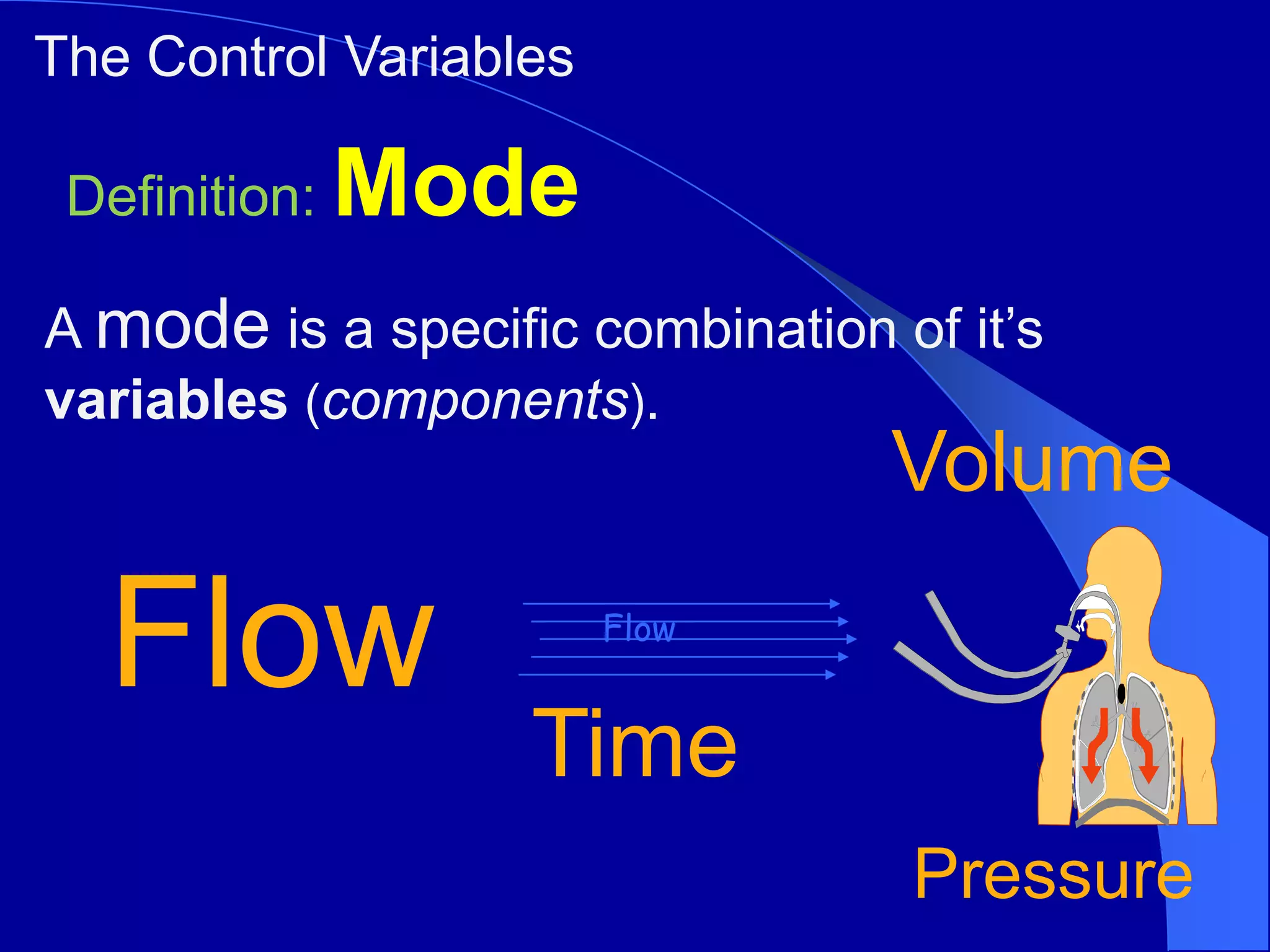
