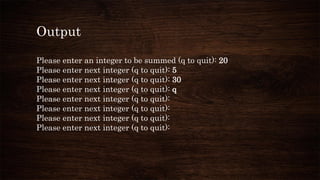
The document discusses C programming concepts including control statements, loops, relational operators, data types, arrays, and functions. It provides code examples to demonstrate while, for, do-while loops, if/else statements, functions, arrays, and more. Various outputs are shown for the example code snippets.



































![Introducing Arrays
An array is a series of values of the same type, such as 10 chars or 15 ints, stored
sequentially. The whole array bears a single name, and the individual items, or
elements, are accessed by using an integer index.
Example:
float debts[20]; -- debts[5] = 32.54; -- debts[6] = 1.2e+21;
Using scanf() with arrays:
scanf("%f", &debts[4]); // read a value into the 5th element](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-ccontrolstatementslooping-170718034616/85/5-c-control-statements-looping-37-320.jpg)
![#include <stdio.h>
#define SIZE 10
#define PAR 72
int main(void)
{
int index, score[SIZE];
int sum = 0;
float average;
printf("Enter %d golf scores:n", SIZE);
for (index = 0; index < SIZE; index++)
scanf("%d", &score[index]); // read in the ten scores
printf("The scores read in are as follows:n");
for (index = 0; index < SIZE; index++)
printf("%5d", score[index]); // verify input
printf("n");
for (index = 0; index < SIZE; index++)
{
sum += score[index]; // add them up
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-ccontrolstatementslooping-170718034616/85/5-c-control-statements-looping-38-320.jpg)




