This document discusses Java generics, collections, streams and related concepts. It provides code examples of:
- Defining generic classes and methods
- Using common collection interfaces like List, Set, Map and their implementations
- Working with streams to perform operations on data in a declarative way
- Using lambda expressions and functional interfaces with streams


![public static BigDecimal minElement(
BigDecimal [] values) {
if (values.length == 0) {
return null;
}
BigDecimal min = values [0];
for (int i = 1; i < values.length; i++) {
if (min.compareTo(values[i]) > 0) {
min = values[i];
}
}
return min;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-151019181905-lva1-app6891/75/6-Generics-Collections-Streams-3-2048.jpg)
![TreeNode rootNode = new TreeNode ();
rootNode.value = "foobar";
// tree manipulation
String value = (String) rootNode.value;
Object [] arrayOfBigDecimals = {...};
BigDecimal min = (BigDecimal)
minElement(arrayOfBigDecimals );](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-151019181905-lva1-app6891/75/6-Generics-Collections-Streams-4-2048.jpg)
![public static <T extends Comparable <T>> T
minElement(T[] values) {
if (values.length == 0) {
return null;
}
T min = values [0];
for (int i = 1; i < values.length; i++) {
if (min.compareTo(values[i]) > 0) {
min = values[i];
}
}
return min;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-151019181905-lva1-app6891/75/6-Generics-Collections-Streams-5-2048.jpg)
![TreeNode <String > stringNode;
TreeNode <Integer > integerNode;
TreeNode <int[]> intArrayNode;
TreeNode <int > intNode;
TreeNode <10> tenNode;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-151019181905-lva1-app6891/75/6-Generics-Collections-Streams-6-2048.jpg)










![T obj = new T();
T[] arr = new T[5];
if (obj instanceof T) {...}
T a = (T) b;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-151019181905-lva1-app6891/75/6-Generics-Collections-Streams-17-2048.jpg)
![import java.io.IOException ;
public class Hack {
public static void main(String [] args) {
throwAsUnchecked (new IOException ());
}
private static void throwAsUnchecked (Exception e) {
Hack.<RuntimeException > genericThrow (e);
}
private static <T extends Throwable >
void genericThrow (Exception e) throws T {
throw (T) e;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-151019181905-lva1-app6891/75/6-Generics-Collections-Streams-18-2048.jpg)
![Number number = new Integer (1);
Number [] numberArray = new Integer [10];
Optional <Integer > optionalInt = Optional.of (1);
Optional <Number > optionalNumber = optionalInt;
optionalNumber.set(new BigDecimal("3.14"));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-151019181905-lva1-app6891/75/6-Generics-Collections-Streams-19-2048.jpg)



![int[] oldArray = ...;
int oldLength = oldArray.length;
int newLength = oldLength + 10;
int[] newArray =
Arrays.copyOf(oldArray , newLength );
newArray[oldLength] = newElement1;
newArray[oldLength + 1] = newElement2;
// ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-151019181905-lva1-app6891/75/6-Generics-Collections-Streams-23-2048.jpg)
![final int[] array = new int[] {1, 2, 3};
array [0] = 10;
array [1] = 11;
array [2] = 12;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-151019181905-lva1-app6891/75/6-Generics-Collections-Streams-24-2048.jpg)










