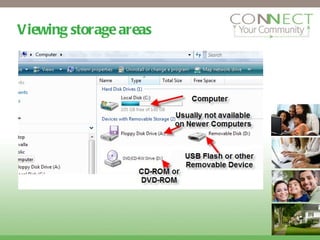
Data refers to any piece of information that is stored in files on a computer. Files have unique filenames and extensions that indicate the file type, such as .jpg for images. Files are measured in bytes, kilobytes, megabytes, and gigabytes. Files are stored in folders on the computer's hard drive or other storage devices like USB drives, similar to paper files in a filing cabinet. Users can create, save, open, and move files between storage locations.