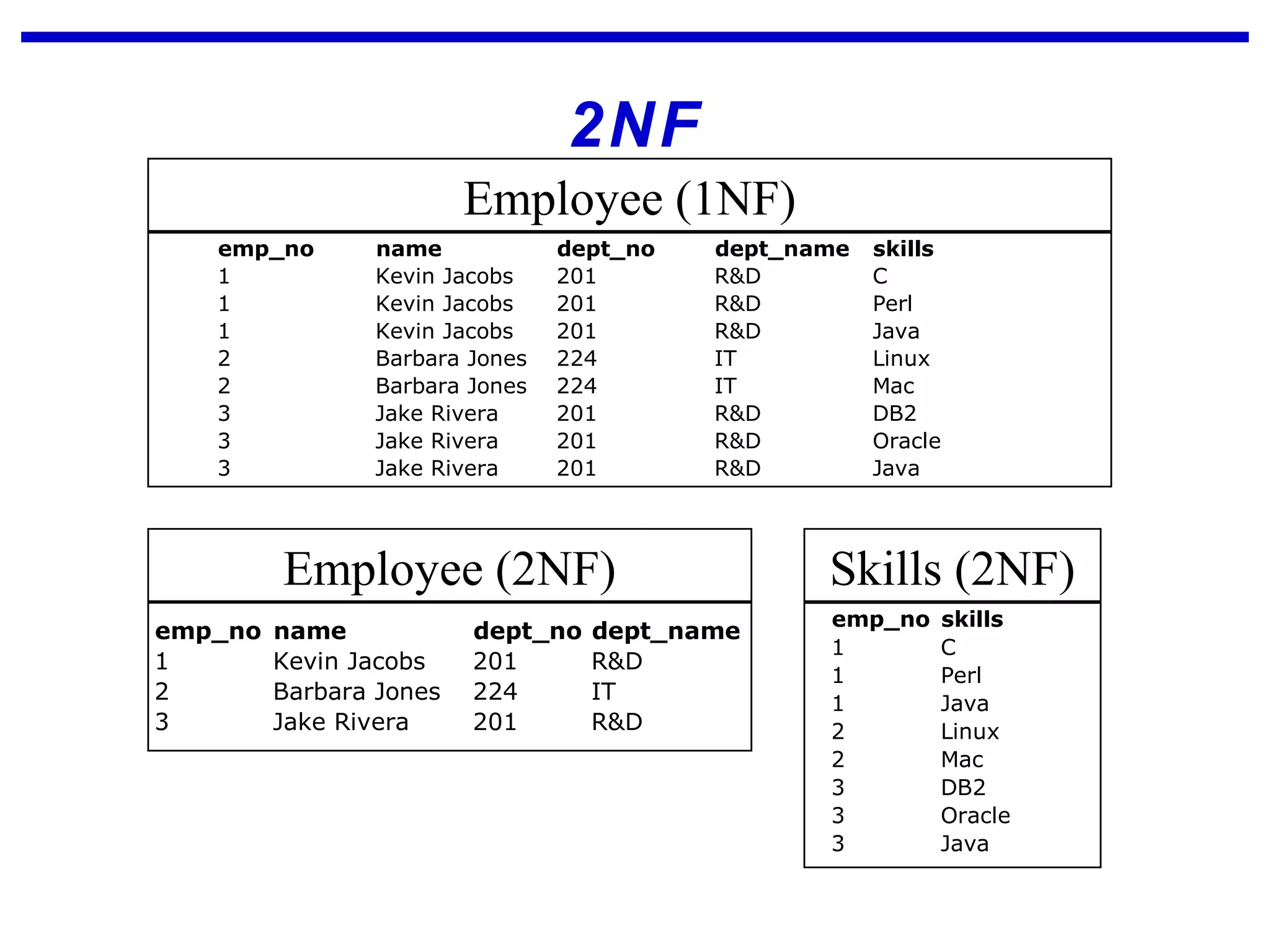
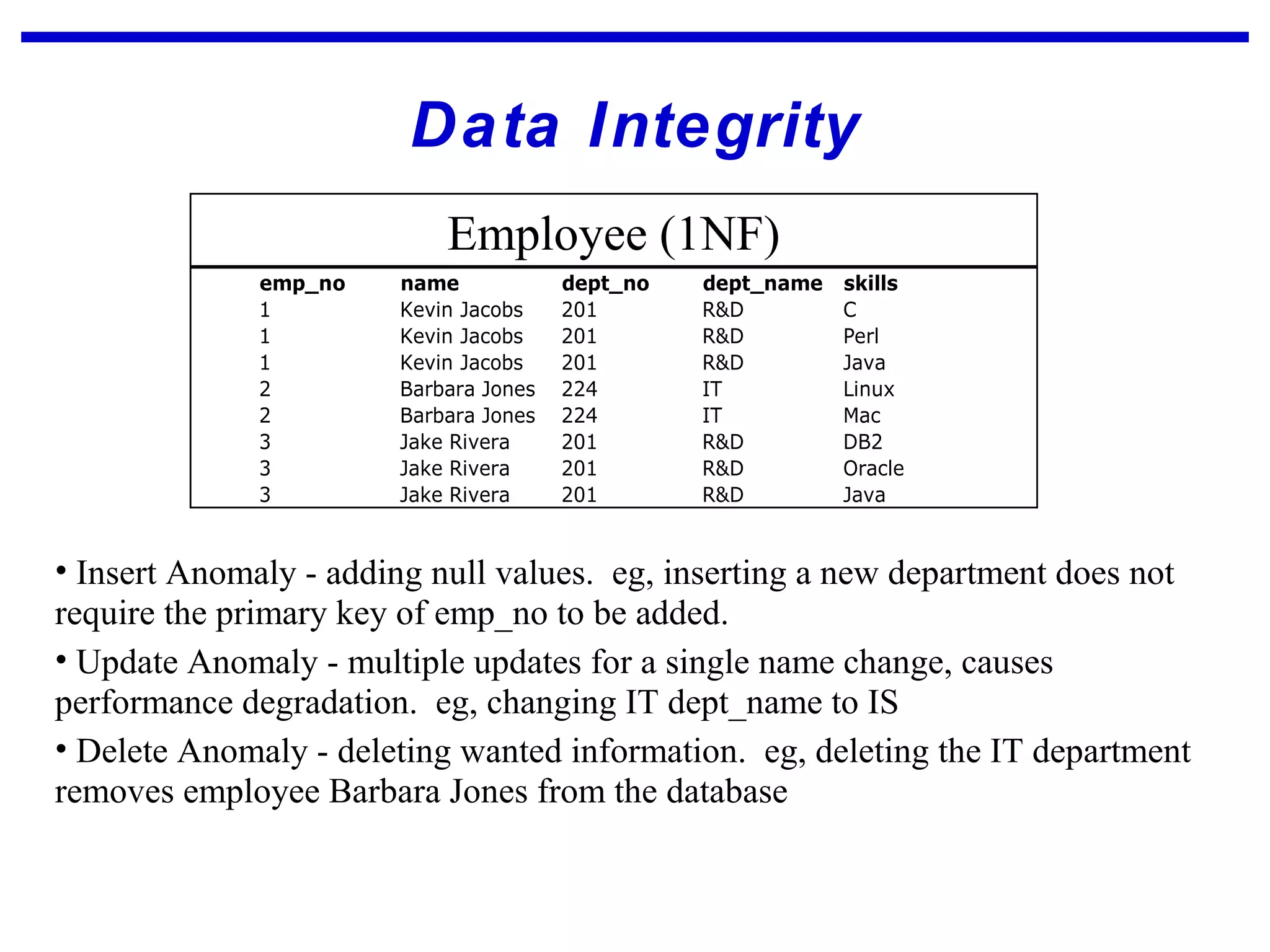
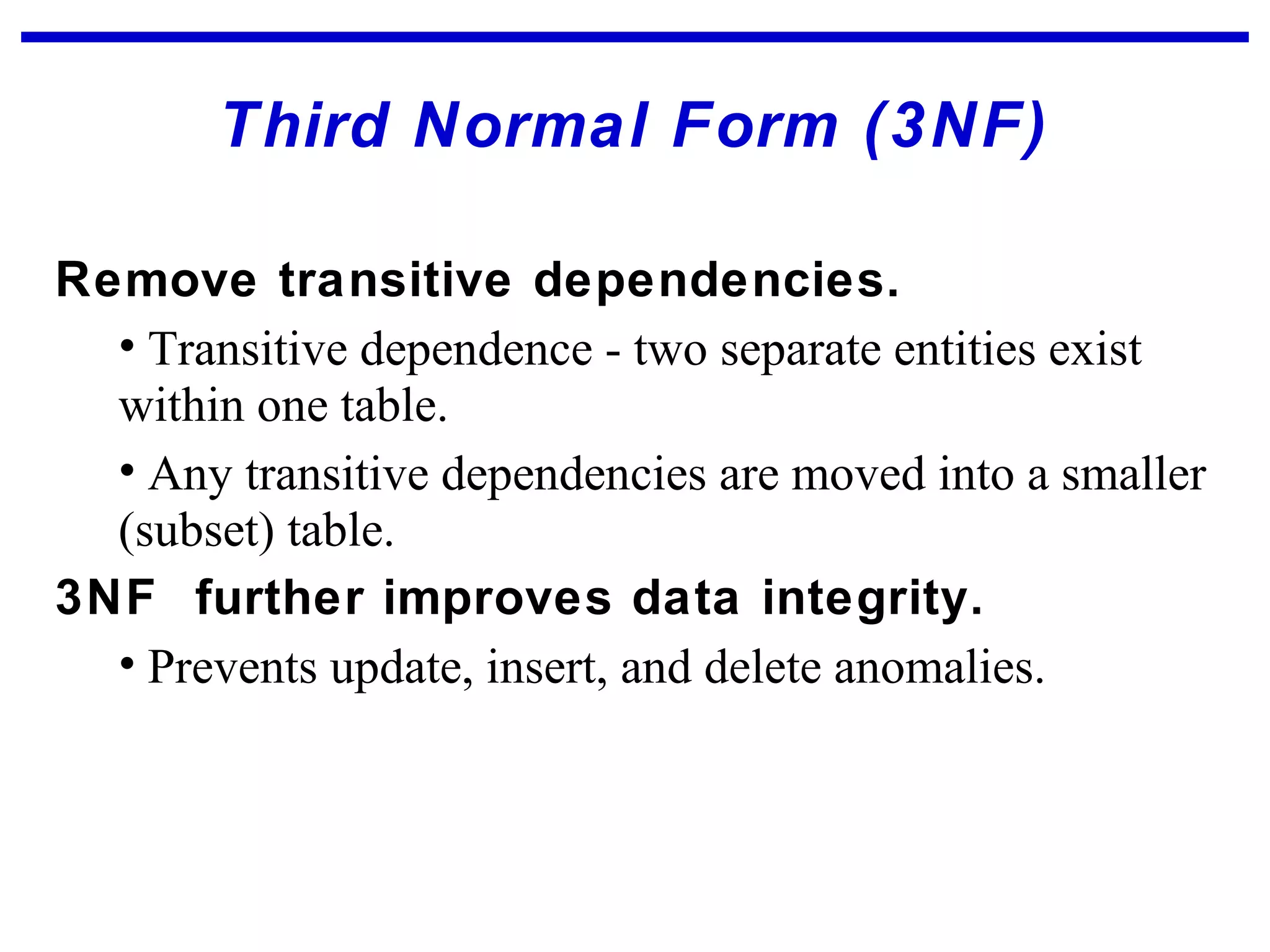
