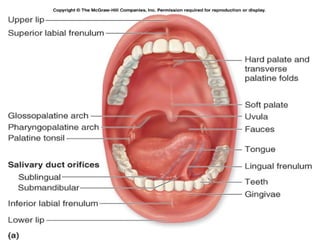
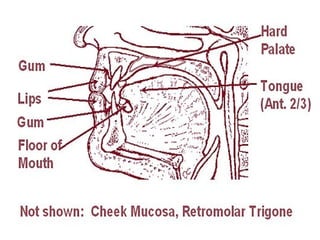
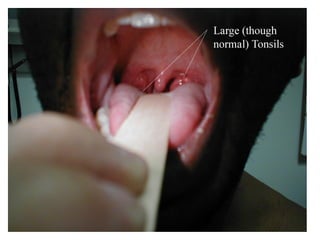
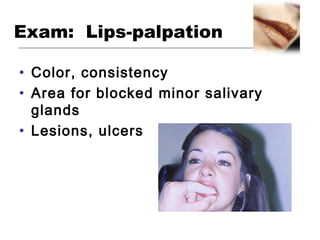
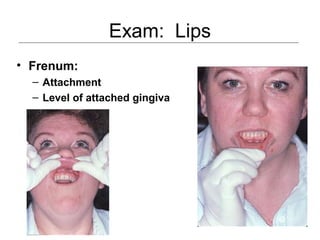
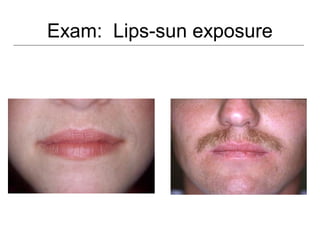
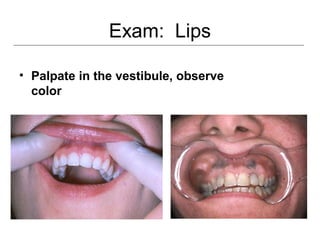
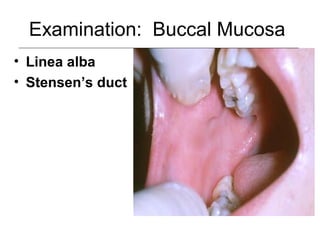
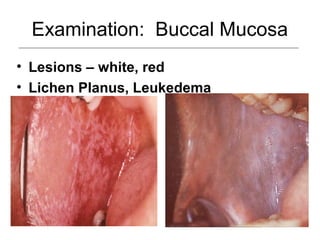
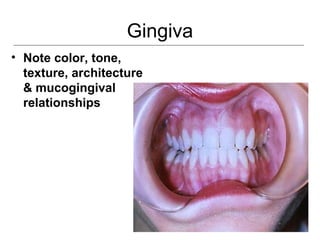
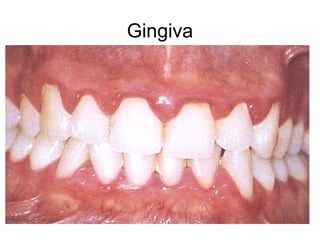
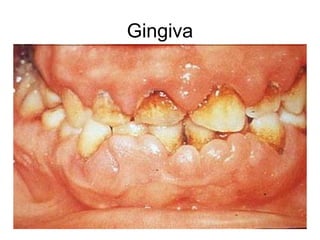
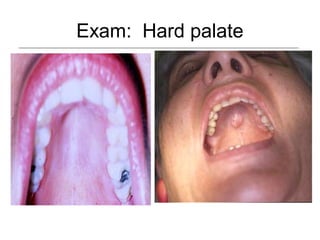
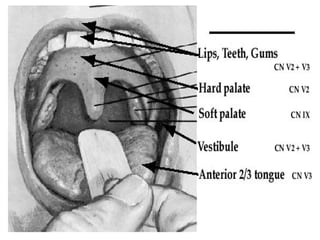
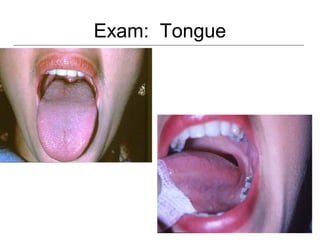
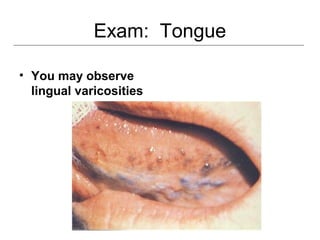
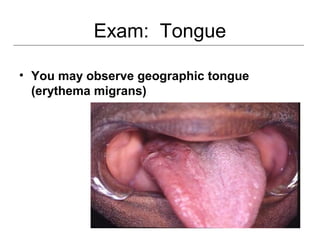
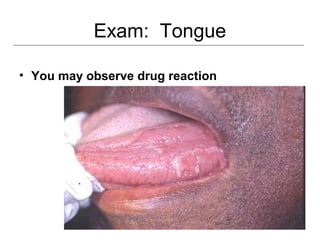
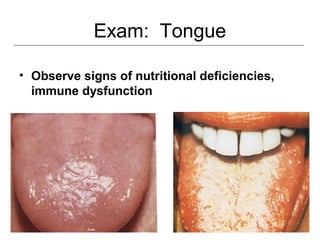
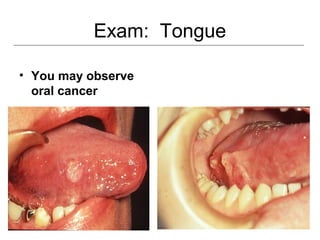
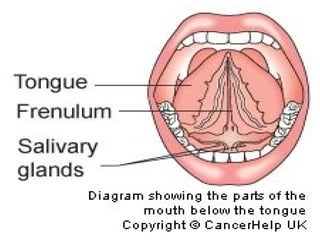
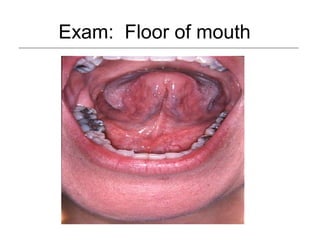
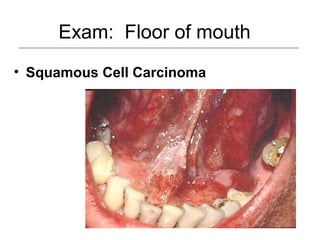
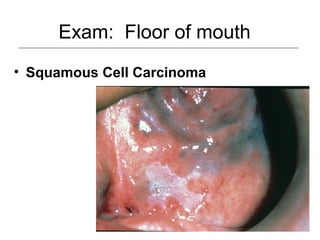
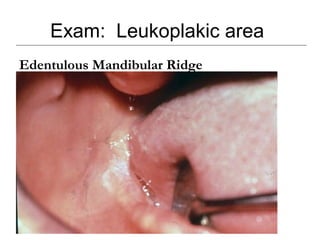