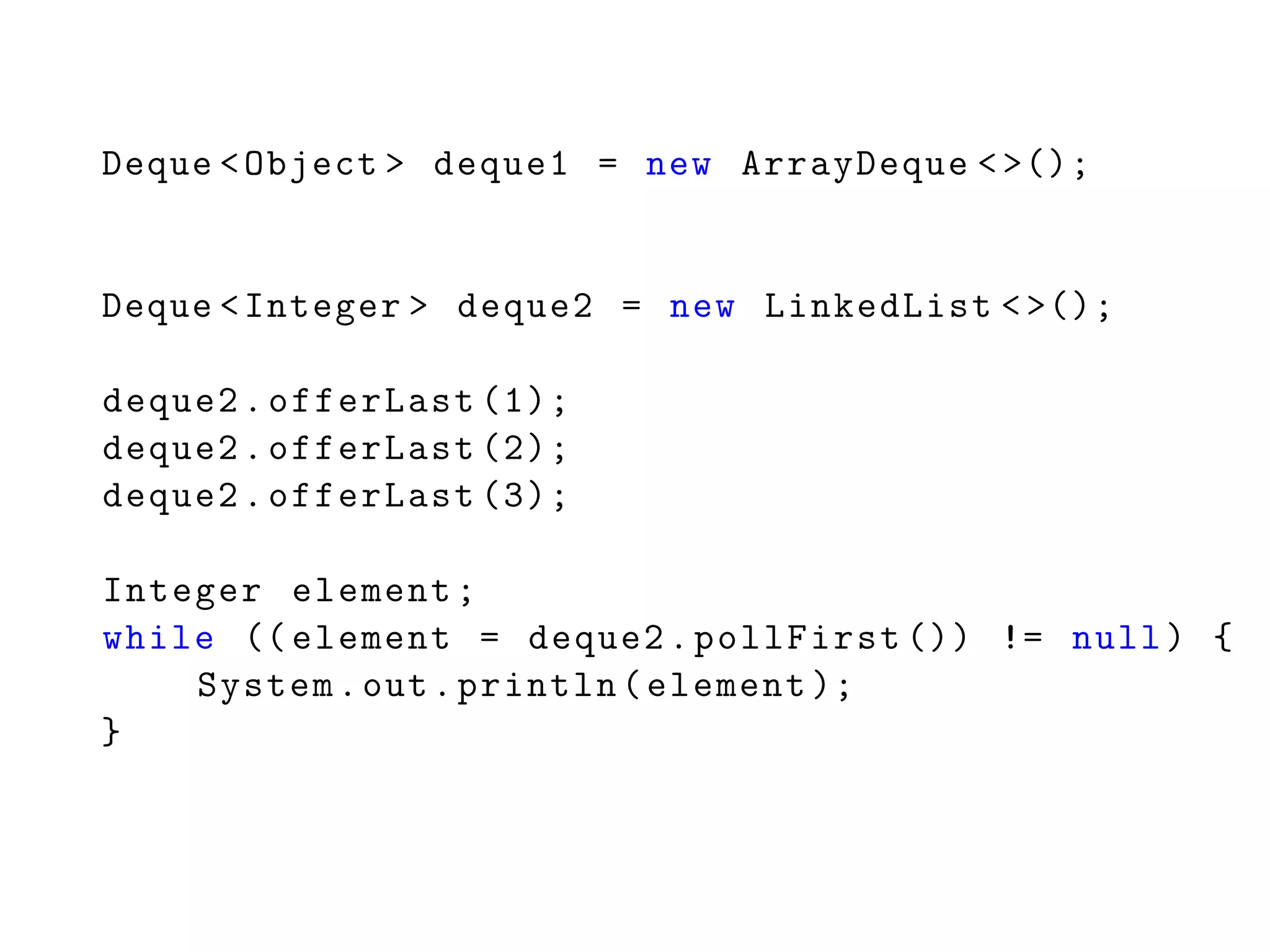












![List <Integer > list = ...;
Object [] array1 = list.toArray ();
Integer [] array2 =
list.toArray(new Integer[list.size ()]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-151019181905-lva1-app6891/75/6-Generics-Collections-Streams-48-2048.jpg)
![String [] array = {"A", "B", "C"};
Set <String > set1 =
new HashSet <>(Arrays.asList(array ));
Set <String > set2 = new HashSet <>();
Collections.addAll(set2 , array );](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-151019181905-lva1-app6891/75/6-Generics-Collections-Streams-49-2048.jpg)

![File directory = ...;
File [] javaSourceFiles = directory.listFiles(
new FileFilter () {
@Override
public boolean accept(File file) {
return file.getName (). endsWith(".java");
}
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-151019181905-lva1-app6891/75/6-Generics-Collections-Streams-51-2048.jpg)








