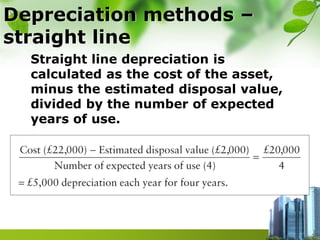
The document discusses depreciation of tangible non-current assets, outlining its definition as a cost allocation based on the asset's economic usefulness. It details causes of depreciation such as physical deterioration and obsolescence, along with various calculation methods including straight line and reducing balance. Additionally, it highlights other depreciation methods like revaluation and units of output, emphasizing the importance of selecting an appropriate method based on asset usage patterns.