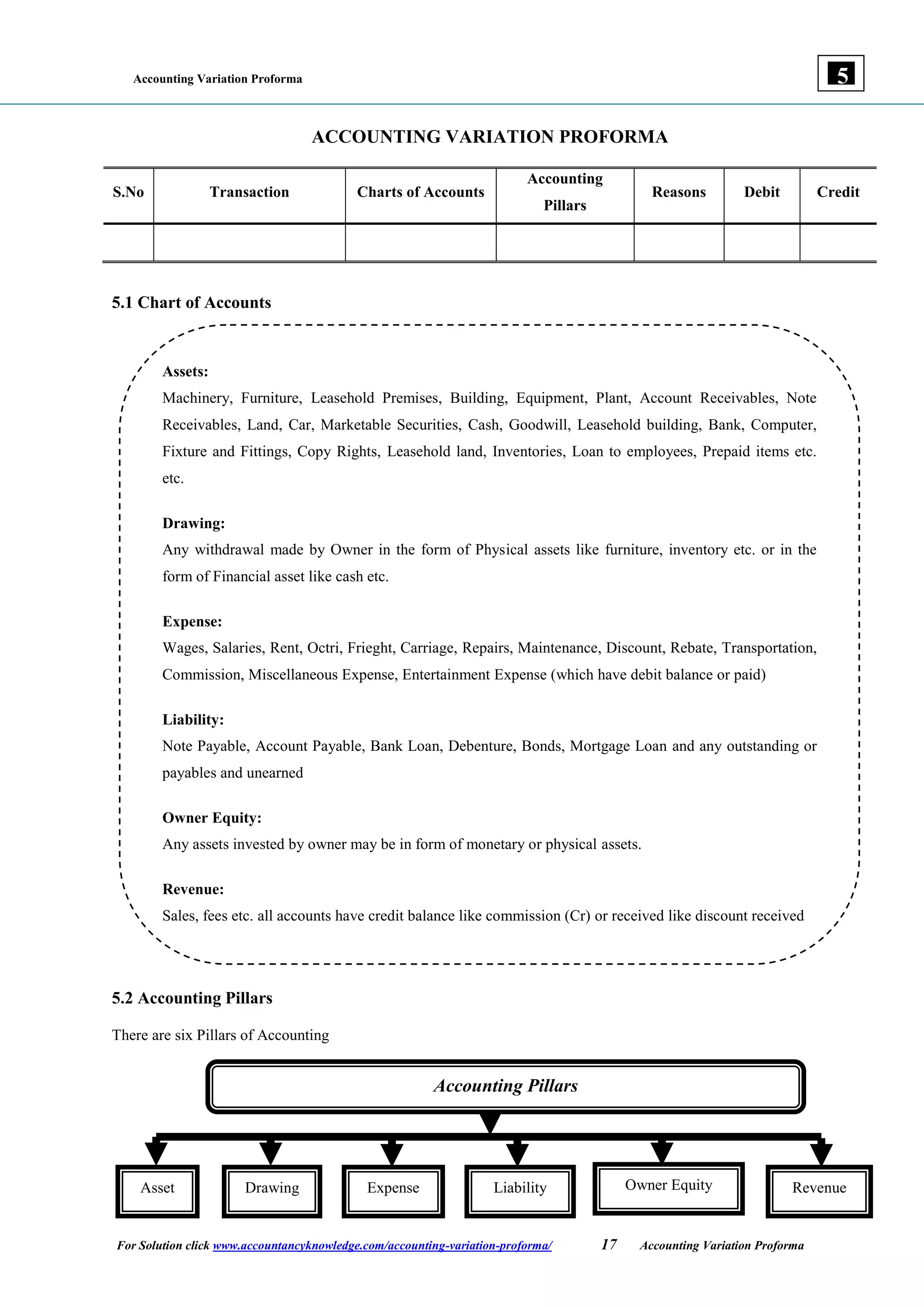
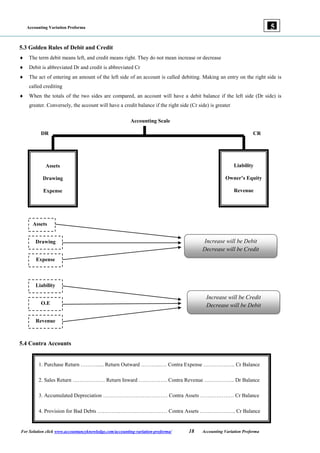
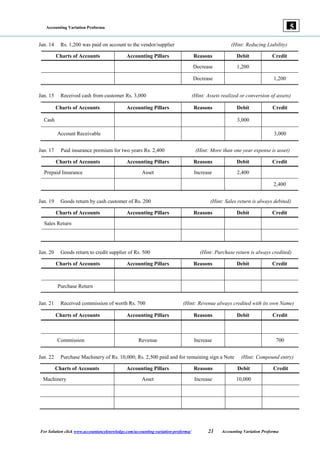
The document provides guidelines on accounting variations, detailing the accounting pillars which include assets, liabilities, expenses, and revenues. It outlines the principles of debit and credit, offering examples of transactions and their corresponding accounting treatments. Additionally, it includes examples to assist with understanding the recording of various financial activities using a pro forma format.