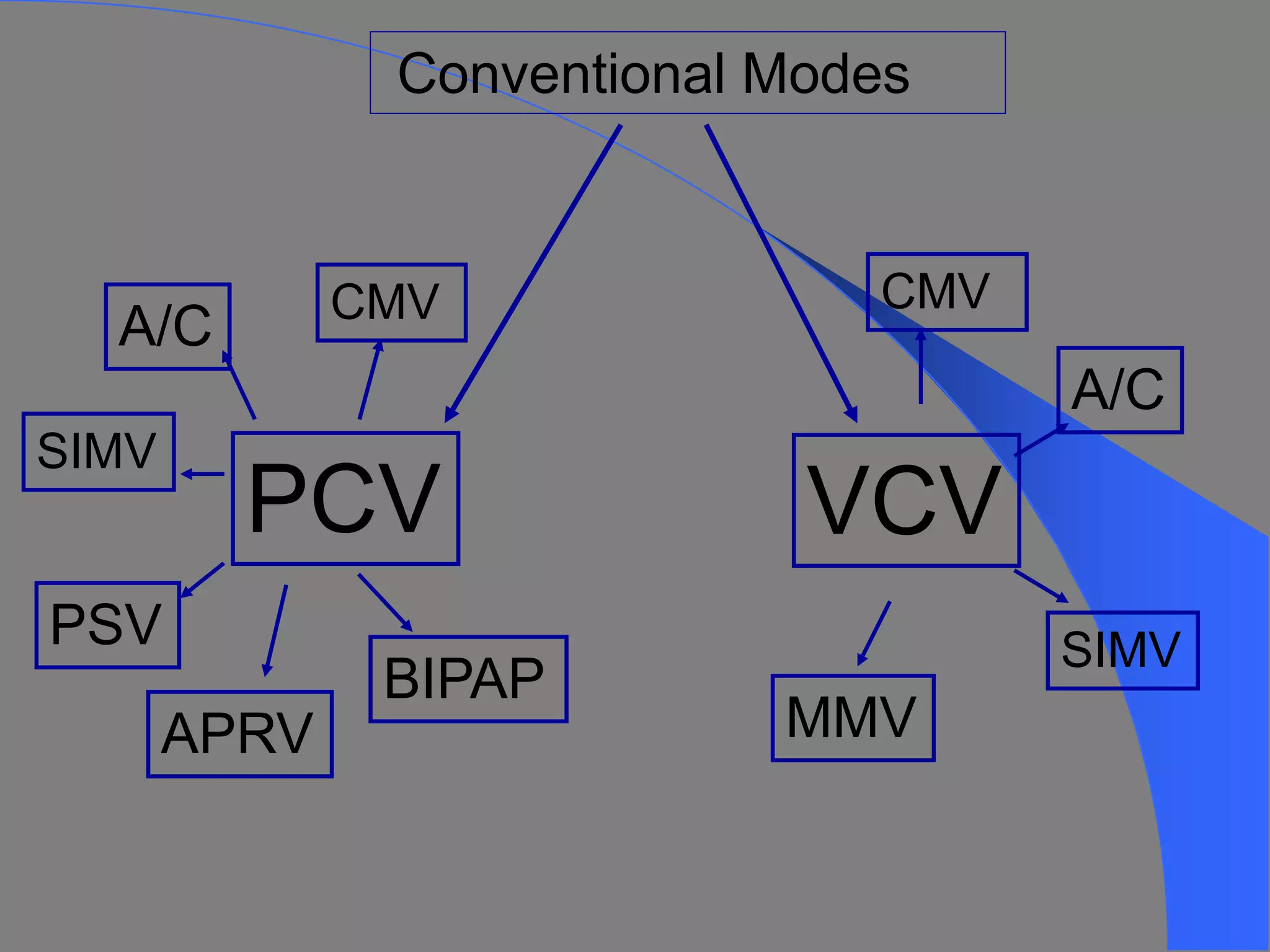
