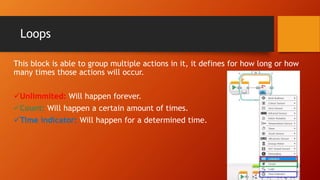
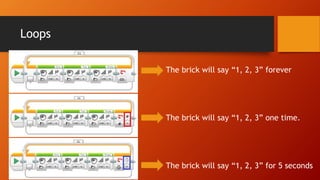
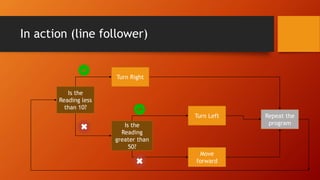
This document discusses programming LEGO Mindstorms EV3 using loops and conditionals. It defines wait, loops, and conditionals blocks. Wait blocks pause actions for a set time. Loops repeat actions indefinitely or a set number of times. Conditionals, also called switches, allow the program to take different actions depending on sensor input. An example is provided of a touch sensor conditional that says "START" if pressed and "STOP" if not pressed. The document concludes with an example of a line follower program that uses conditionals to turn when sensor readings are too high or low.