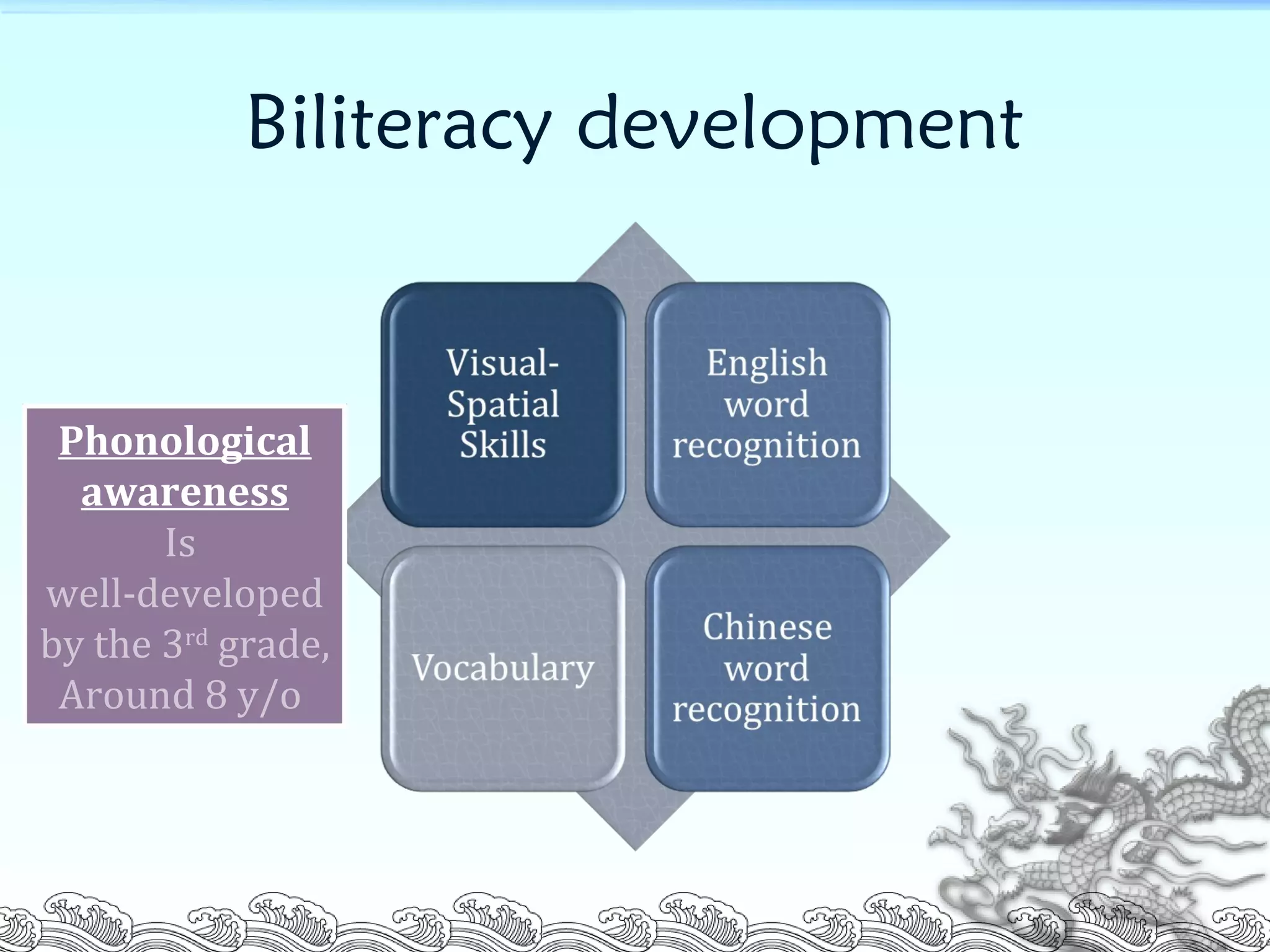
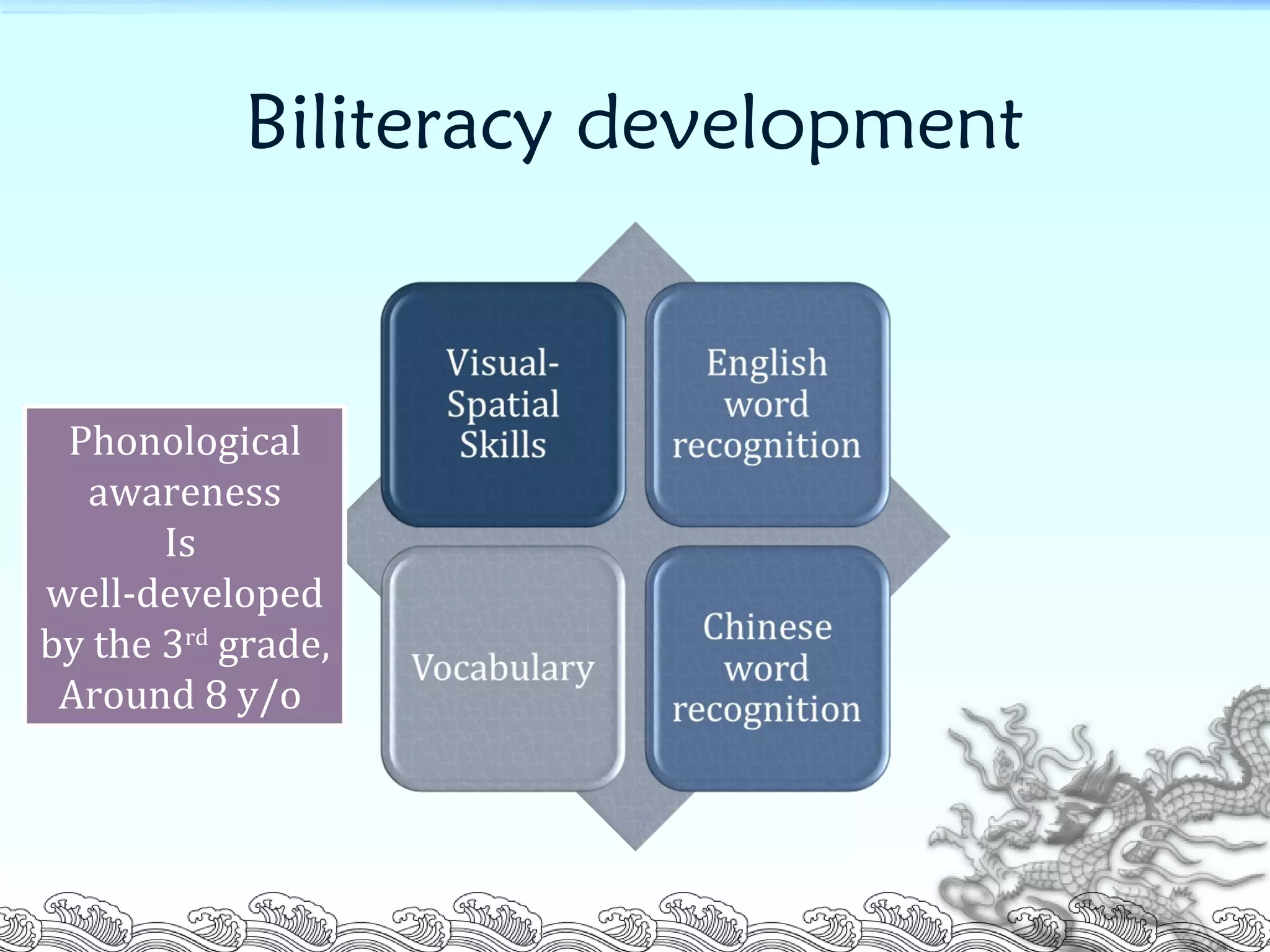
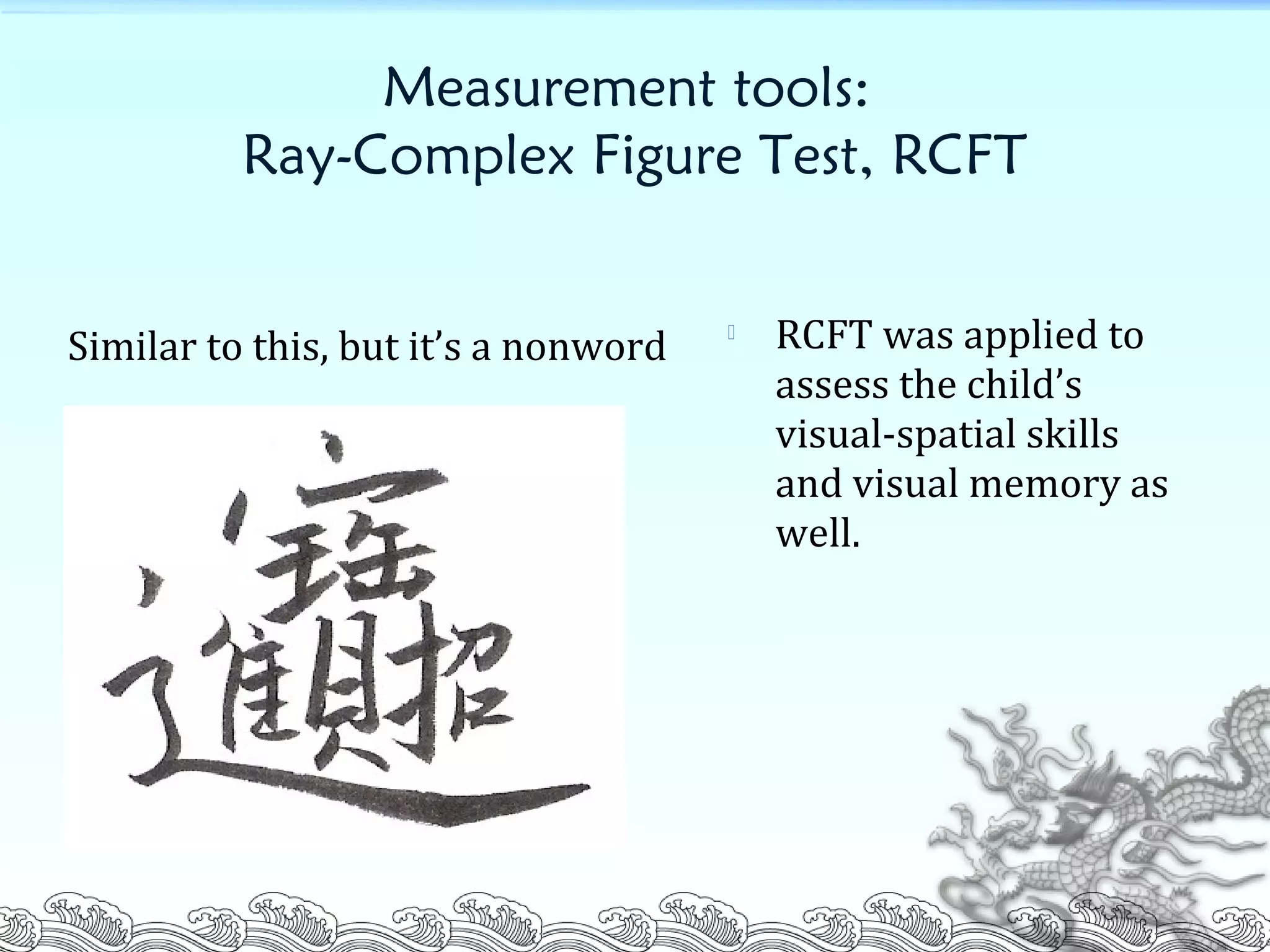
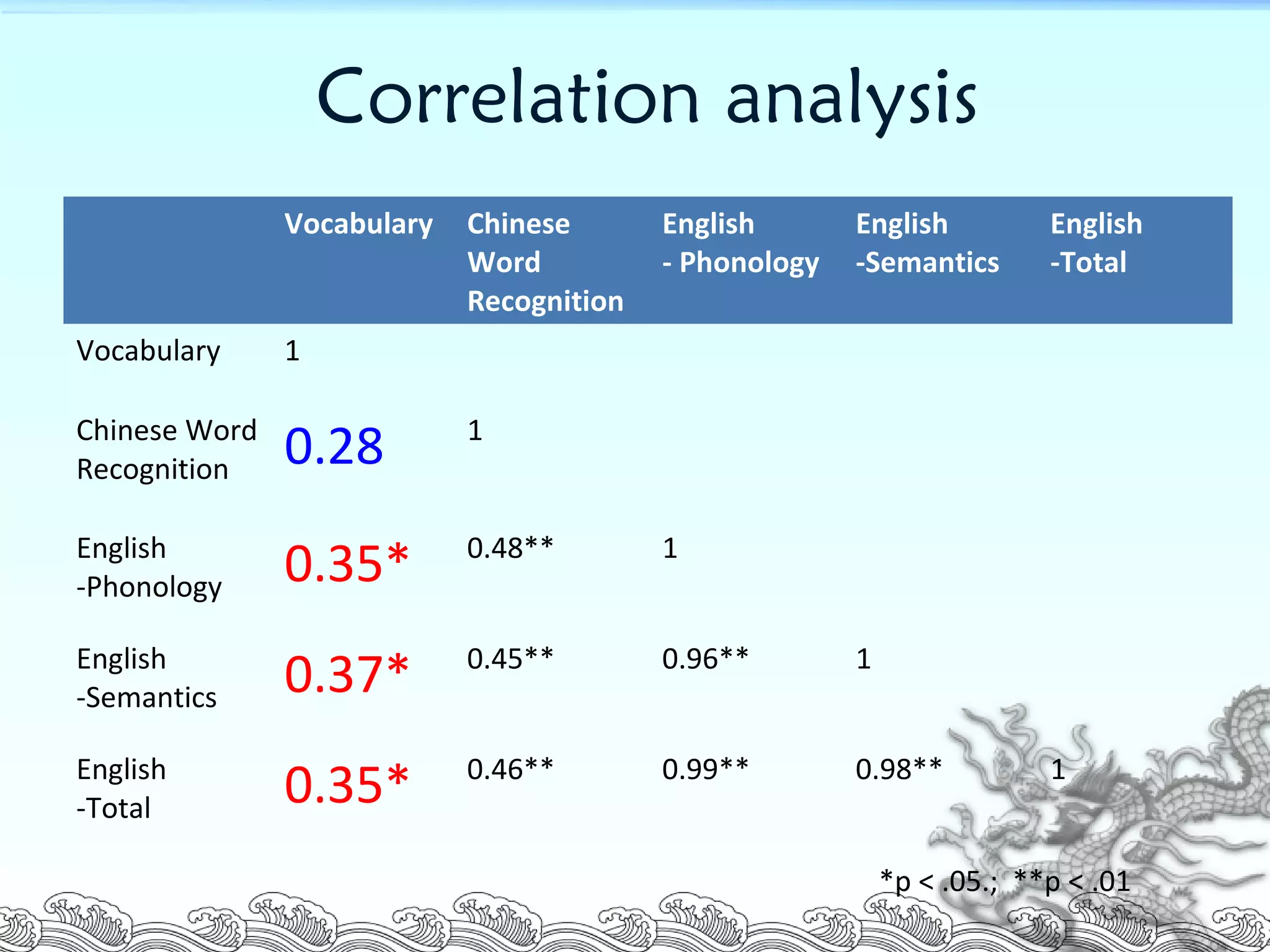
This document summarizes a research study that examined the influence of visual-spatial skills on Chinese and English word recognition in fourth-grade students in Taiwan. The study found that vocabulary knowledge was related to English word recognition but not Chinese word recognition. It also found that visual-spatial skills as measured by a complex figure test were correlated with and could help explain Chinese word recognition performance but not English word recognition. The researchers concluded that visual-spatial abilities are more important for recognizing ideographic Chinese characters than alphabetic English words.