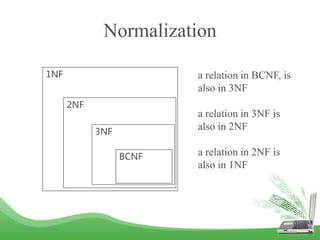
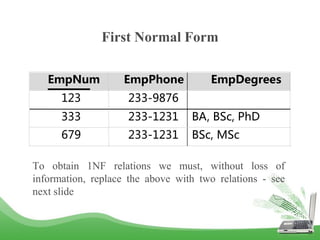
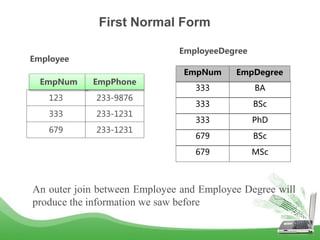
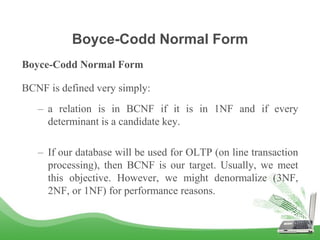
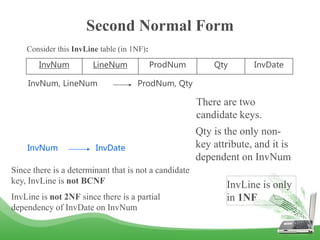
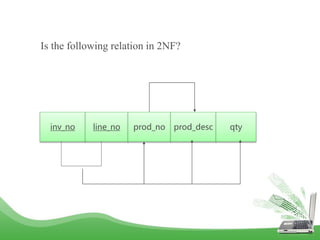
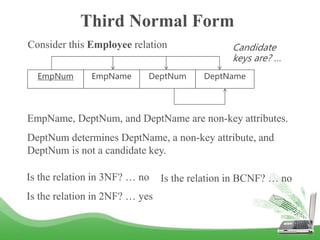
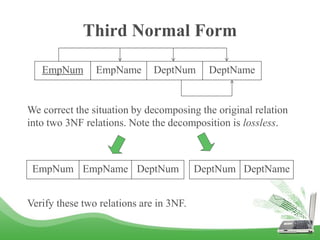
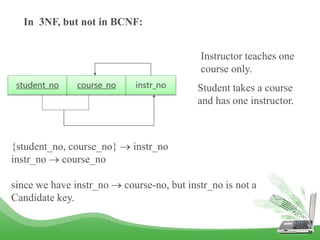
The document discusses database normalization and different normal forms including 1NF, 2NF, 3NF, and BCNF. It explains that normalization improves database design by generating relations of higher normal forms. The goal of normalization is to eliminate dependencies on non-key attributes. Higher normal forms like BCNF and 3NF ensure relations are dependent only on candidate keys to reduce data anomalies and redundancies. Examples are provided to illustrate the different normal forms.