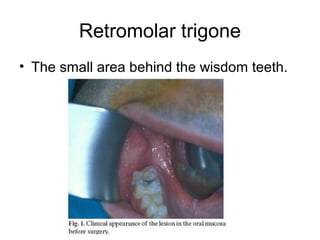
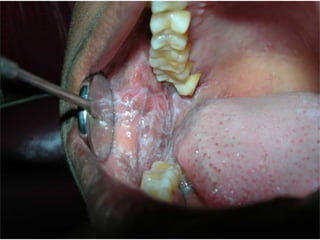
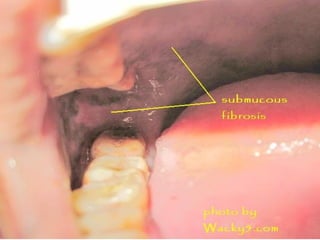
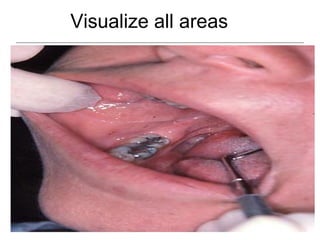
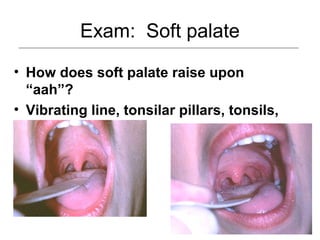
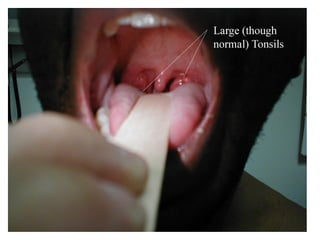
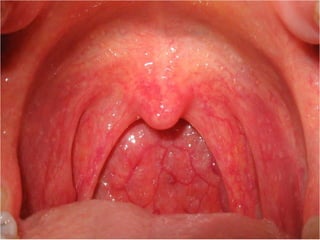
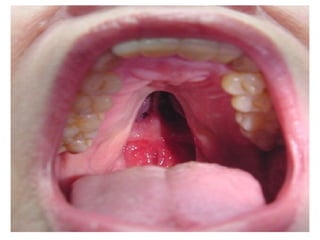
This document provides guidance on examining the oral cavity and oropharynx. Key areas to examine include the lips, checking for color, consistency, lesions or abnormalities; the buccal mucosa, looking for lesions; the gingiva, noting color, tone and architecture; the hard and soft palates; the tongue, checking all surfaces for lesions or signs of nutritional deficiencies; the floor of the mouth, visualizing and palpating for lesions or masses; and the oropharynx, checking for normal color and consistency of tissues. The lateral borders of the tongue and floor of the mouth are the most common sites for oral cancer, so these areas require close examination. A systematic and complete examination of all oral tissues