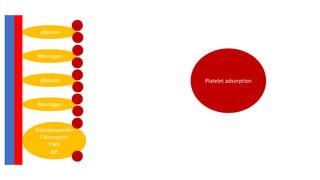
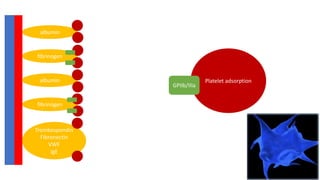
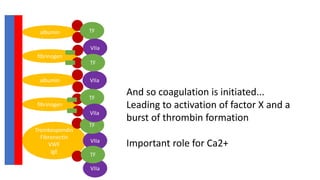
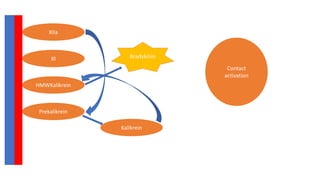
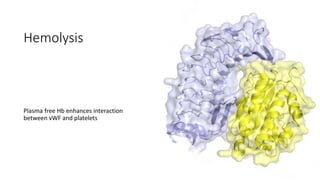
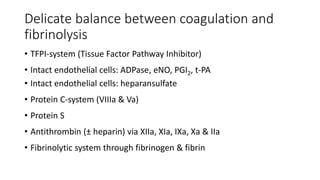
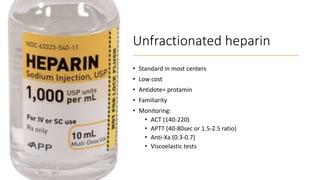
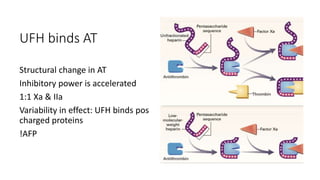
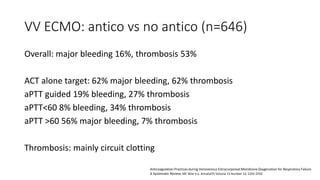
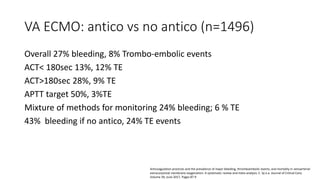
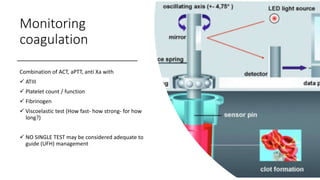
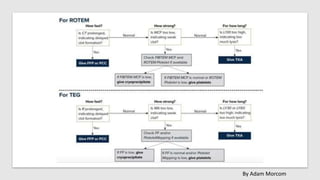
The document discusses anticoagulation management during veno-venous and venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), highlighting the balance between bleeding and thromboembolic events. It presents various anticoagulation strategies, including unfractionated heparin, low-molecular-weight heparin, and direct thrombin inhibitors, along with monitoring parameters like ACT, APTT, and anti-Xa levels. The review emphasizes the importance of tailored anticoagulation practices to minimize complications during ECMO therapy.