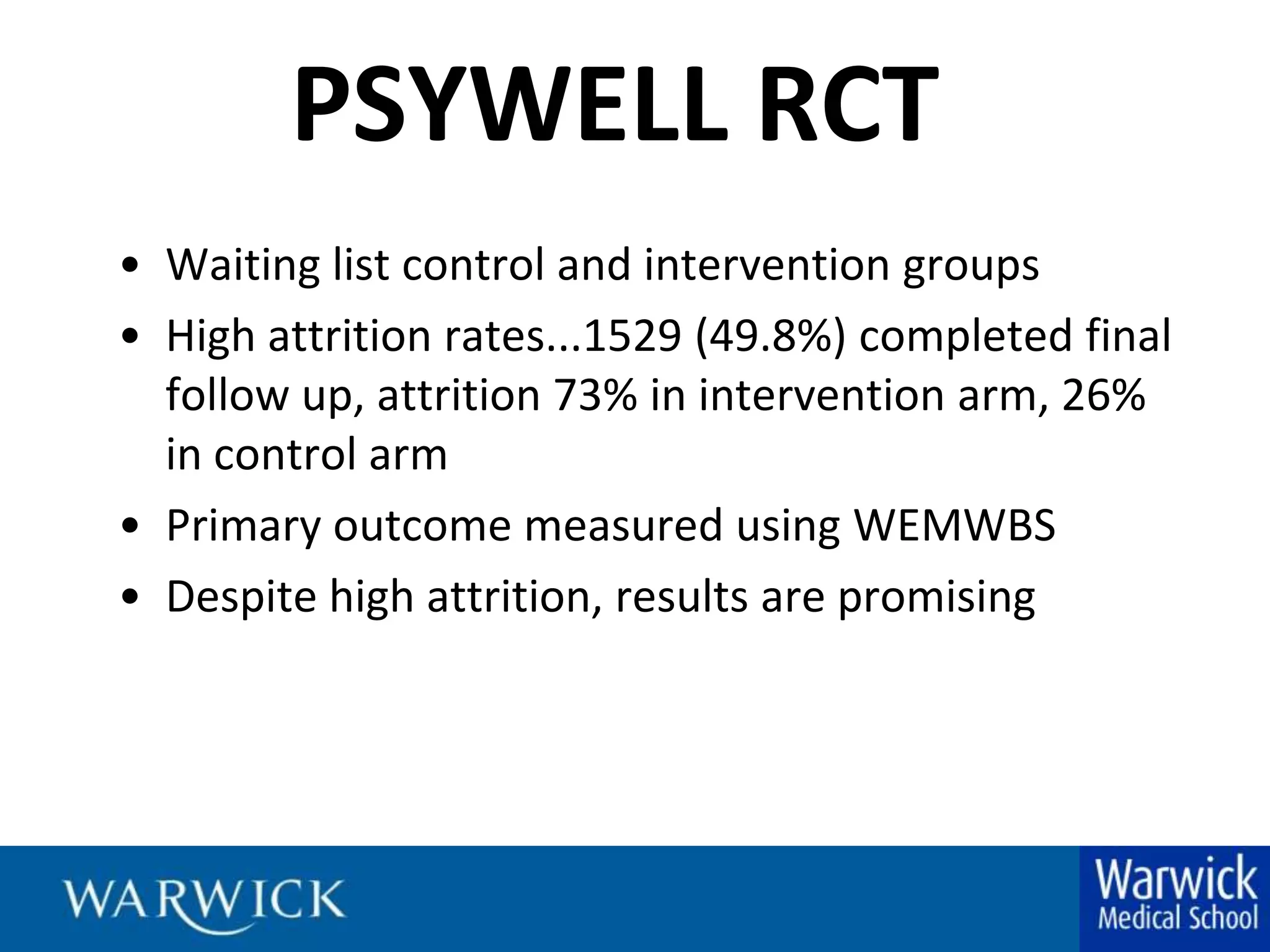
The document summarizes a study on participants' experiences in an online mental health intervention and randomized control trial. Key findings include: (1) Participants were motivated to enroll due to experiencing low mood; (2) Benefits of the online format included privacy, 24/7 availability, and increased self-efficacy; (3) Many reported positive behavior changes in thinking patterns and relationships; (4) Trusting branding of the university increased security providing personal information; (5) Language was perceived as aimed at younger Americans rather than a UK audience.