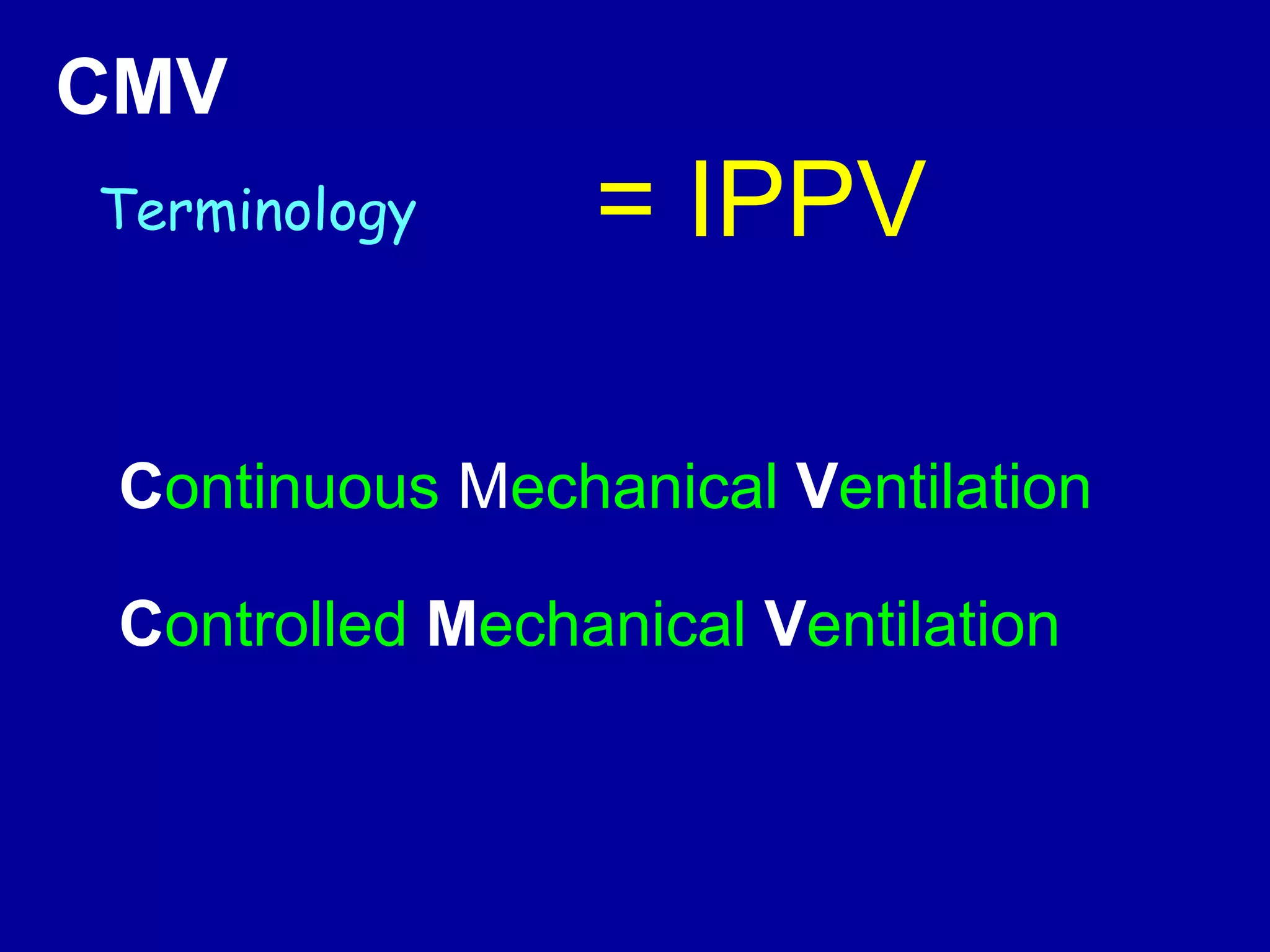
