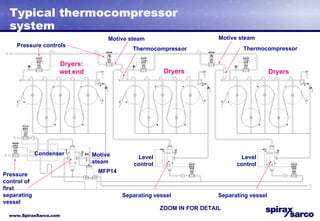
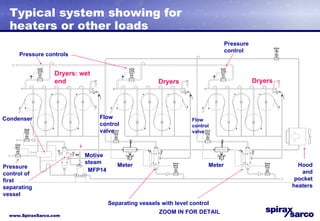
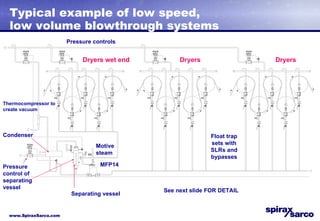
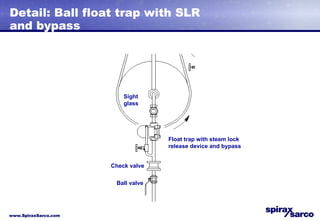
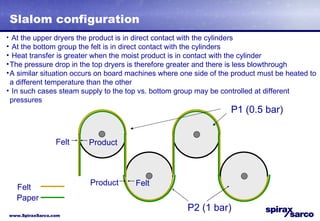
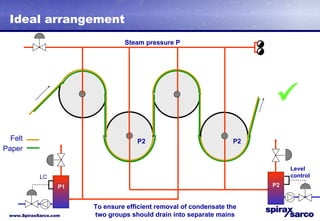
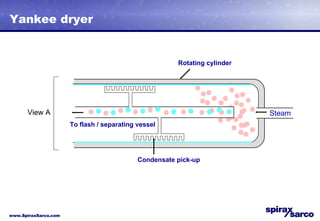
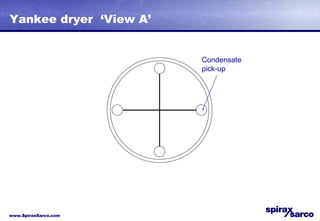
The document discusses steam systems used in paper drying processes. It describes the dryer section and factors that influence temperature control. It then explains how pressure builds up in drying cylinders and ducts due to moisture and ventilation. Various steam systems are outlined, including cascade, thermocompressor, and blowthrough configurations used to supply steam to dryers, heaters, and other loads. Details are provided on condensate drainage and the need for steam lock release devices.