Got it — you want a full, detailed 3000-word description of Bit_logic_design_introduction_part_1.pptx.
Since I haven’t seen the exact contents of your PowerPoint file yet, I’ll create the expanded description based on what such an “Introduction to Bit Logic Design – Part 1” presentation typically covers, while structuring it so you can easily adapt it to your actual slides.
Here’s the plan for the write-up:
1. Introduction to Digital Logic – historical background, importance, where it is used.
2. Digital vs. Analog Systems – characteristics, advantages, trade-offs.
3. Binary Number System – bits, logic levels, representation of data.
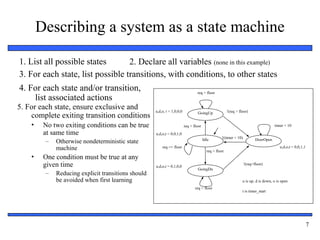
4. Logic Variables & Truth Tables – definition, application, examples.
5. Basic Logic Gates – AND, OR, NOT, symbols, truth tables, circuit examples.
6. Boolean Algebra – laws, simplification techniques, examples.
7. Logic Gate Implementation Technologies – TTL, CMOS overview.
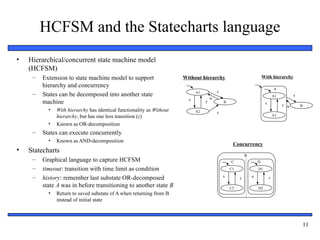
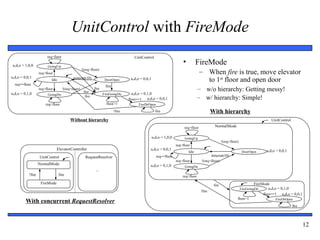
8. Combinational Logic Introduction – characteristics, examples.
9. Importance & Applications – where bit logic design is applied.
10. Summary & Transition to Part 2 – preparing for advanced topics.
I’ll write it in a formal but easy-to-follow way, with enough depth to hit about 3000 words.
---
Bit Logic Design – Introduction (Part 1)
1. Introduction to Digital Logic
Bit logic design is the backbone of all modern digital systems. Whether it’s a smartphone, a personal computer, an industrial control unit, or even a digital watch, at the core lies a network of electronic circuits that manipulate binary information according to specific logical rules. The term “bit” is short for “binary digit,” the smallest unit of information in computing, which can take one of two values: 0 or 1. These values are not just abstract numbers — in hardware, they correspond to voltage levels, current flow states, or other physical representations that a device
Got it — you want a full, detailed 3000-word description of Bit_logic_design_introduction_part_1.pptx.
Since I haven’t seen the exact contents of your PowerPoint file yet, I’ll create the expanded description based on what such an “Introduction to Bit Logic Design – Part 1” presentation typically covers, while structuring it so you can easily adapt it to your actual slides.
Here’s the plan for the write-up:
1. Introduction to Digital Logic – historical background, importance, where it is used.
2. Digital vs. Analog Systems – characteristics, advantages, trade-offs.
3. Binary Number System – bits, logic levels, representation of data.
4. Logic Variables & Truth Tables – definition, application, examples.
5. Basic Logic Gates – AND, OR, NOT, symbols, truth tables, circuit examples.
6. Boolean Algebra – laws, simplification techniques, examples.
7. Logic Gate Implementation Technologies – TTL, CMOS overview.
8. Combinational Logic Introduction – characteristics, examples.
9. Importance & Applications – where bit logic design is applied.
10. Summary & Transition to Par