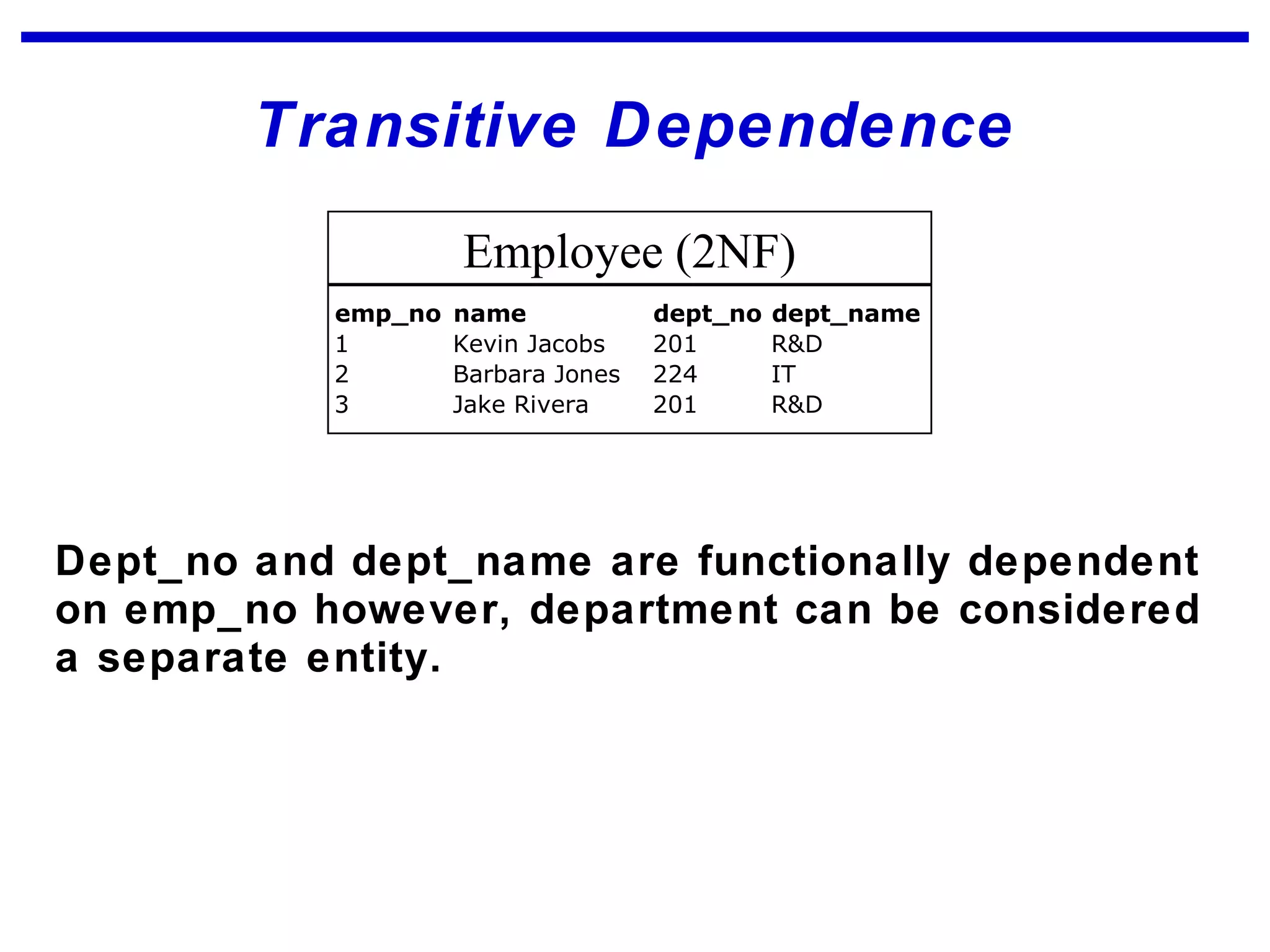
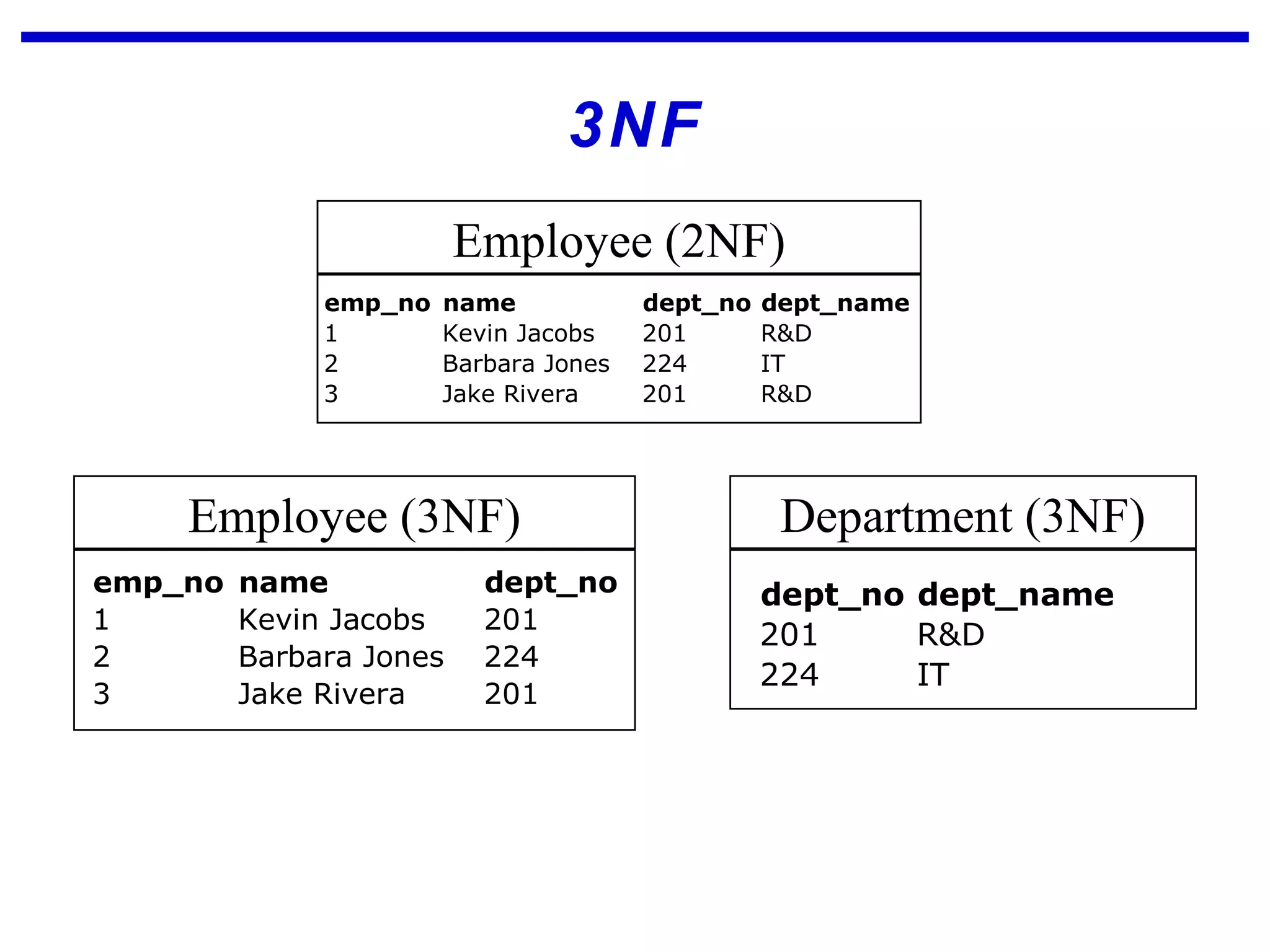
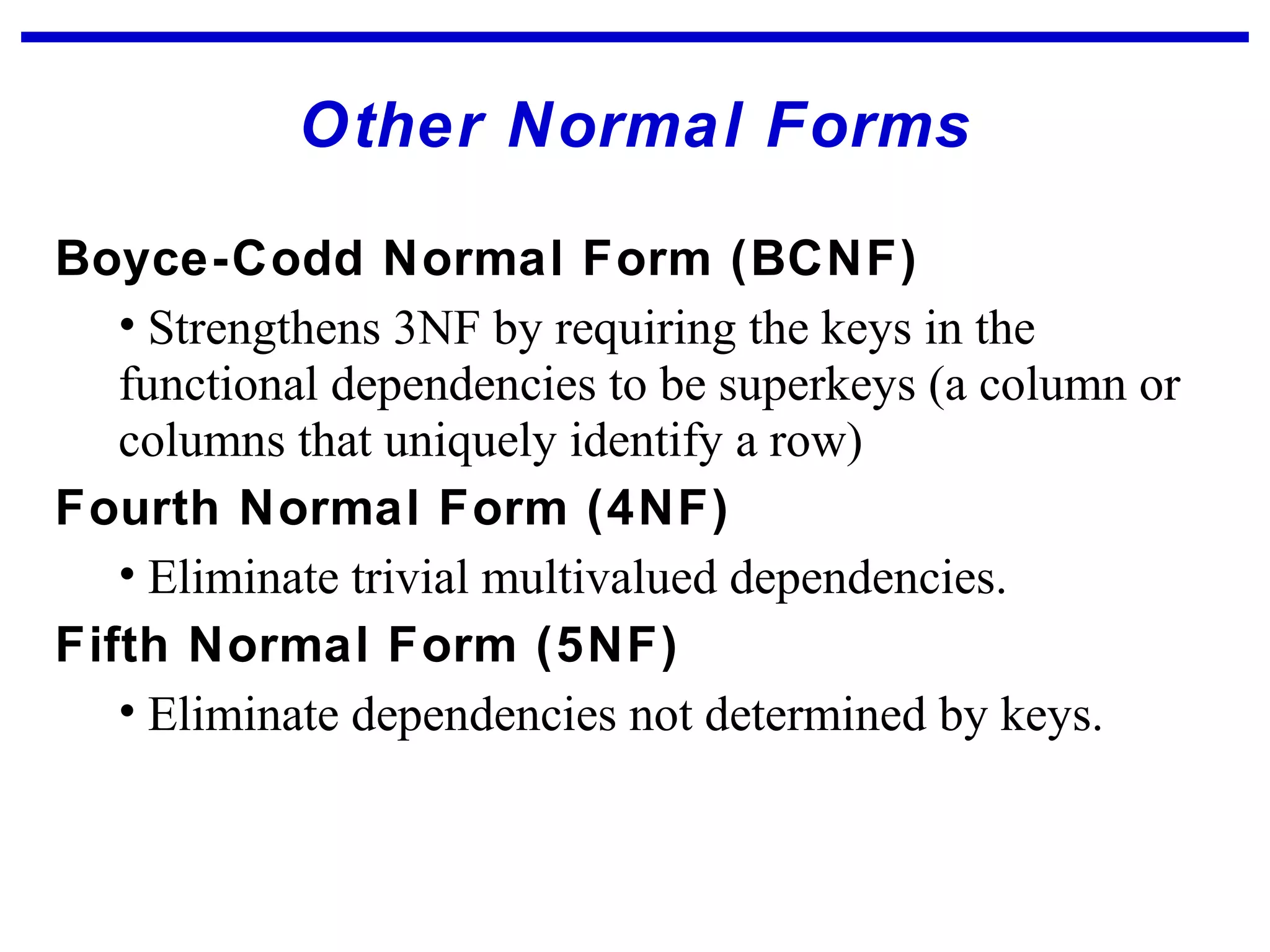
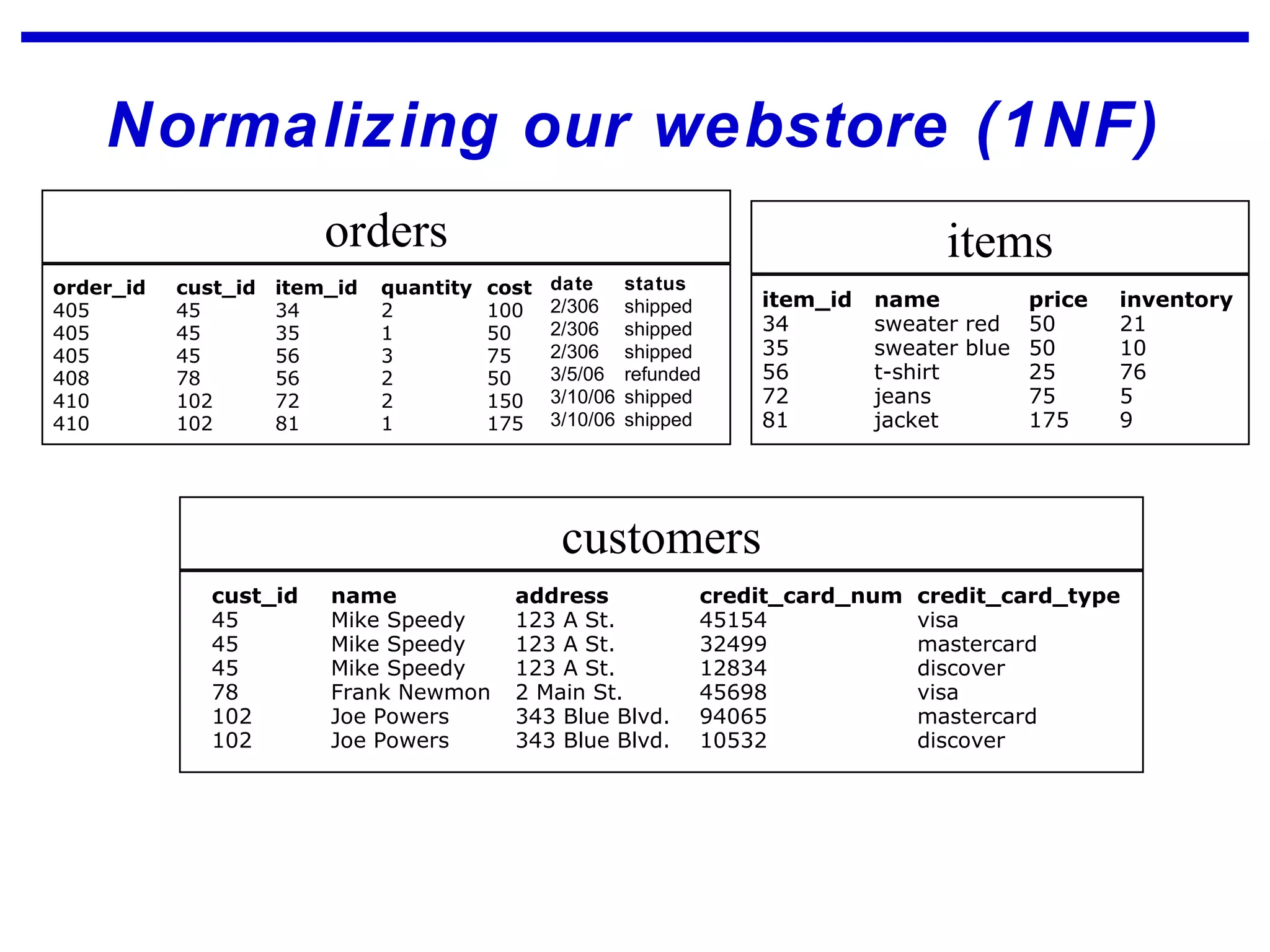
