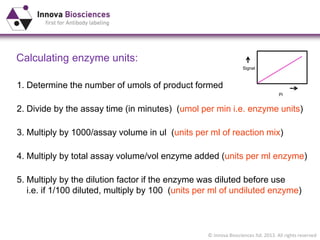
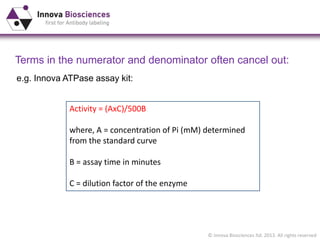
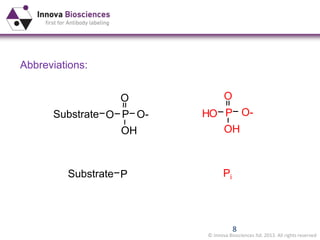
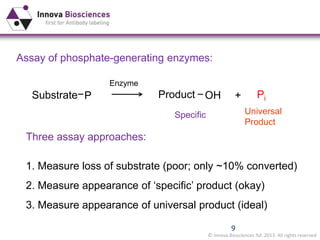
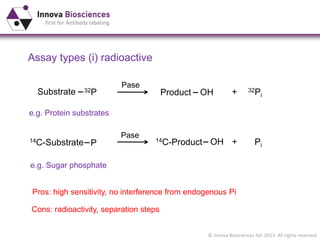
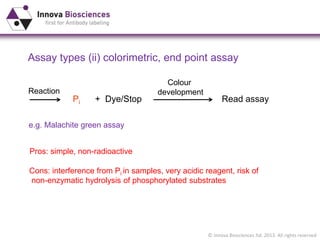
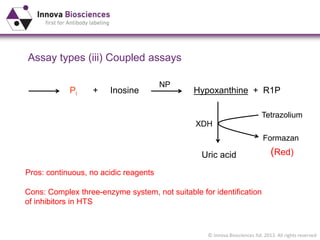
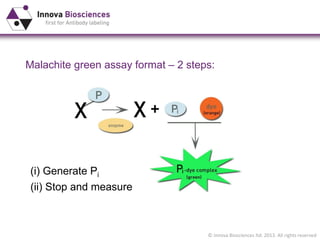
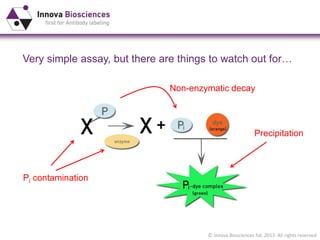
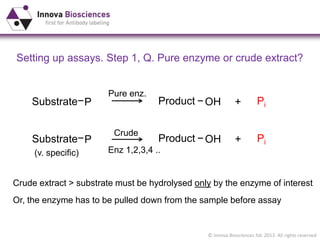
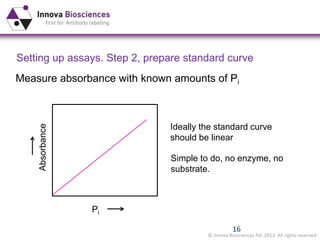
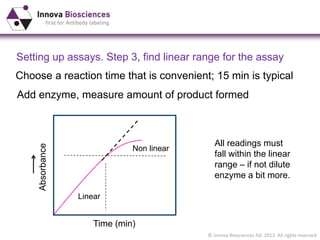
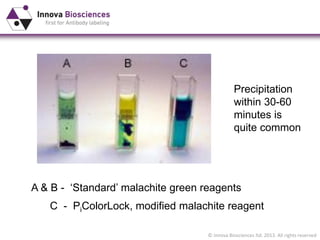
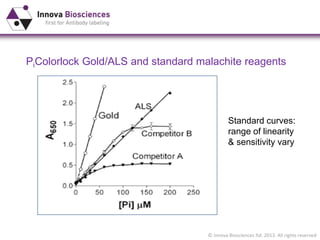
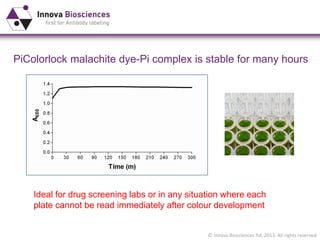
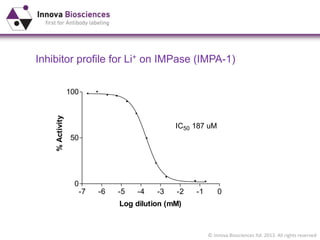
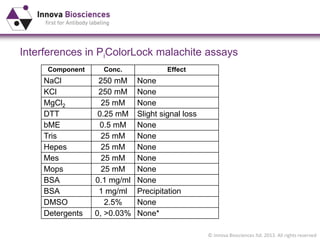
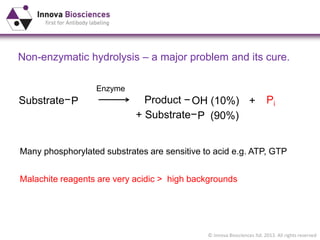
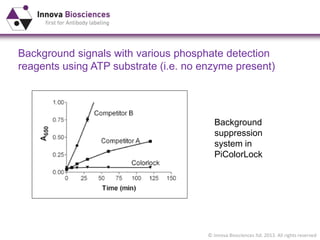
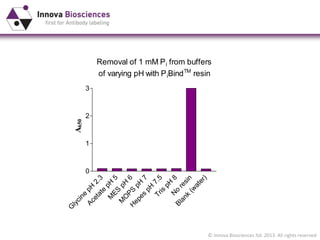
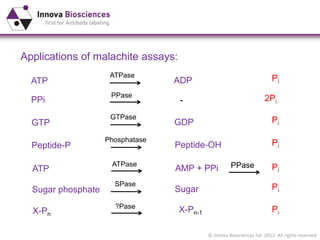
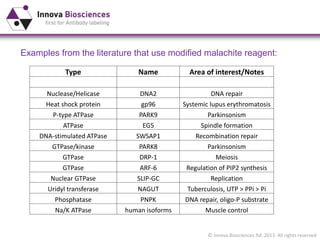
The document outlines methods for phosphate detection and assays for phosphate-generating enzymes, emphasizing the importance of enzyme activity calculations and various assay types such as malachite green assays and coupled assays. It discusses the setup of assays, including considerations for enzyme purity and potential contamination with inorganic phosphate, while also highlighting the advantages of modified reagents for improved performance. Additionally, it provides information on relevant products and resources available through Innova Biosciences for conducting assays effectively.