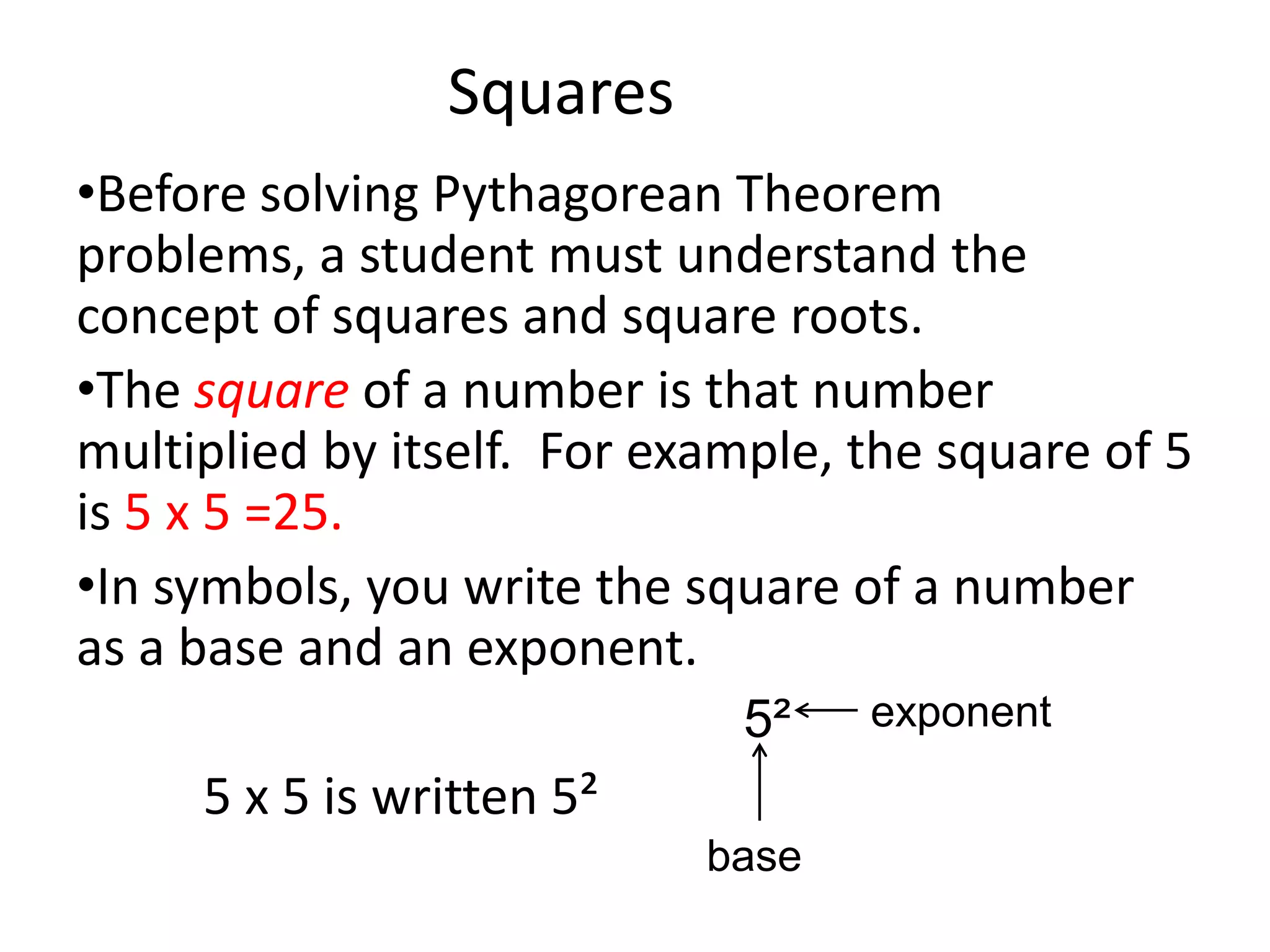
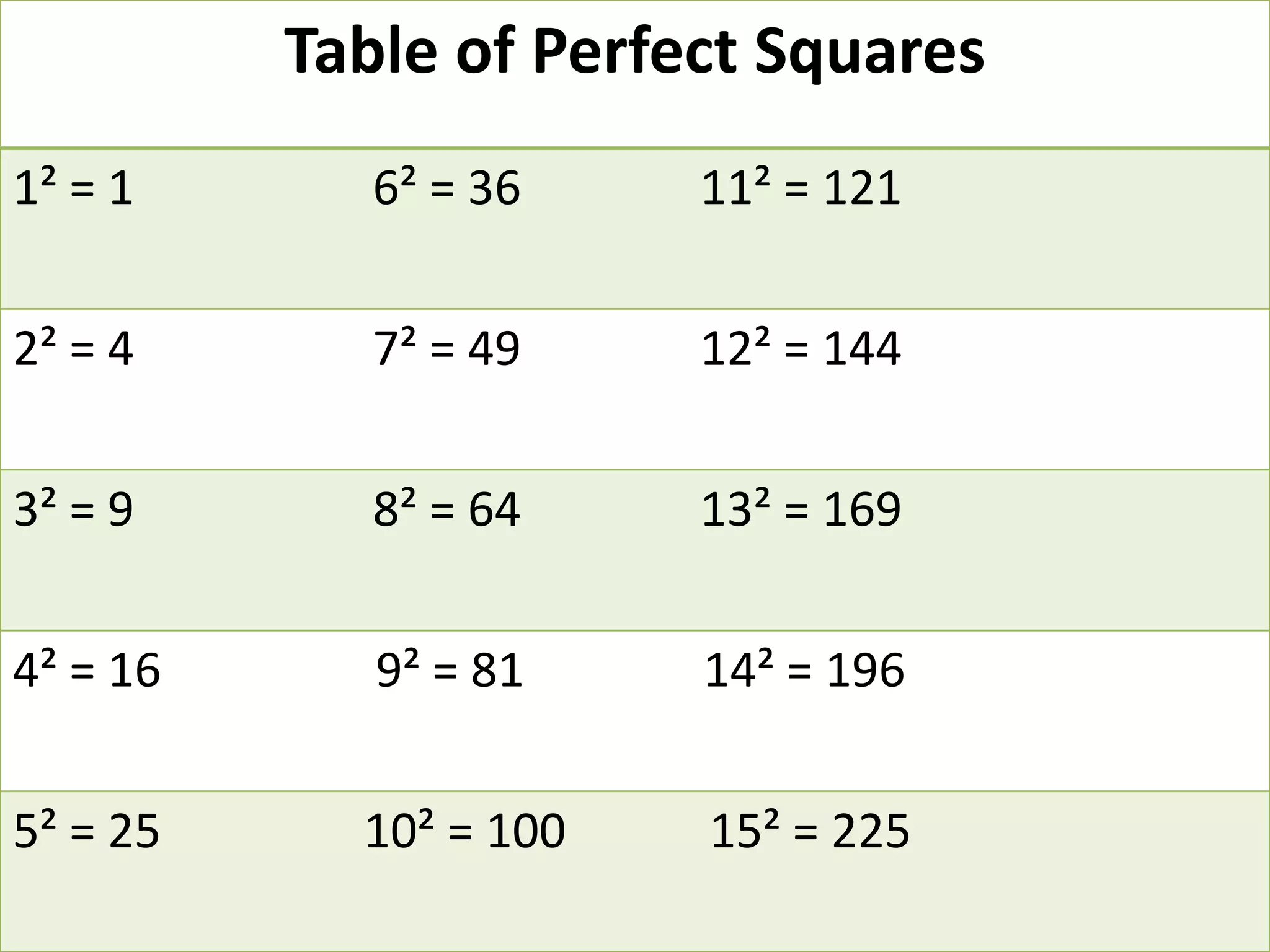
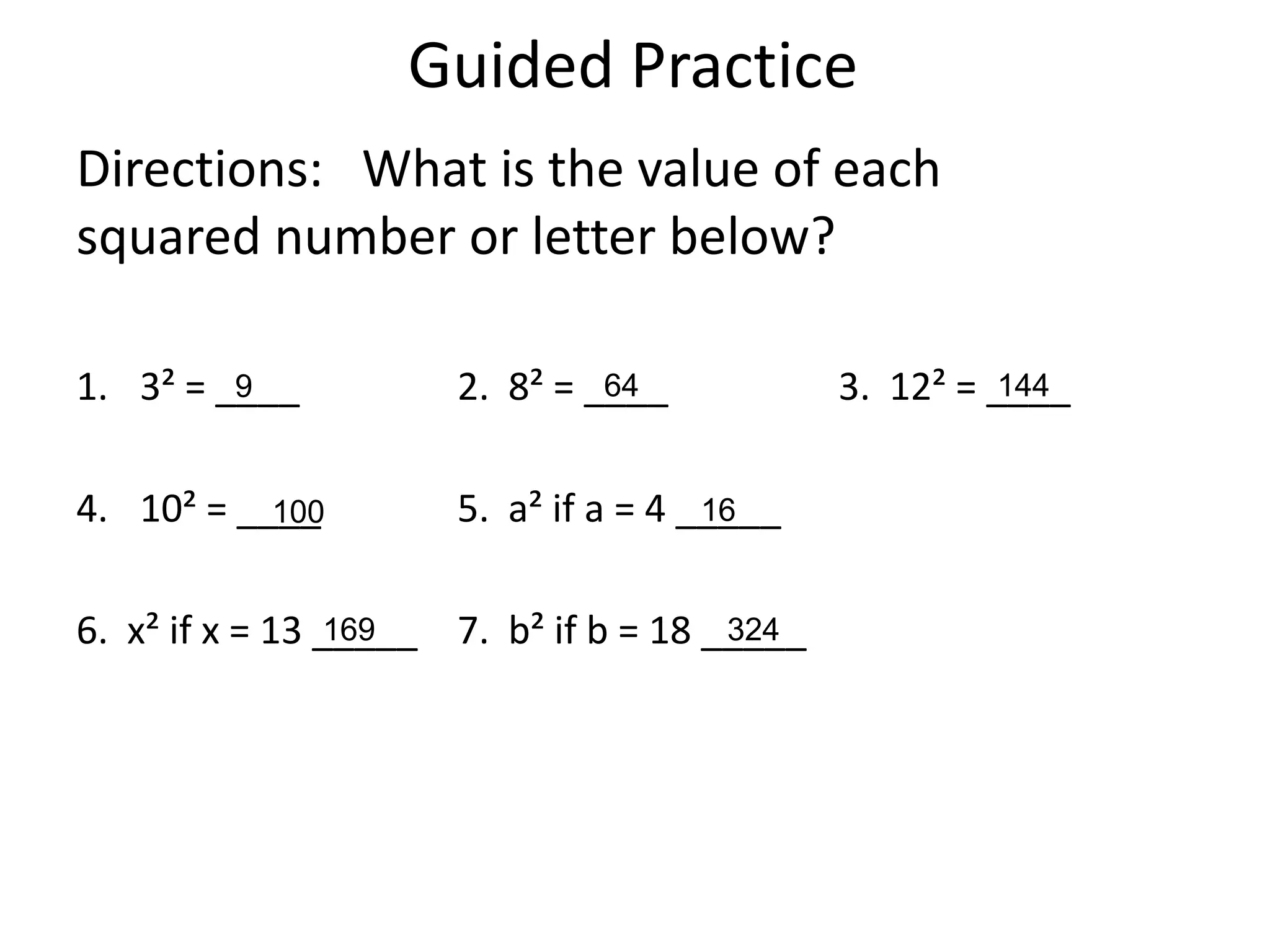