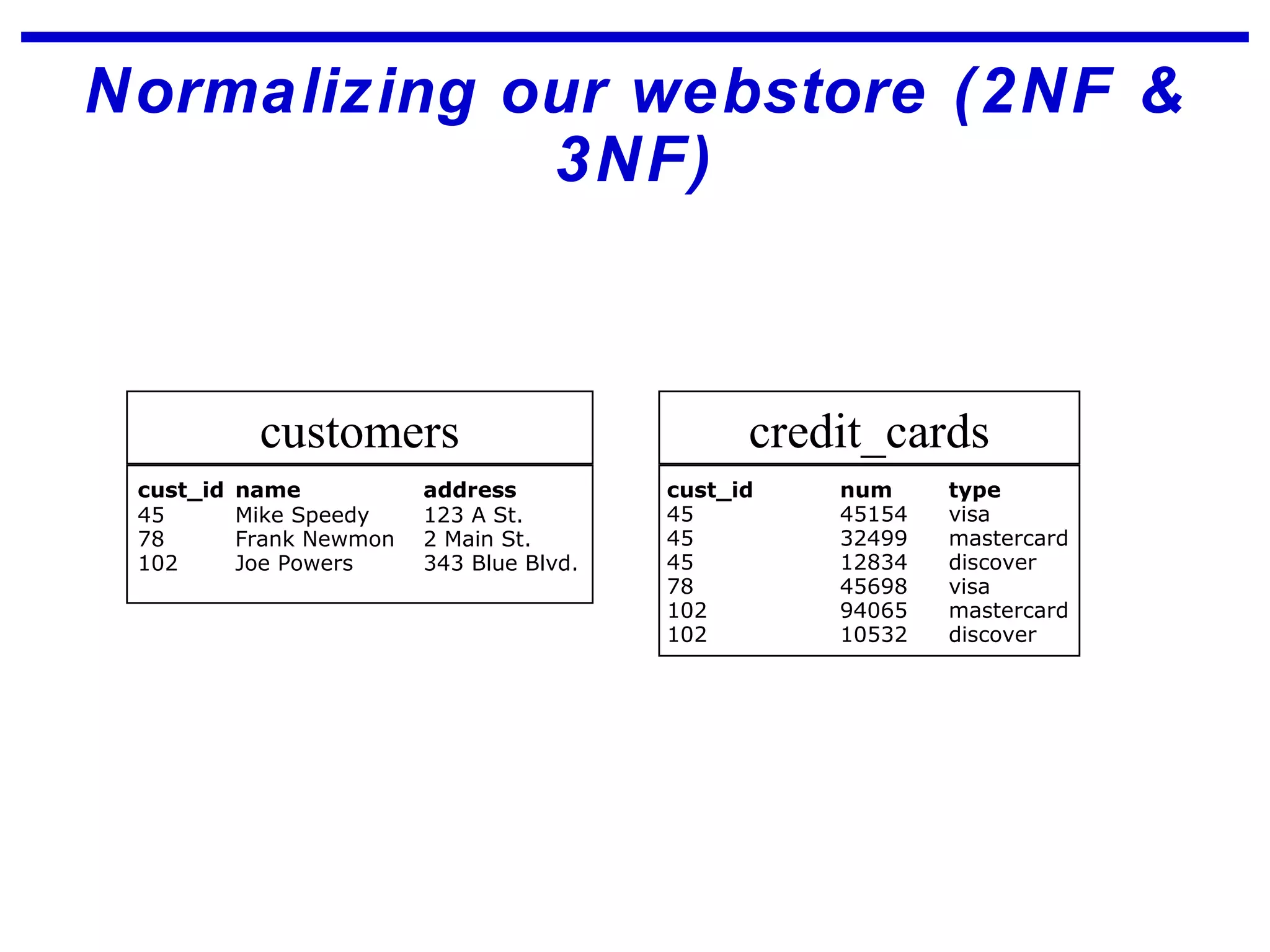
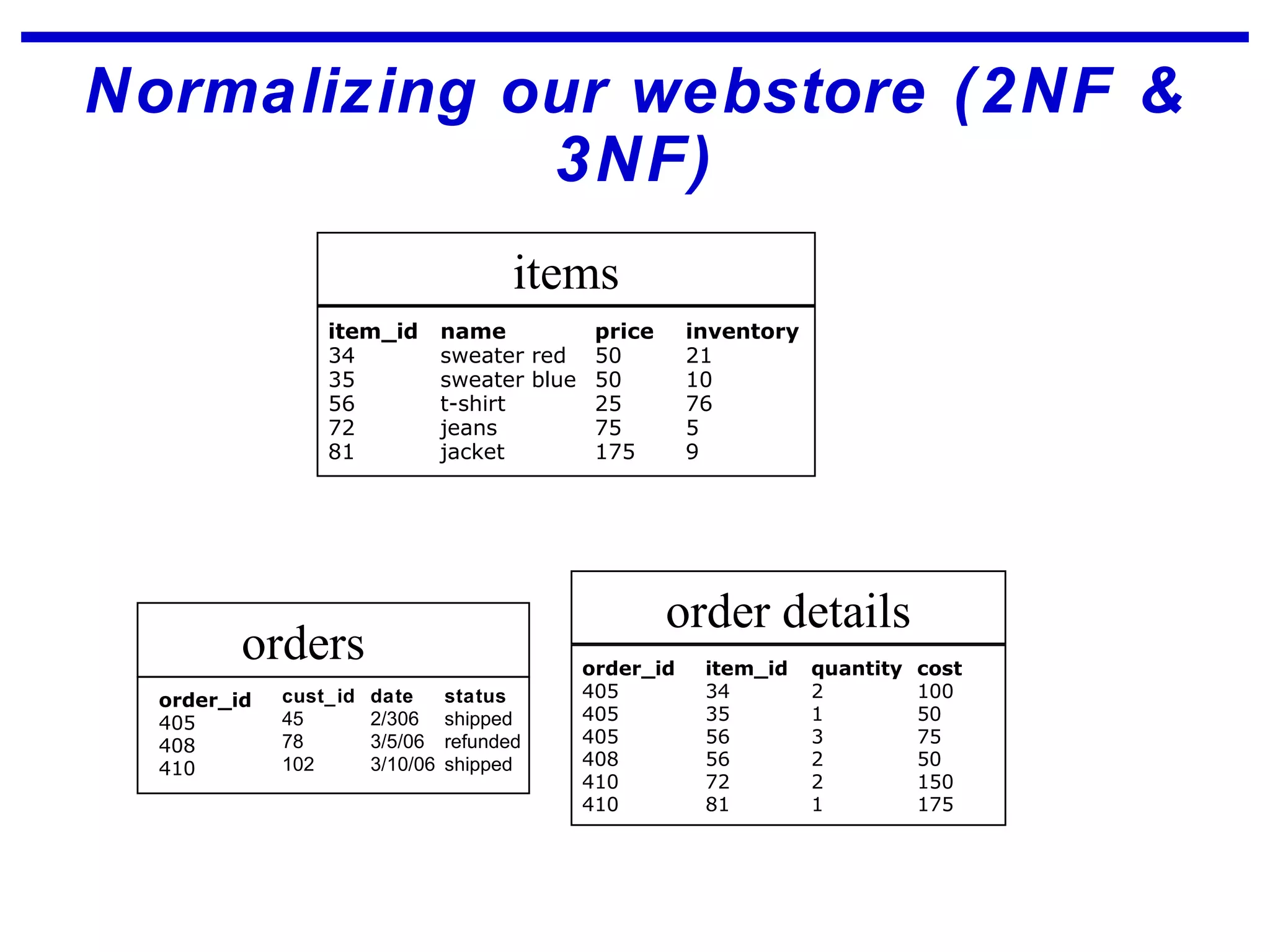
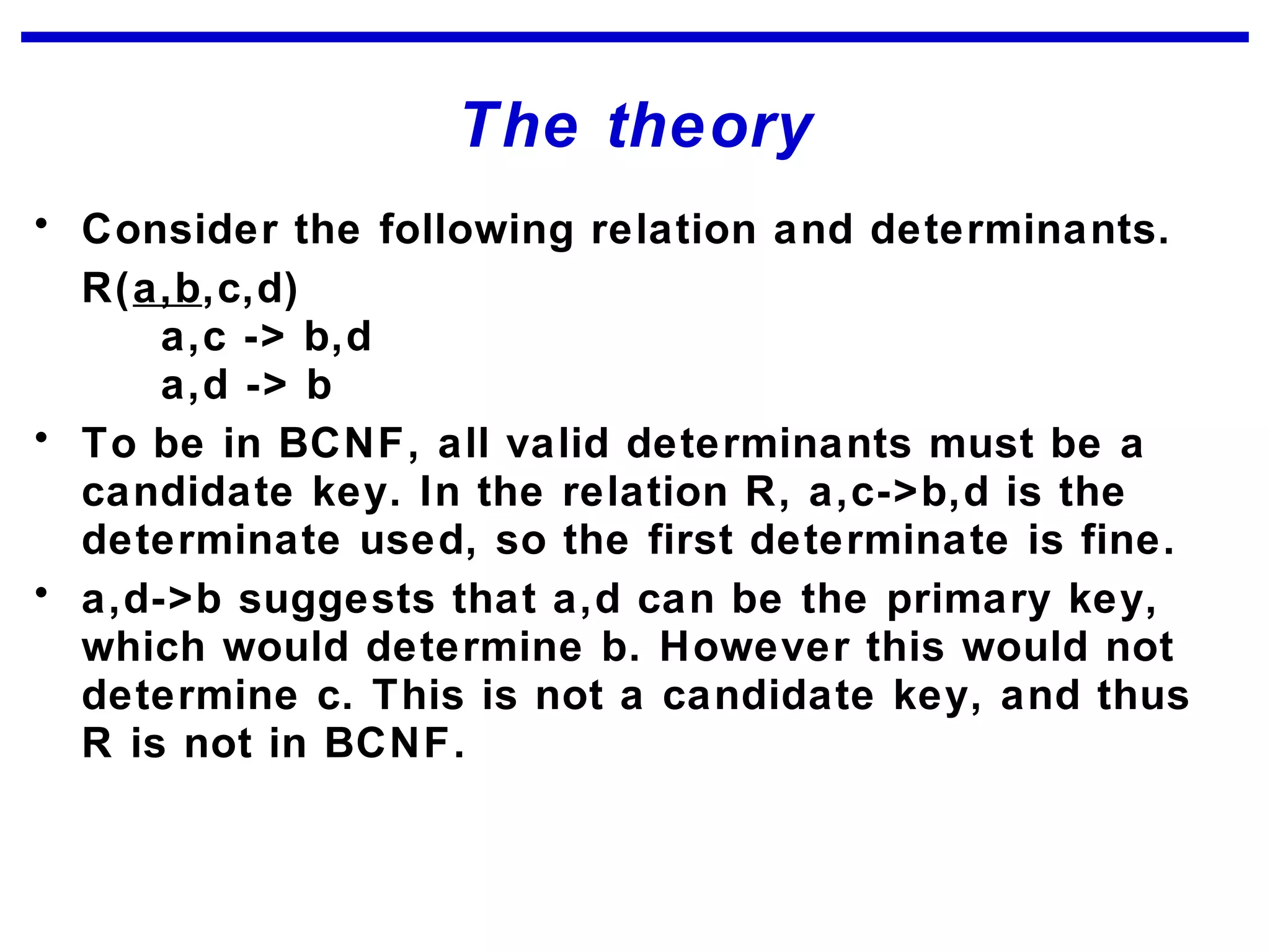
