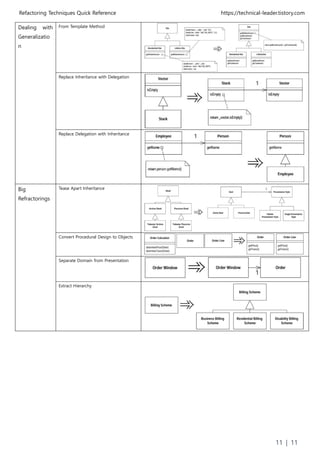
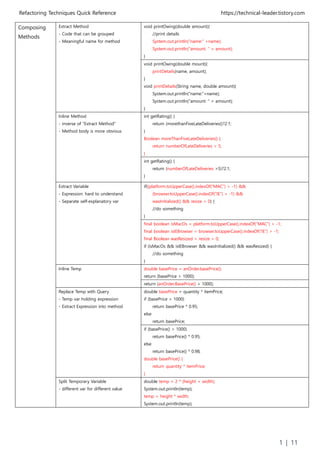
The document discusses various refactoring techniques for restructuring code to improve design, readability, and extensibility without changing external behavior. It provides examples of techniques like extracting methods, replacing temporary variables, simplifying conditional expressions, and dealing with generalization through inheritance/polymorphism. The techniques are organized into categories like composing methods, organizing data, simplifying method calls, and dealing with generalization.
![Refactoring Techniques Quick Reference https://technical-leader.tistory.com
2 | 11
Composing
Methods
final double perimeter = 2 * (height + width);
System.out.println(perimeter);
final double area = height * width;
System.out.println(area);
Remove Assignments to Param
- use temp var instead
int discount(int inputVal, int Quantity, int yearToDate){
if (intputVal>50)
inputVal -=2;
}
int discount(int inputVal, int Quantity, int yearToDate) {
int result = inputVal;
if (inputVal > 50)
result - = 2;
}
Replace Method with Method Obj
- Extract Method cannot be applied
- Separate class
class Order {
…
double price() {
double primaryBasePrice;
double secondaryBasePrice;
double TeriaryBasePrice;
//long computation
…
}
}
class Order {
…
public double price() {
return new PriceCalculator(this).compute();
}
}
class PriceCalculator {
private double primaryBasePrice;
private double seconadaryBasePrice;
private double tertiaryBasePrice;
PriceCalculator(Order order) {
//copy relevant info
}
public double compute() {
//…
}
}
Substitute Algorithm
- Replace existing algorithm
- Replace body of the method
String foundPerson(String[] people) {
for(int I = 0;i<people.length;i++) {
if(people[i].equals(“Don”))
return “Don”;
if((people[i].equals(“John”))
return “John”;
if(people[i].equals(“Kent”))
return “Kent”;
}
return “”;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/refactoringtechniques-180902120625/85/Martin-Fowler-s-Refactoring-Techniques-Quick-Reference-2-320.jpg)
![Refactoring Techniques Quick Reference https://technical-leader.tistory.com
3 | 11
Composing
Methods
String foundPerson(String[] people) {
ListCandidates = Arrays.asList(new String[] {“Don”, “John”, “Kent”});
for(int i = 0;i<people.length;;i++) {
if (candidates.contains(people[i])) {
return people[i];
}
}
return “”;
}
Moving
Feature btwn
Obj
Move Method
- Use more features in another class
Move Field
- Field used by another class more
Extract Class
- One class does the work of two
Inline Class
- Class does almost nothing
Hide Delegate
- use A for getting B info
- new method of A delegating B
Remove Middle Man
- too many methods that simply
delegate
- force the client to call the end methods
directly
Introduce Foreign method
- server class cannot contain the needed
class
- add a method in the client
Date newStart = new Date(previousEnd.getYear(), previousEnd.getMonth(),
previousEnd.getDate() + 1);
Date newStart = nextDay(previousEnd);
private static Date nextDay(Date arg) {
return new Date(arg.getYear(), arg.getMonth(), arg.getDate() + 1);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/refactoringtechniques-180902120625/85/Martin-Fowler-s-Refactoring-Techniques-Quick-Reference-3-320.jpg)
![Refactoring Techniques Quick Reference https://technical-leader.tistory.com
4 | 11
Moving
Feature btwn
Obj
Introduce Local Extension
- server class cannot contain some
methods that you need
Organizing
Data
Self Encapsulate Field
- Create a getter and setter
private int low, high
Boolean includes(int arg) {
return arg >= low && arg <= high;
}
private int low, high
Boolean includes(int arg) {
return arg >= getLow() && arg <= getHigh();
}
int getLow() {
return low;
}
int getHigh() {
rturn high;
}
Replace Data Value with Object
- Contain a data field with its own
behavior and associated data
- Change the data item into an object
Change Value to Reference
- Many identical instances of a single
class
- Converted to a single reference object
Change Reference to Value
- Reference object is too small
- Converted it into a value object
Replace Array with Object
- Arrays containing various types of data
- Replace array with an object
String[] row = new String[];
row[0] = “Liverpool”;
row[1] = “15”;
Performance row = new Performance();
