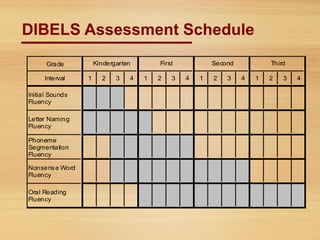
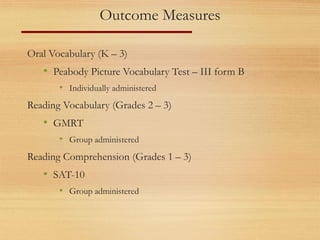
The document discusses reading assessments used in Reading First programs including DIBELS measures. It provides an overview of various DIBELS measures administered at different grade levels to screen students and monitor their progress in developing early reading skills. The schedule and flowchart show how assessments are administered throughout the K-3 years. Outcome data is used at the student, teacher, principal and district level to evaluate programs, identify needs for support or intervention, and enhance professional development.