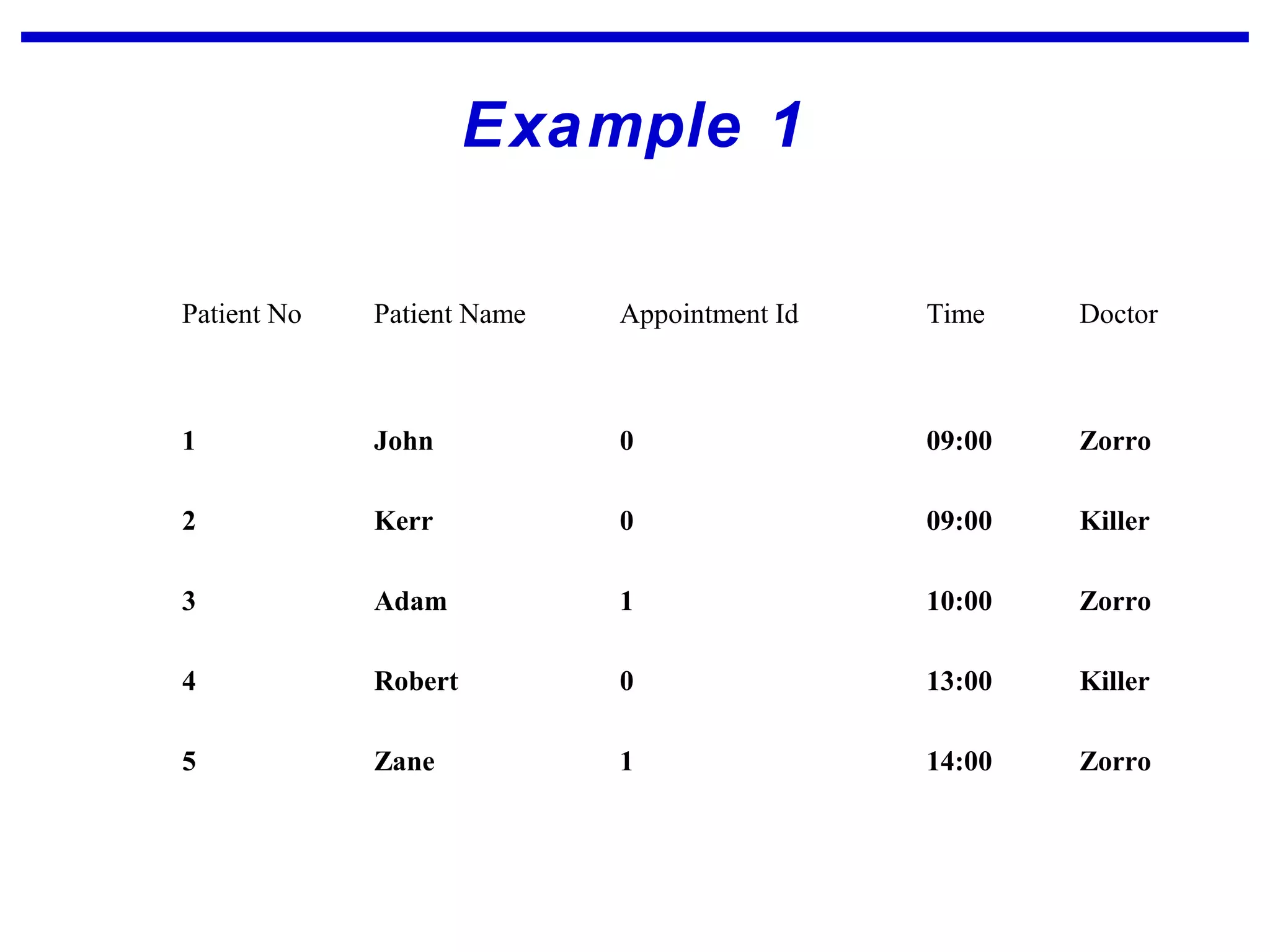
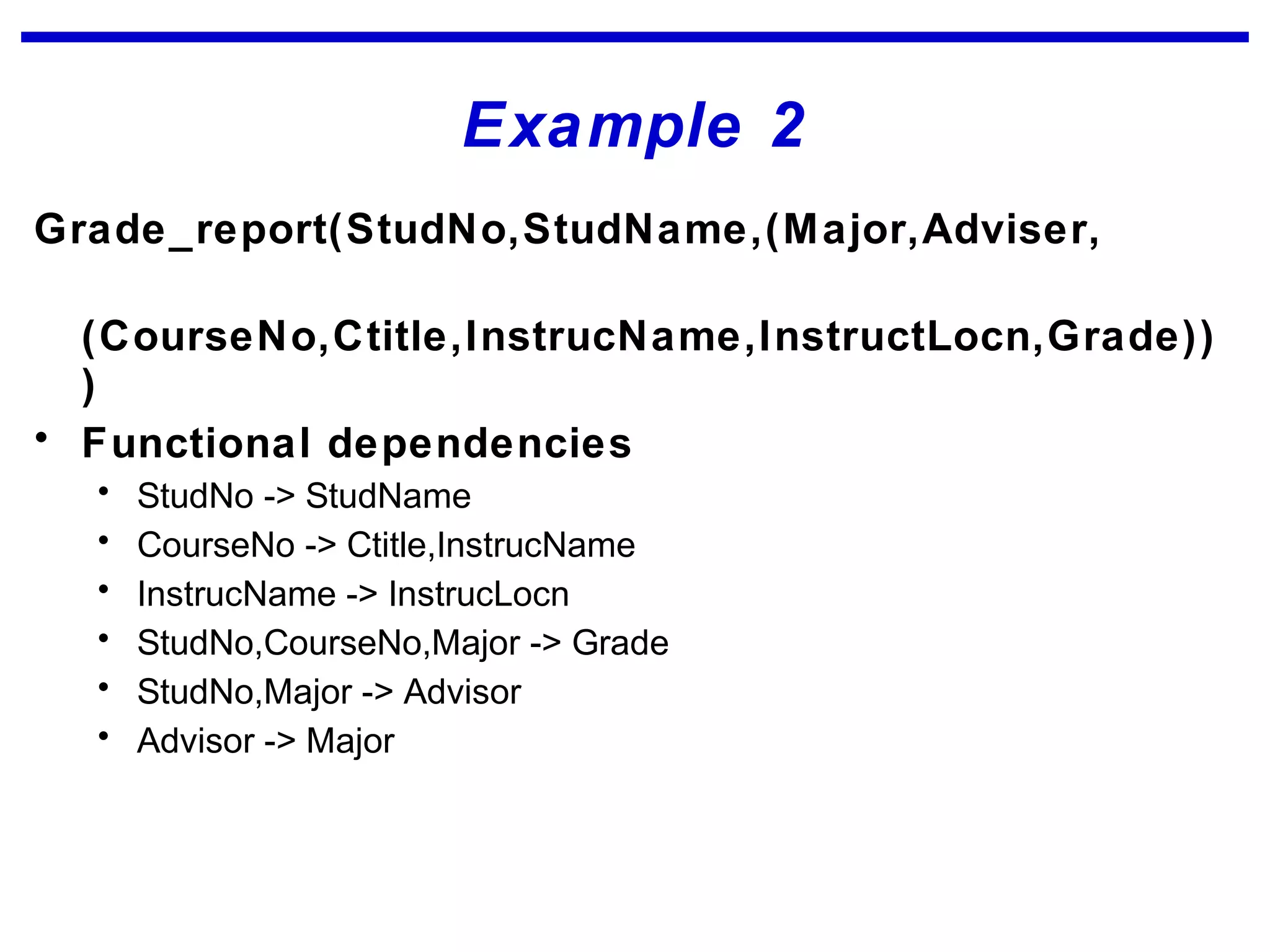
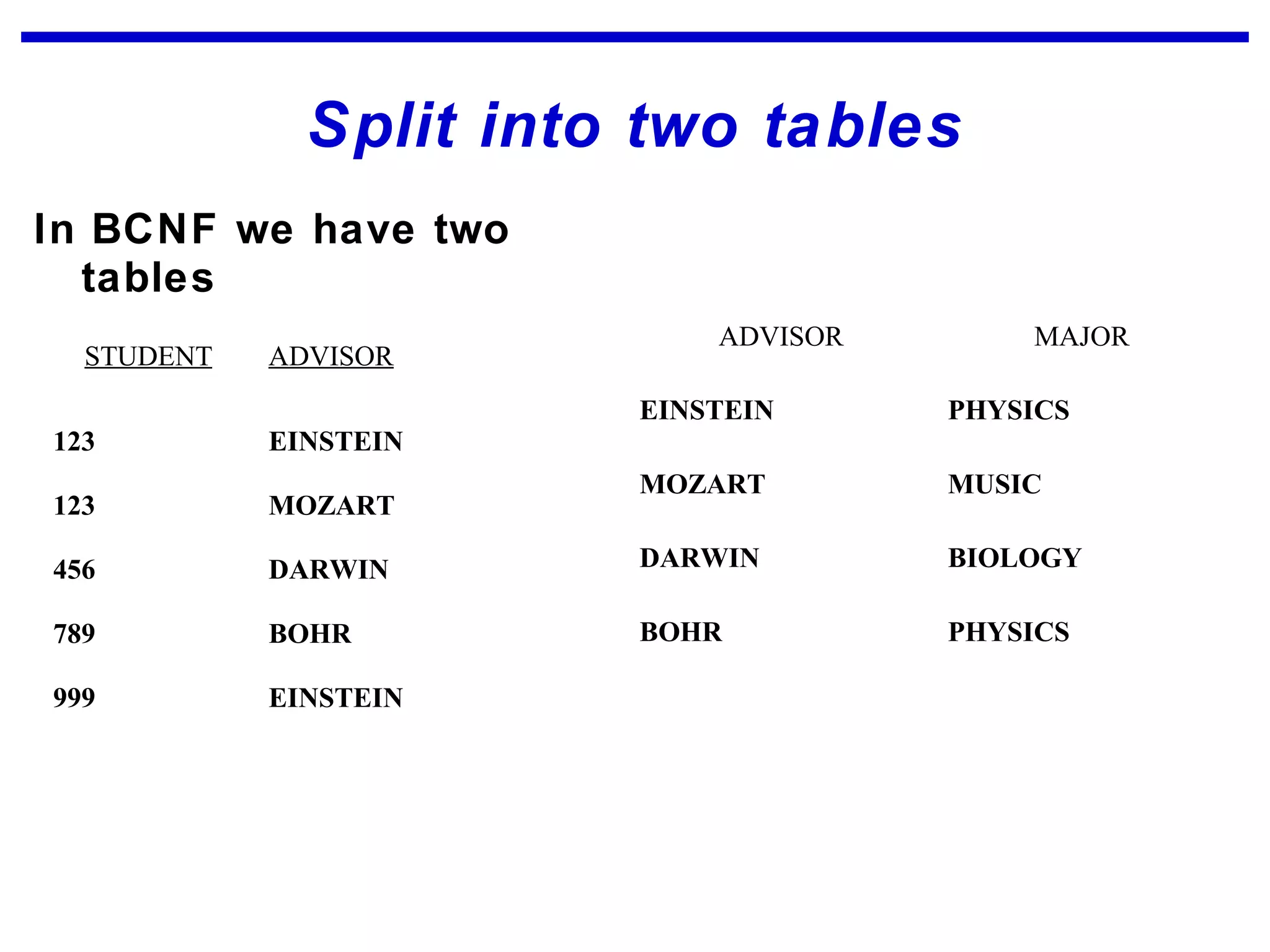
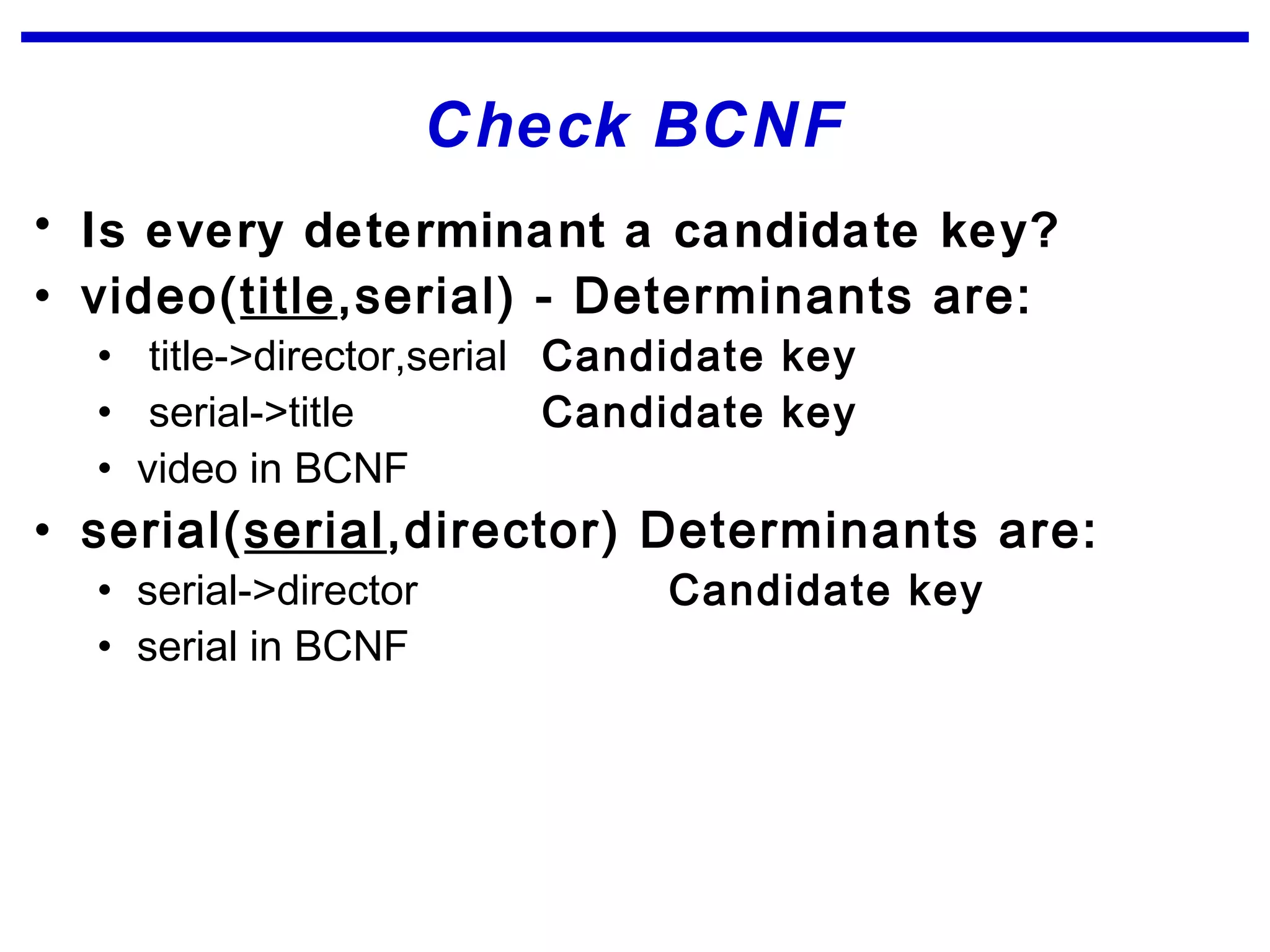
Normalization is a logical database design method that minimizes data redundancy and reduces design flaws. It involves applying normal forms like 1NF, 2NF, and 3NF to break large tables into smaller subsets. The normal forms improve data integrity by preventing anomalies like insertion, update, and deletion anomalies. Applying the normal forms can result in relations that are in first, second, and third normal form, but additional steps may be needed to attain Boyce-Codd normal form, which further reduces anomalies from overlapping candidate keys.