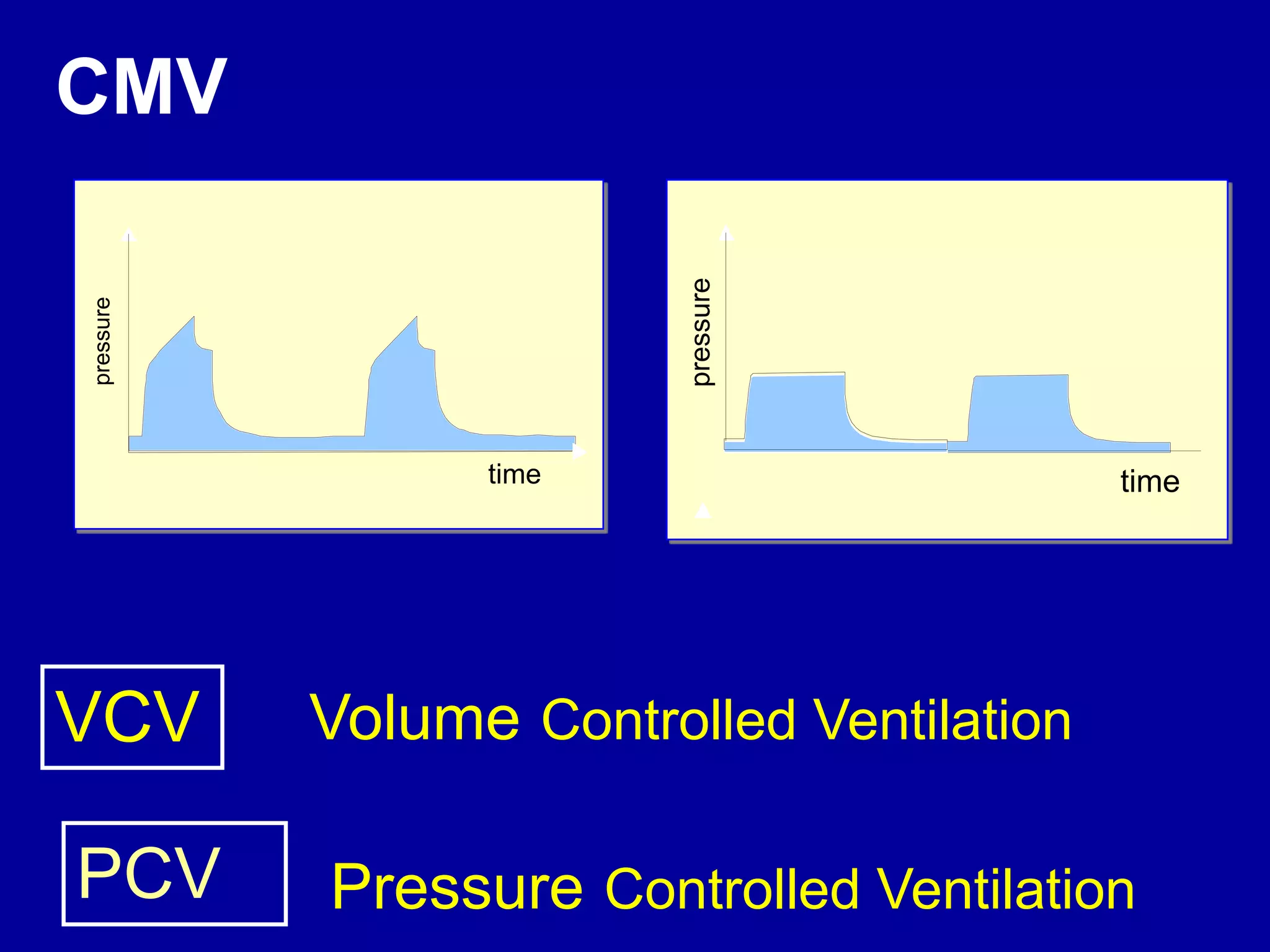
