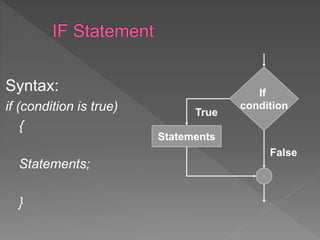
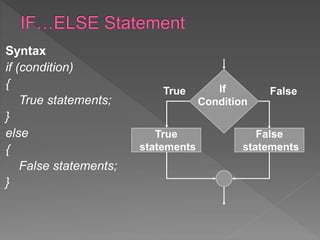
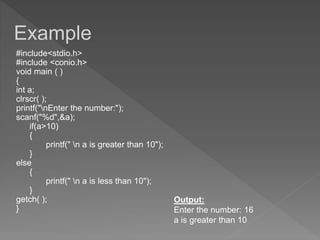
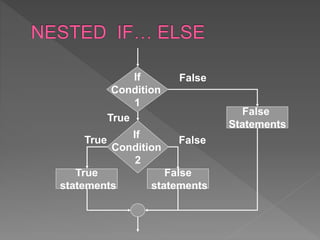
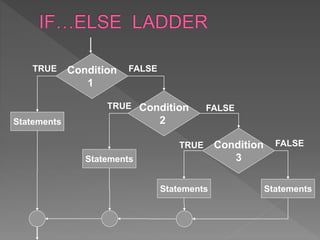
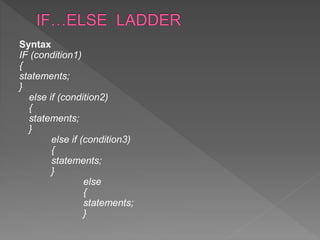
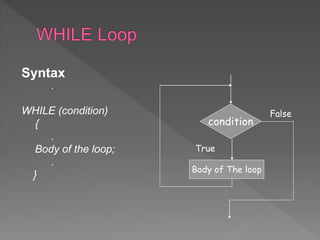
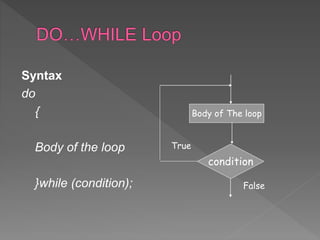
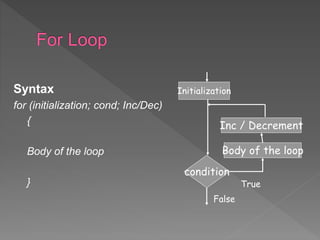
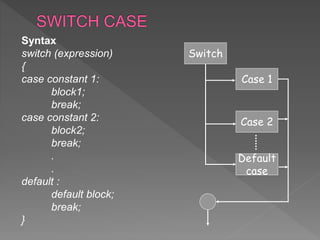
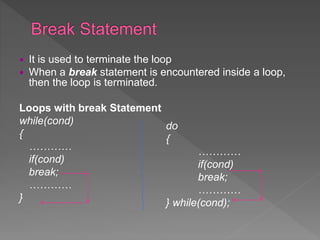
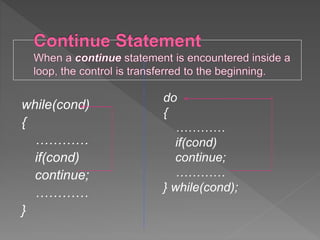
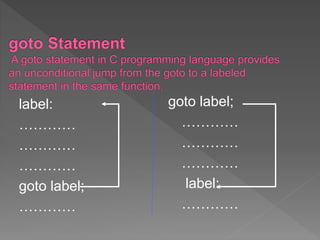
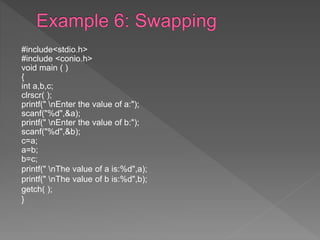
The document discusses different types of selection and looping structures in C programming such as if-else statements, switch statements, while loops, for loops, and nested loops. It provides syntax examples and sample code to demonstrate if-else ladders, nested if statements, while, do-while and for loops. Examples include calculating grades based on marks, finding roots of quadratic equations, Fibonacci series, swapping values and reversing numbers.