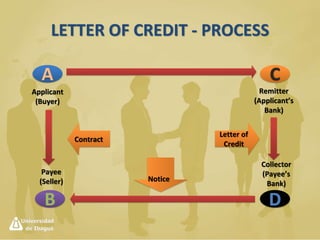
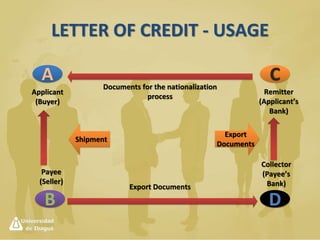
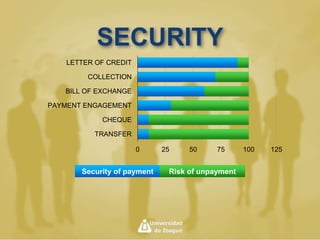
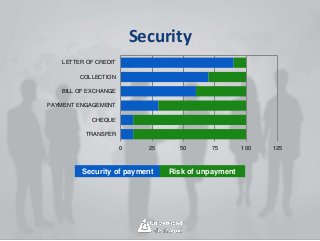
International payment methods provide security for international trade transactions. The main methods include letters of credit, documentary collections, bills of exchange, and open accounts. Letters of credit provide the highest security and involve a bank guarantee of payment if documents are presented on time. Documentary collections provide more security than open accounts but less than letters of credit by requiring documents before releasing goods. The payment method chosen depends on balancing security, cost, and risk assumed by buyers and sellers.