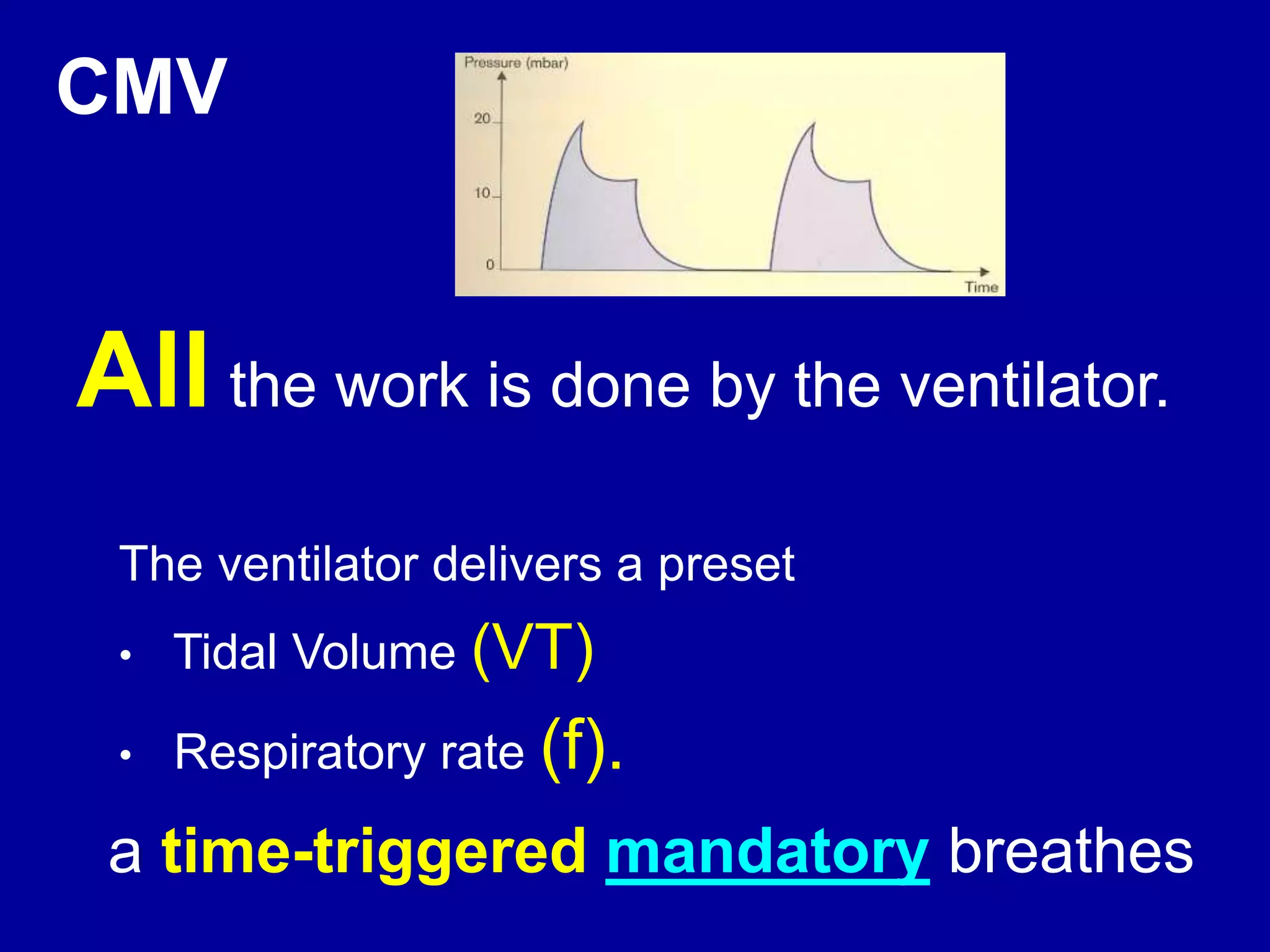