row.setName(“Liverpool”);
row.setWins(“15”);
Duplicate Observed Data
- Domain data in GUI control
- Copy data to model and set up
observer
Change Unidirectional Association to
Bidirectional
- Add missing association
Change Bidirectional Association to
Unidirectional
- Remove unused association](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/refactoringtechniques-180902120625/85/Martin-Fowler-s-Refactoring-Techniques-Quick-Reference-4-320.jpg)
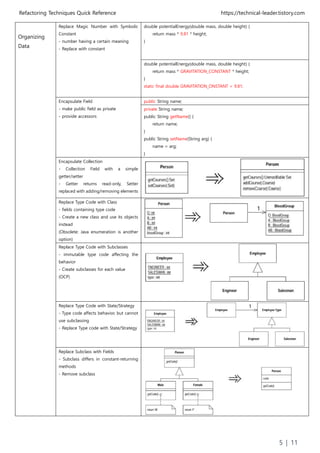
![Refactoring Techniques Quick Reference https://technical-leader.tistory.com
6 | 11
Simplifying
Conditional
Expression
Decompose conditional
- Complex conditional
- Decompose to separate methods
if(data.before(SUMMER_START)||date.after(SUMMER_END))
charge = quantity * winterRate + winterServiceCharge;
else
charge = quantity * summerRate;
if(notSummer(date))
charge = winterCharge(quantity);
else
charge = summerCharge(quantity);
Consolidate Conditional Expression double disabilityAmount() P
if (seniority < 2)
return 0;
if(mounthsDisabled > 12)
return 0;
if (isPatTime)
return 0;
…
}
double disabilityAmount() {
if(isNortEligableForDisability())
return 0;
…
}
Consolidate Duplicate Conditional
Fragments
if (isSpecialDeal()) {
total = price* 0.95;
send();
} else {
total = price * 0.98;
send();
}
if (isSpecialDeal()) {
total = price* 0.95;
} else {
total = price * 0.98;
}
send();
Remove Control Flag void checkSecurity(String[] people) {
boolean found = false;
for (int i = 0; i < people.length; i++) {
if (! found) {
if (people[i].equals ("Don")){
sendAlert();
found = true;
}
if (people[i].equals ("John")){
sendAlert();
found = true;
}
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/refactoringtechniques-180902120625/85/Martin-Fowler-s-Refactoring-Techniques-Quick-Reference-6-320.jpg)
![Refactoring Techniques Quick Reference https://technical-leader.tistory.com
7 | 11
Simplifying
Conditional
Expression
Remove Control Flag void checkSecurity(String[] people) {
boolean found = false;
for (int i = 0; i < people.length; i++) {
if (people[i].equals ("Don")){
sendAlert();
found = true;
break;
}
if (people[i].equals ("John")){
sendAlert();
found = true;
break;
}
}
}
Replace Nested Conditional with Guard
Clauses
double getPayAmount() {
double result;
if (_isDead) result = deadAmount();
else {
if (_isSeparated) result = separatedAmount();
else {
if (_isRetired) result = retiredAmount();
else result = normalPayAmount();
};
}
return result;
};
double getPayAmount() {
if (_isDead) return deadAmount();
if (_isSeparated) return separatedAmount();
if (_isRetired) return retiredAmount();
return normalPayAmount();
};
Replace Conditional with Polymorphism
Introduce Null Object
Introduce Assertion double getExpenseLimi() {
//should have either expense limit or a primary project
return (expenseLimit != NULL_EXPSENSE)? expenseLimit
;:primaryProject.getMemberExpenseLimit()
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/refactoringtechniques-180902120625/85/Martin-Fowler-s-Refactoring-Techniques-Quick-Reference-7-320.jpg)
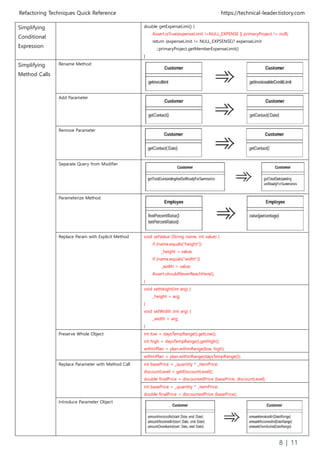
![Refactoring Techniques Quick Reference https://technical-leader.tistory.com
9 | 11
Simplifying
Method Calls
Remove Setting Method
Hide Method
Replace Constructor With Factory
Method
Employee (int type) {
_type = type;
}
static Employee create(int type) {
return new Employee(type);
}
Encapsulate Downcast
(Needed?)
Object lastReading() {
return readings.lastElement();
}
Reading lastReading() {
return (Reading) readings.lastElement();
}
Replace Error Code With Exception int withdraw(int amount) {
if (amount > _balance)
return -1;
else {
_balance -= amount;
return 0;
}
}
void withdraw(int amount) throws BalanceException {
if (amount > _balance) throw new BalanceException();
_balance -= amount;
}
Replace Exception With Test double getValueForPeriod (int periodNumber) {
try {
return _values[periodNumber];
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
return 0;
}
}
double getValueForPeriod (int periodNumber) {
if (periodNumber >= _values.length) return 0;
return _values[periodNumber];
}
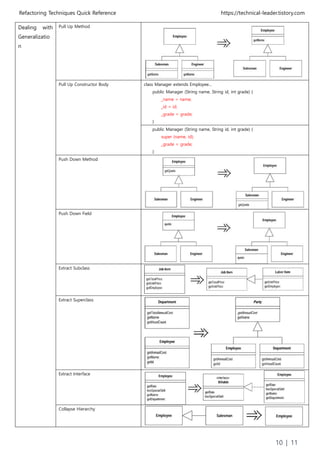
Dealing with
Generalizatio
n
Pull Up Field](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/refactoringtechniques-180902120625/85/Martin-Fowler-s-Refactoring-Techniques-Quick-Reference-9-320.jpg)