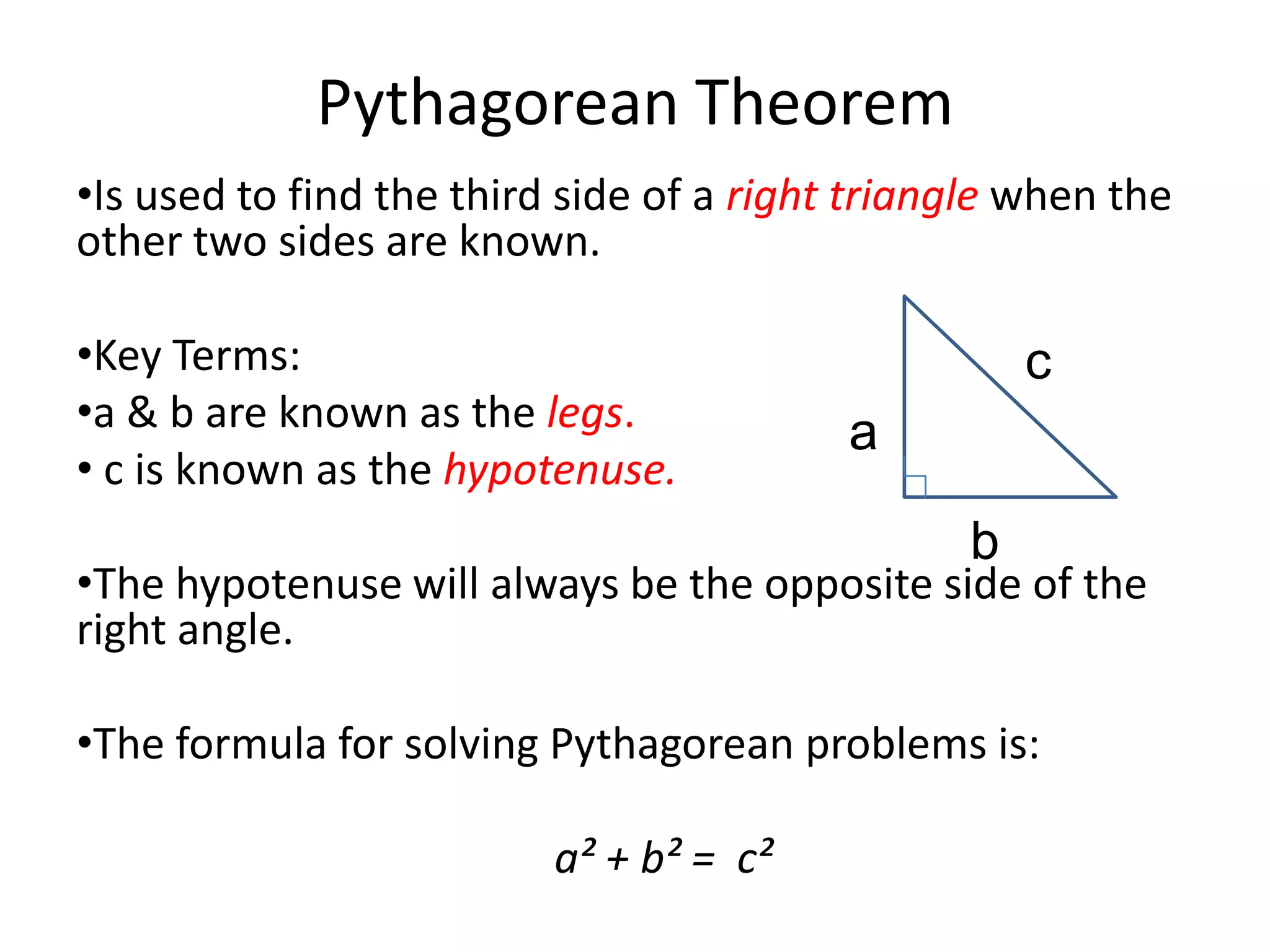
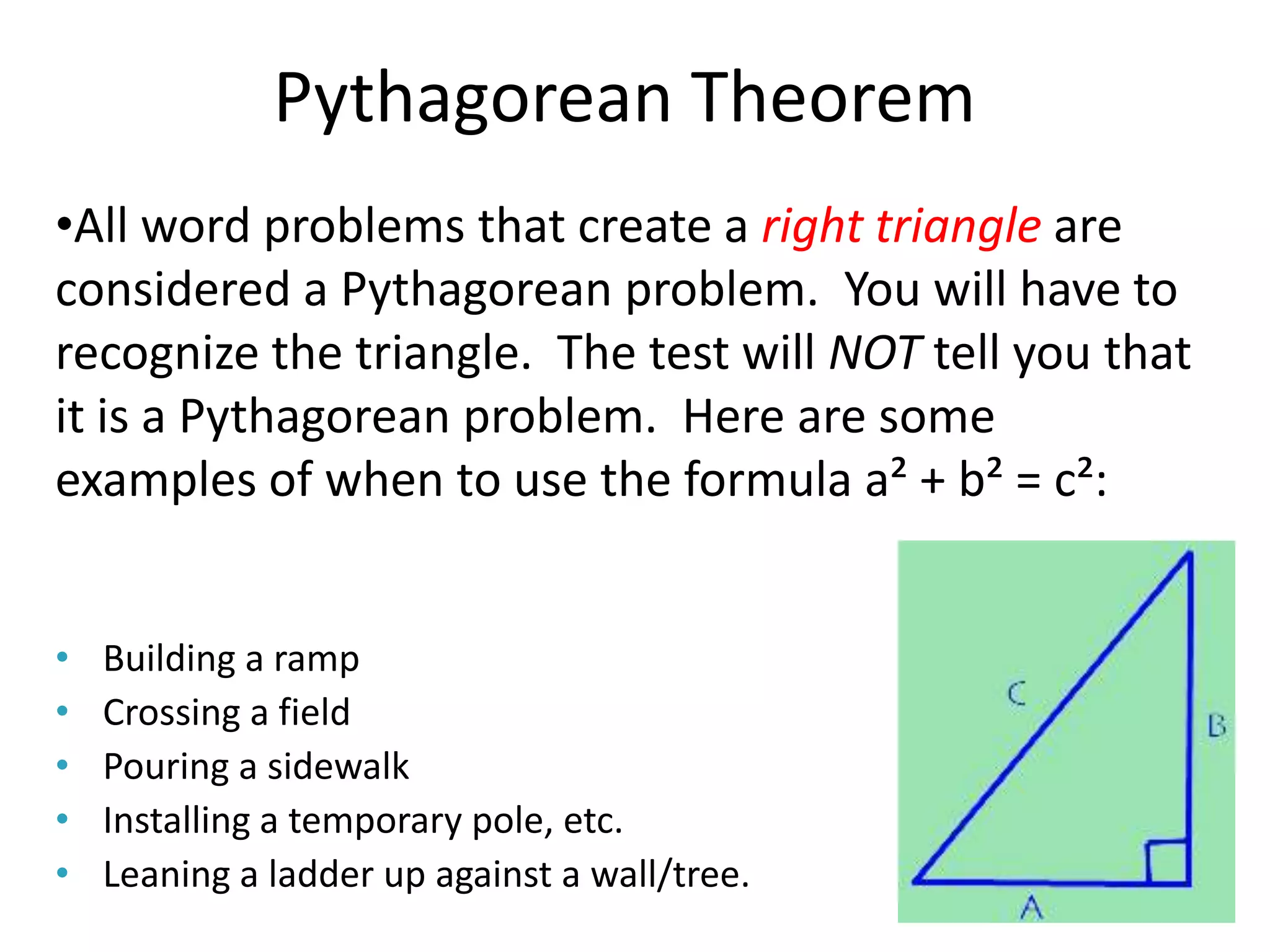
