Embed presentation
Downloaded 24 times

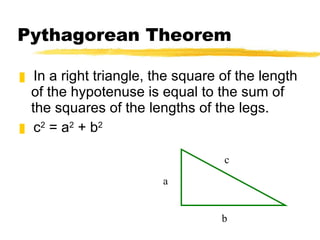



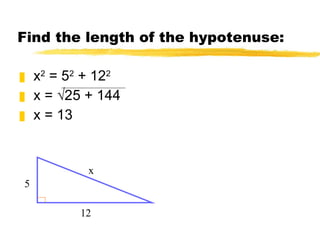
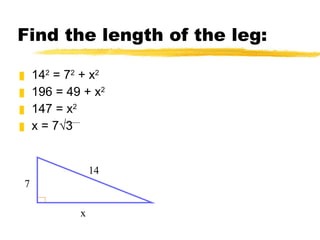
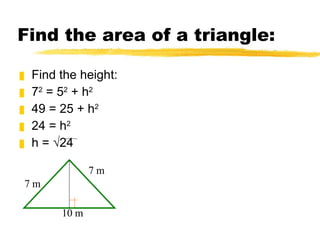
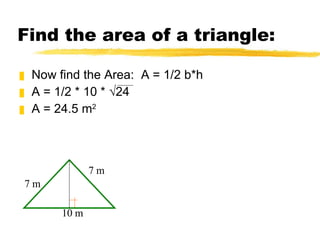



The document discusses the Pythagorean theorem, which states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the two legs. It provides examples of using the theorem to find missing sides of right triangles and the area of a triangle when two sides and a height are known.











