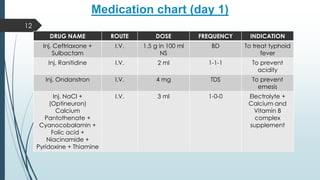
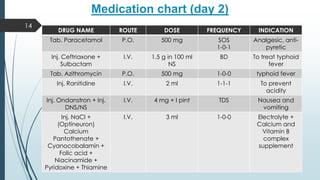
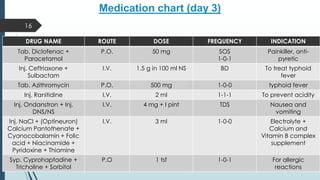
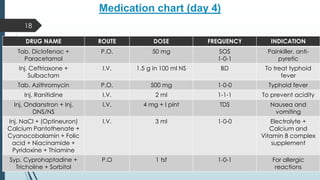
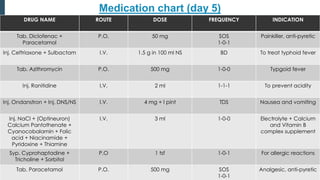
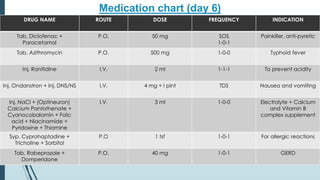
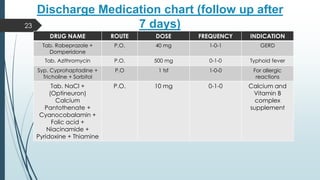
This document presents a case study of a 21-year-old male diagnosed with typhoid fever, detailing his symptoms, laboratory findings, and comprehensive treatment plan. The patient was admitted with fever, body ache, and yellowish sclera, and was treated over six days with antibiotics and supportive care. It emphasizes the importance of prevention strategies, hygiene practices, and patient education regarding medication and lifestyle modifications to avoid typhoid transmission.





![LAB. INVESTIGATION REPORTS [first day]
LABORATORY PARAMETERS OBSERVED VALUE NORMAL RANGE UNIT
Hb 14.0 11.5-18 g%
Neutrophils 69.6 40-70 %
Lymphocytes 45 20-40 /cu mm
Monocytes 04 2-10 /cu mm
ESR 45 1-20 mm/hr
Platelets 348000 1.5-4 /cu mm
ALT 55 <40 IU/L
6
PS for MP: Malarial parasite not seen
Widal Test: Positive
HIV test: negative
OTHERS (2nd day)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8-200326130704/85/8-a-case-study-on-typhoid-fever-6-320.jpg)