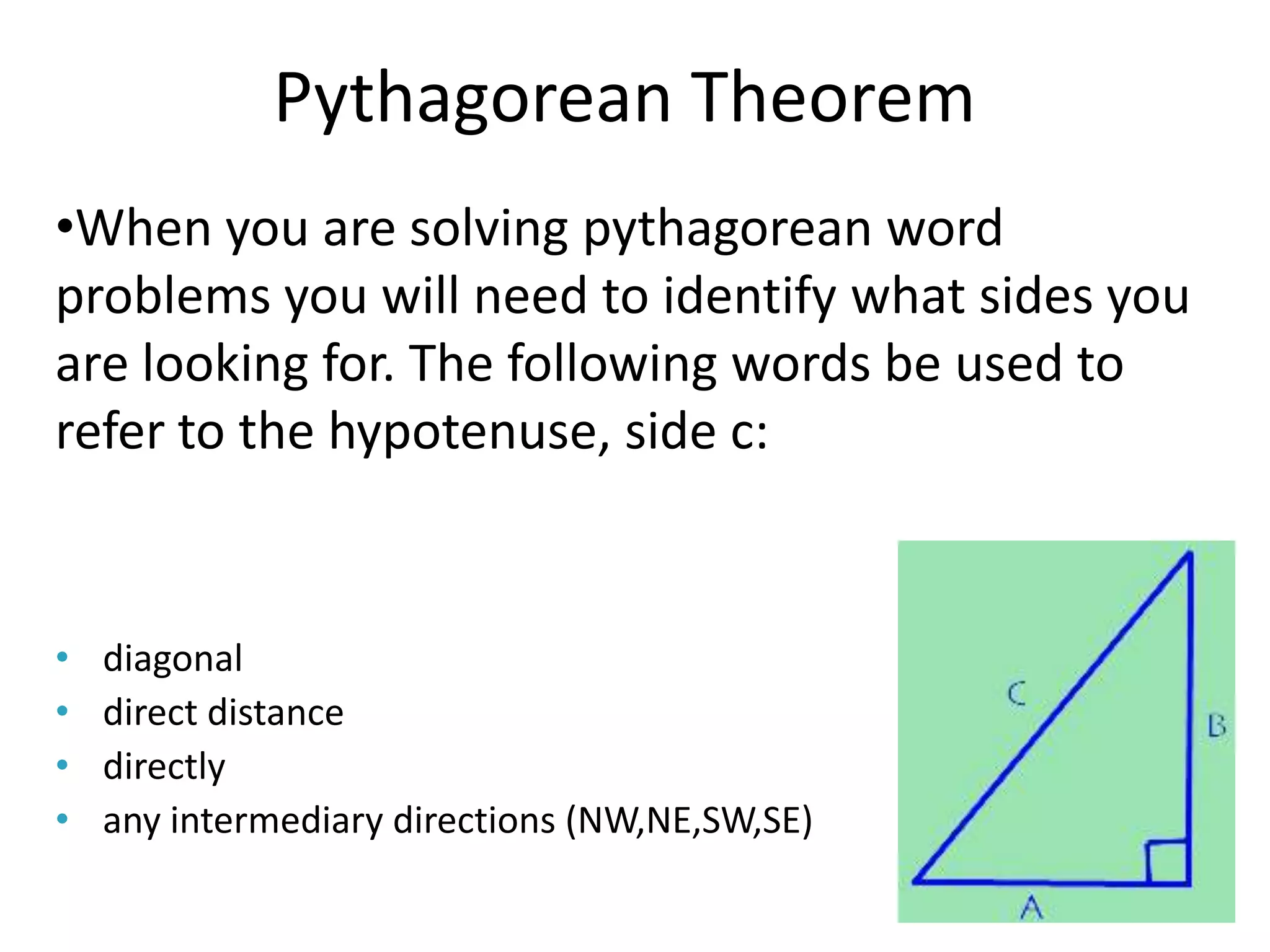
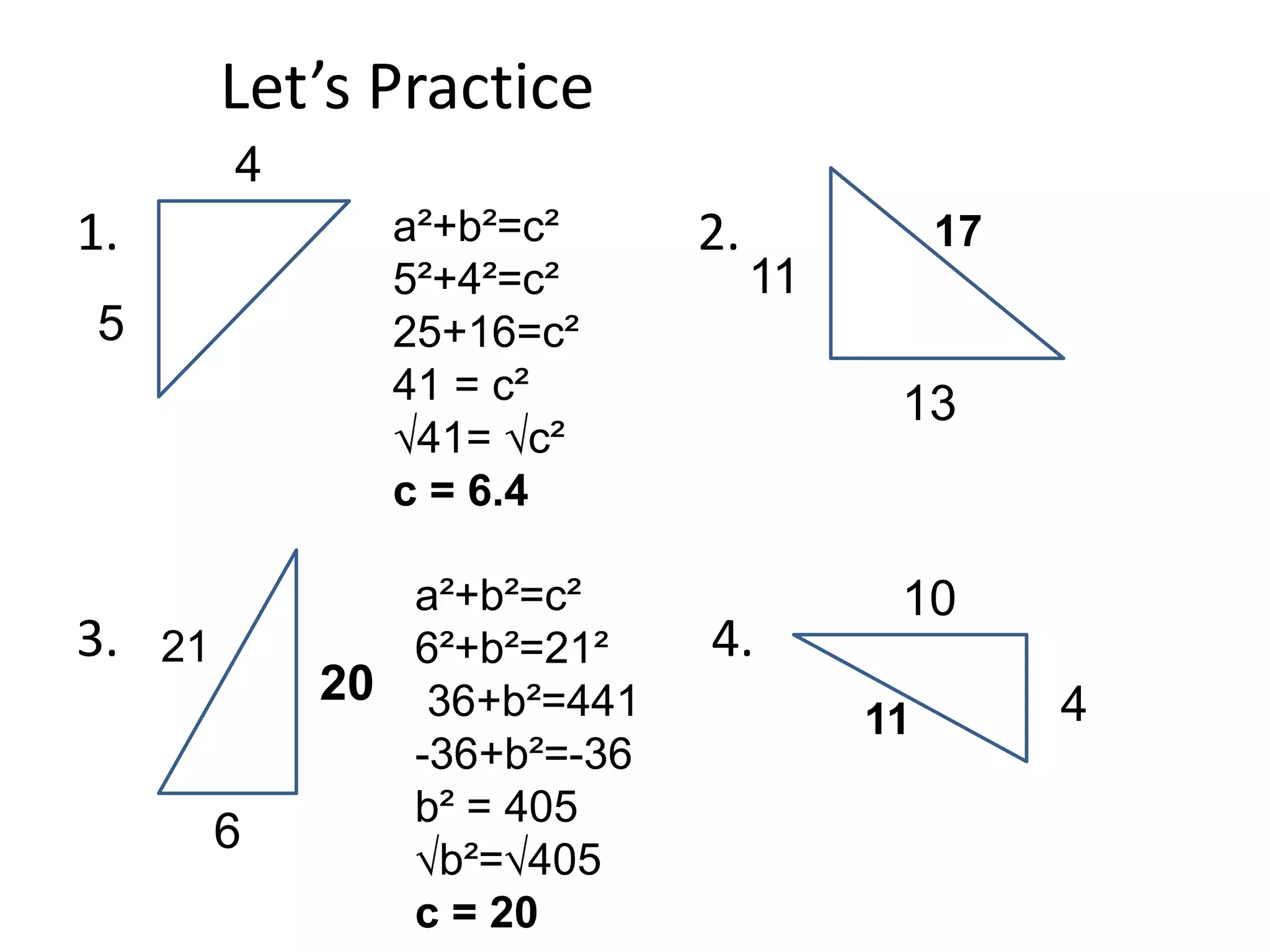
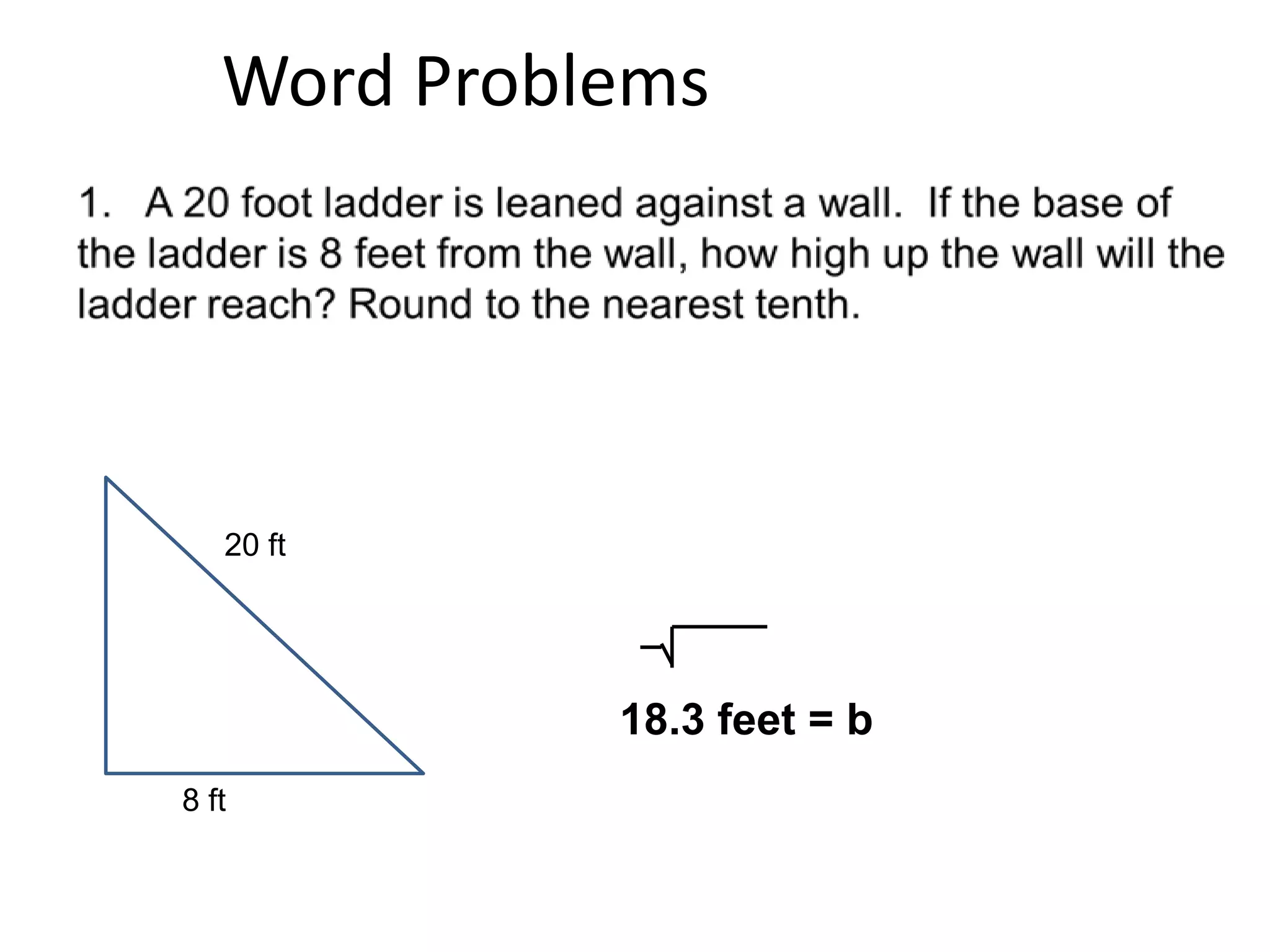