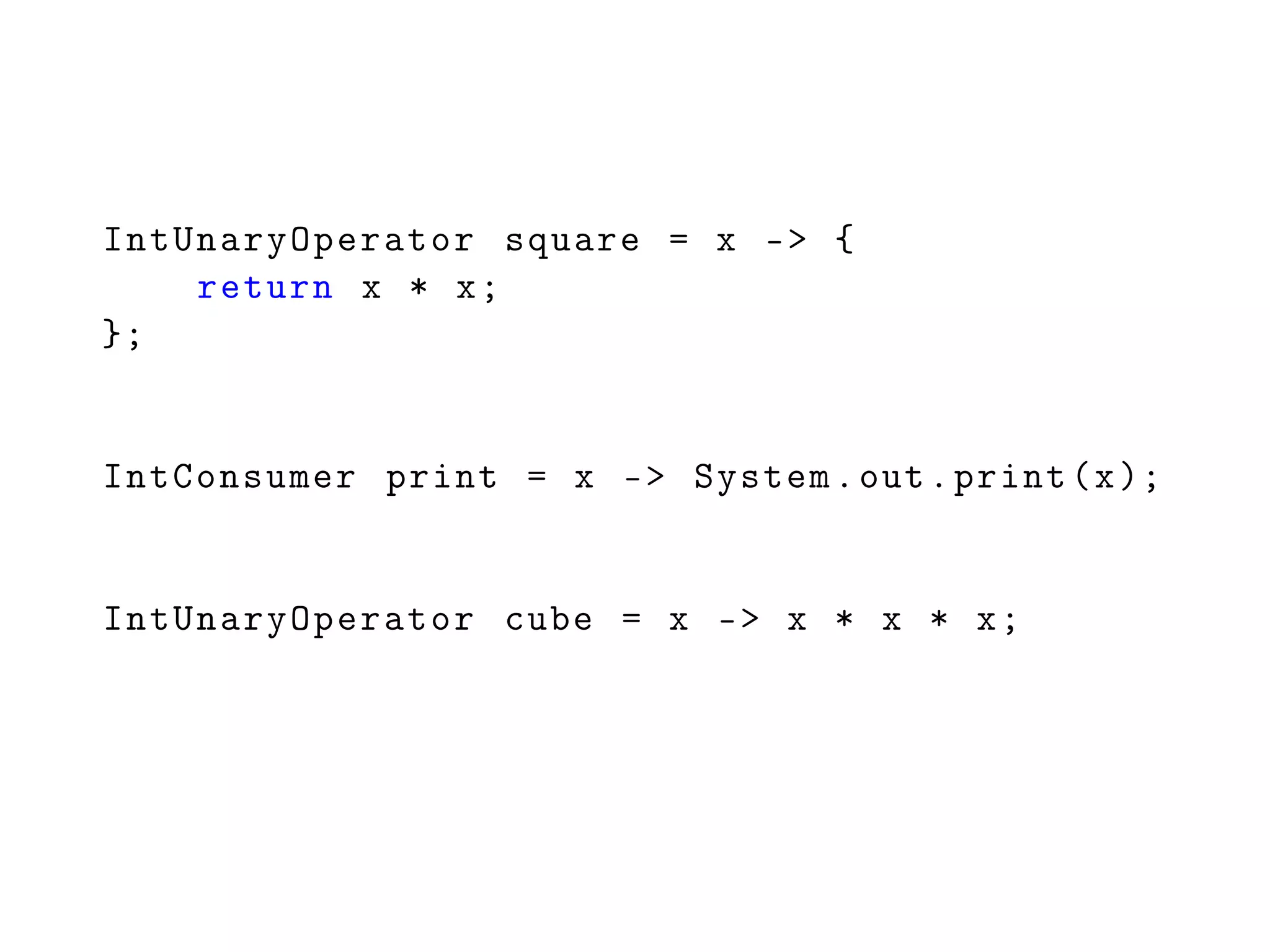
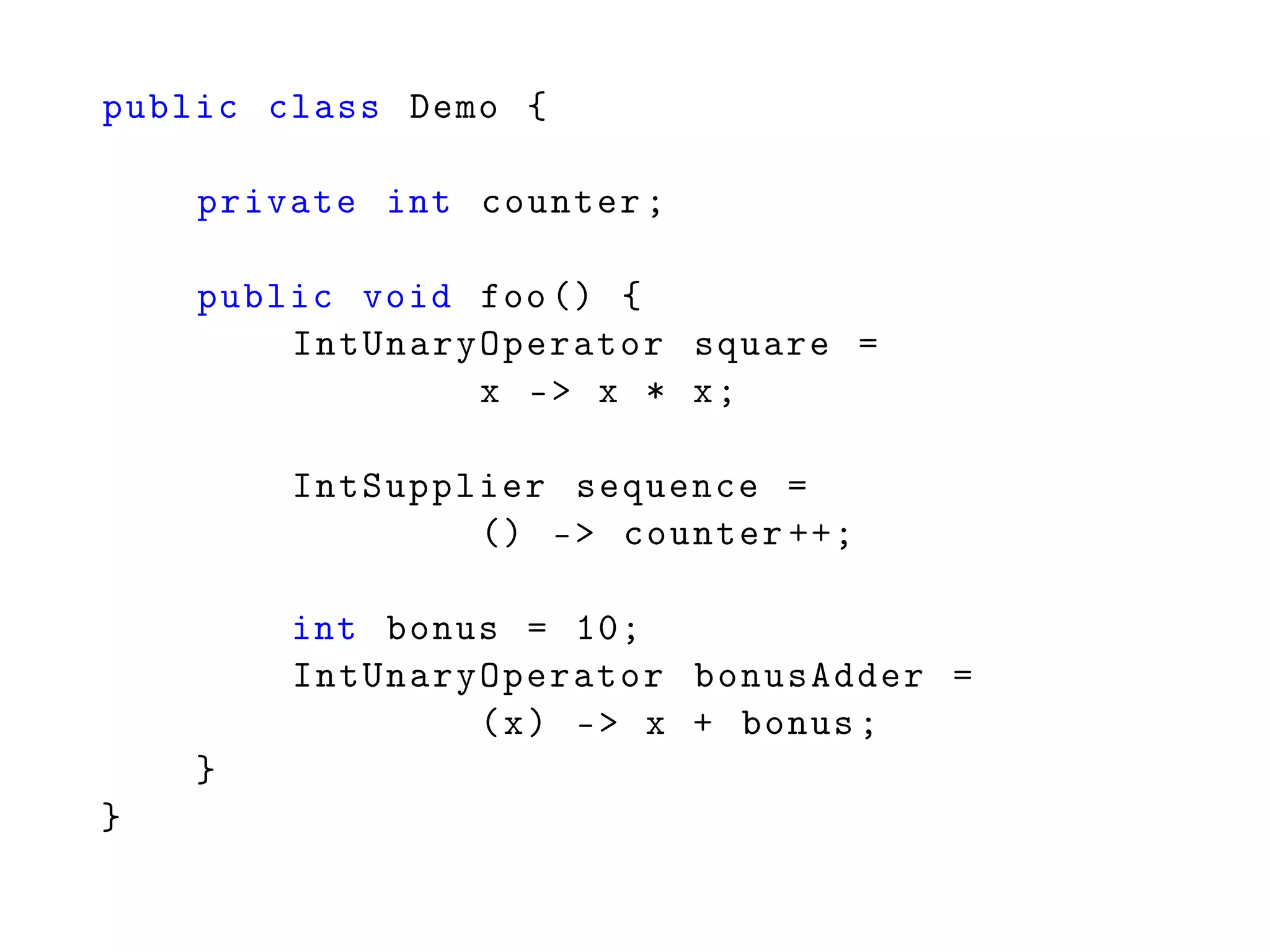
![int[] counter = new int[] {0};
IntSupplier sequence = () -> counter [0]++;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-151019181905-lva1-app6891/75/6-Generics-Collections-Streams-62-2048.jpg)
![ToIntFunction <String > intParser =
Integer :: parseInt;
Consumer <Object > printer =
System.out:: println;
Function <Object , String > objectToString =
Object :: toString;
IntFunction <String []> arrayAllocator =
String []:: new;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-151019181905-lva1-app6891/75/6-Generics-Collections-Streams-63-2048.jpg)






