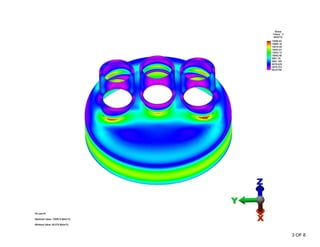
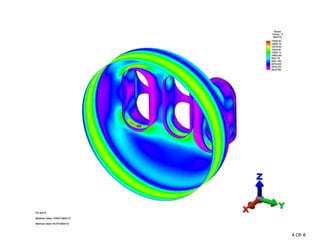
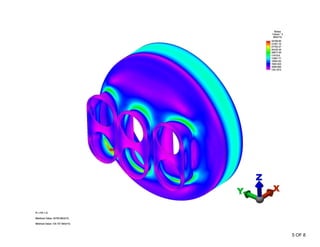
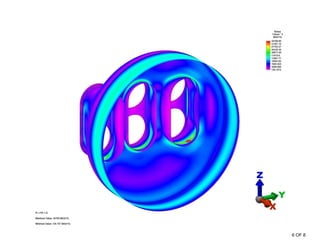
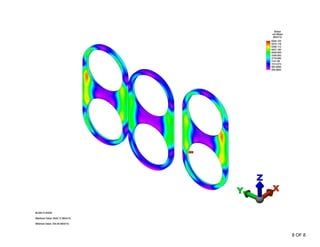
The document summarizes a stress analysis of a vessel head with 3 fire tubes. A finite element analysis was performed to analyze stresses under 100 PSI pressure. The analysis found that local primary membrane stress, general primary membrane stress on the vessel and head, and total stresses including primary membrane, bending, and secondary stresses all met the stress limits defined in the ASME code. The stresses were below the material's ultimate strength of 70 ksi and satisfied the specific stress limits given in ASME VIII-2.