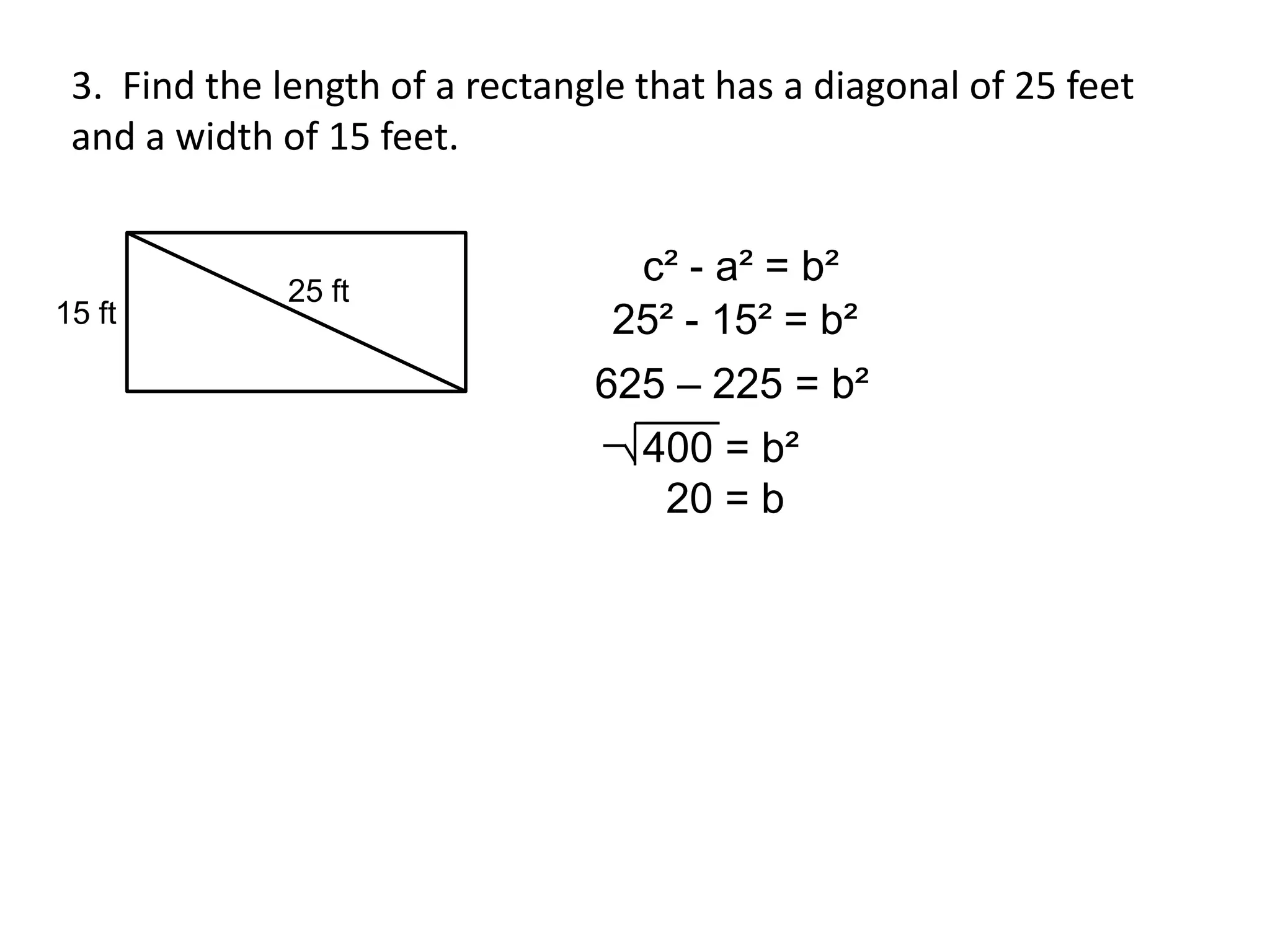
The document provides instruction on the Pythagorean theorem. It defines squares and square roots, provides examples of perfect squares, and explains how to find the square root of a number. It then introduces the Pythagorean theorem, which states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. The document provides examples of when the theorem can be used and how to set up and solve Pythagorean theorem problems and word problems. Finally, it provides examples of solving word problems using the Pythagorean theorem.