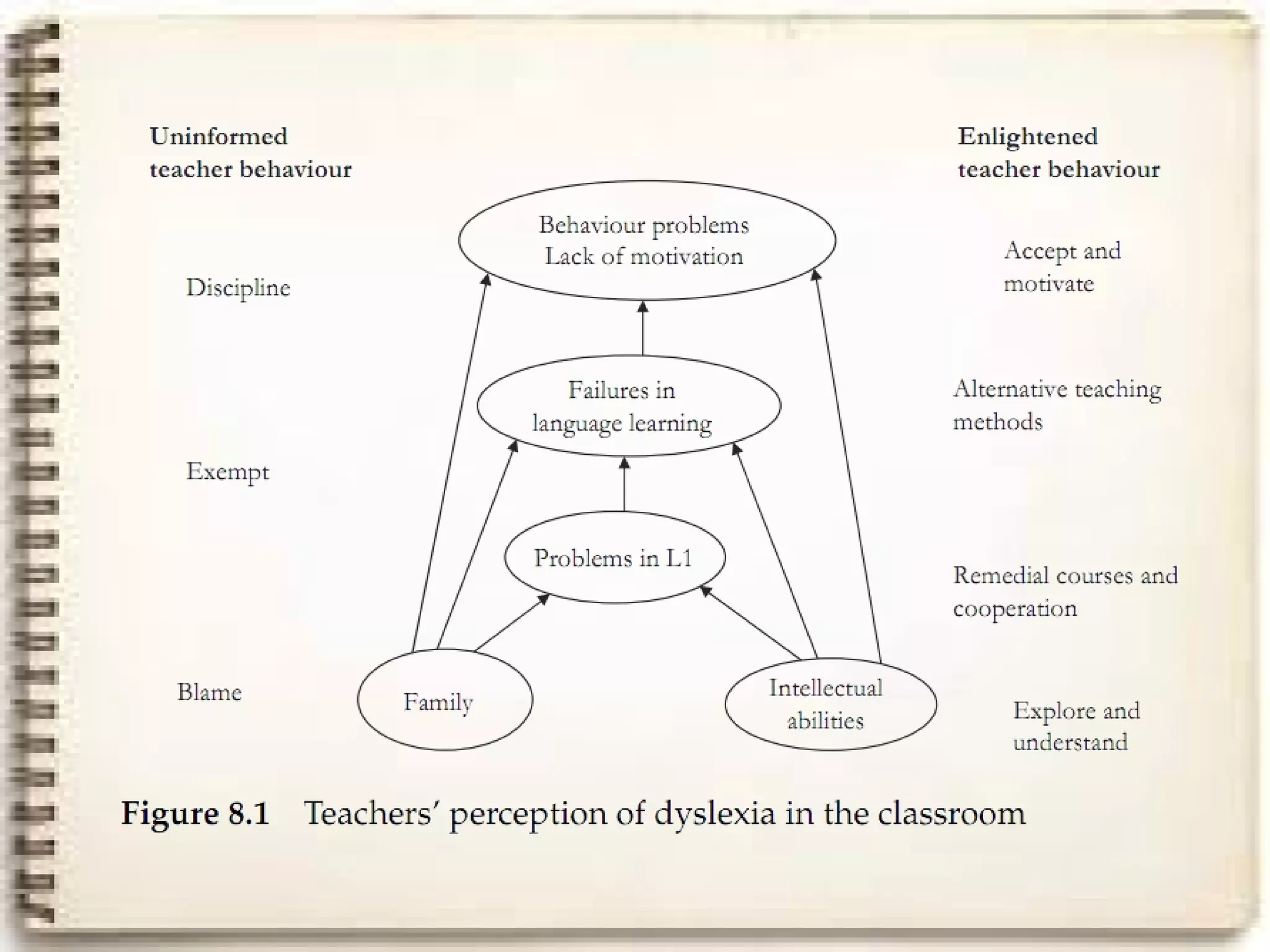
The document summarizes research on Hungarian teachers' perceptions of students with dyslexia learning foreign languages. It identifies symptoms teachers observed in speaking, reading, and writing and personal factors like family problems, lack of confidence, and motivation issues. It concludes that raising teacher awareness of symptoms and alternative teaching methods is needed, as well as cooperation between language teachers and other specialists to help dyslexic students.