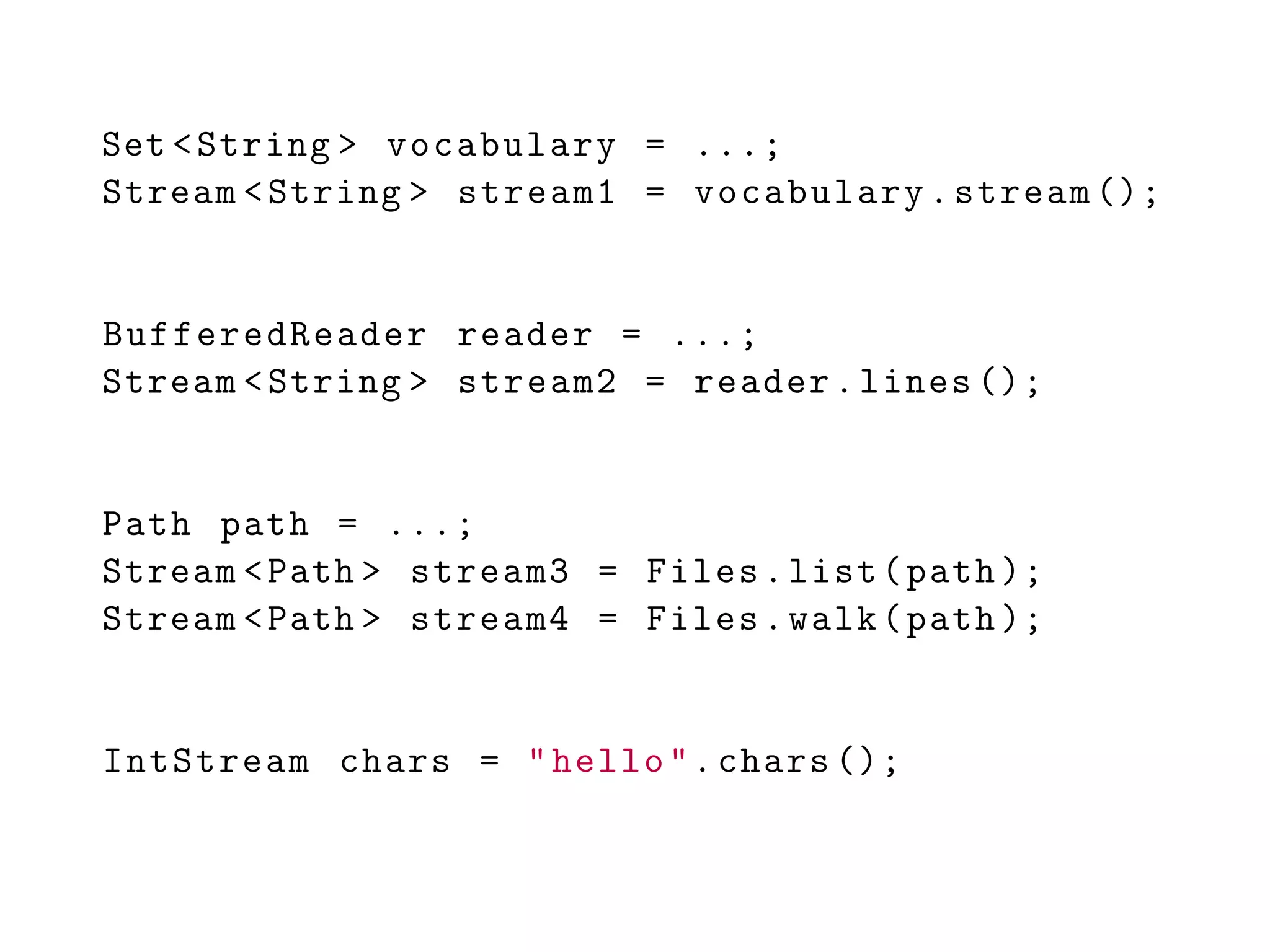

![IntStream combinedStream =
IntStream.concat(stream1 , stream2 );
IntStream empty = IntStream.empty ();
double [] array = ...;
DoubleStream streamFromArray =
Arrays.stream(array );
IntStream streamOfElements =
IntStream.of(2, 4, 6, 8, 10);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-151019181905-lva1-app6891/75/6-Generics-Collections-Streams-72-2048.jpg)