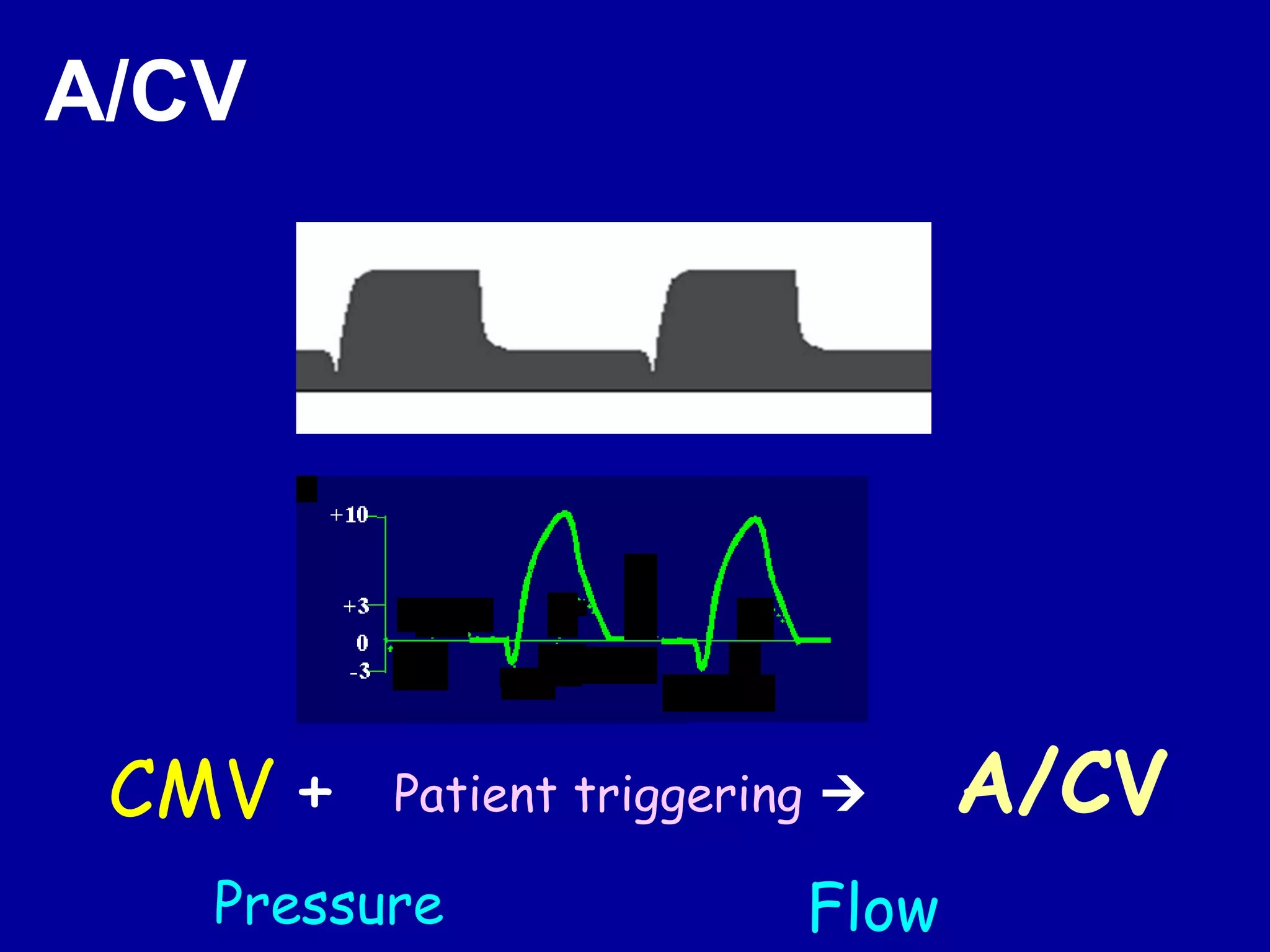
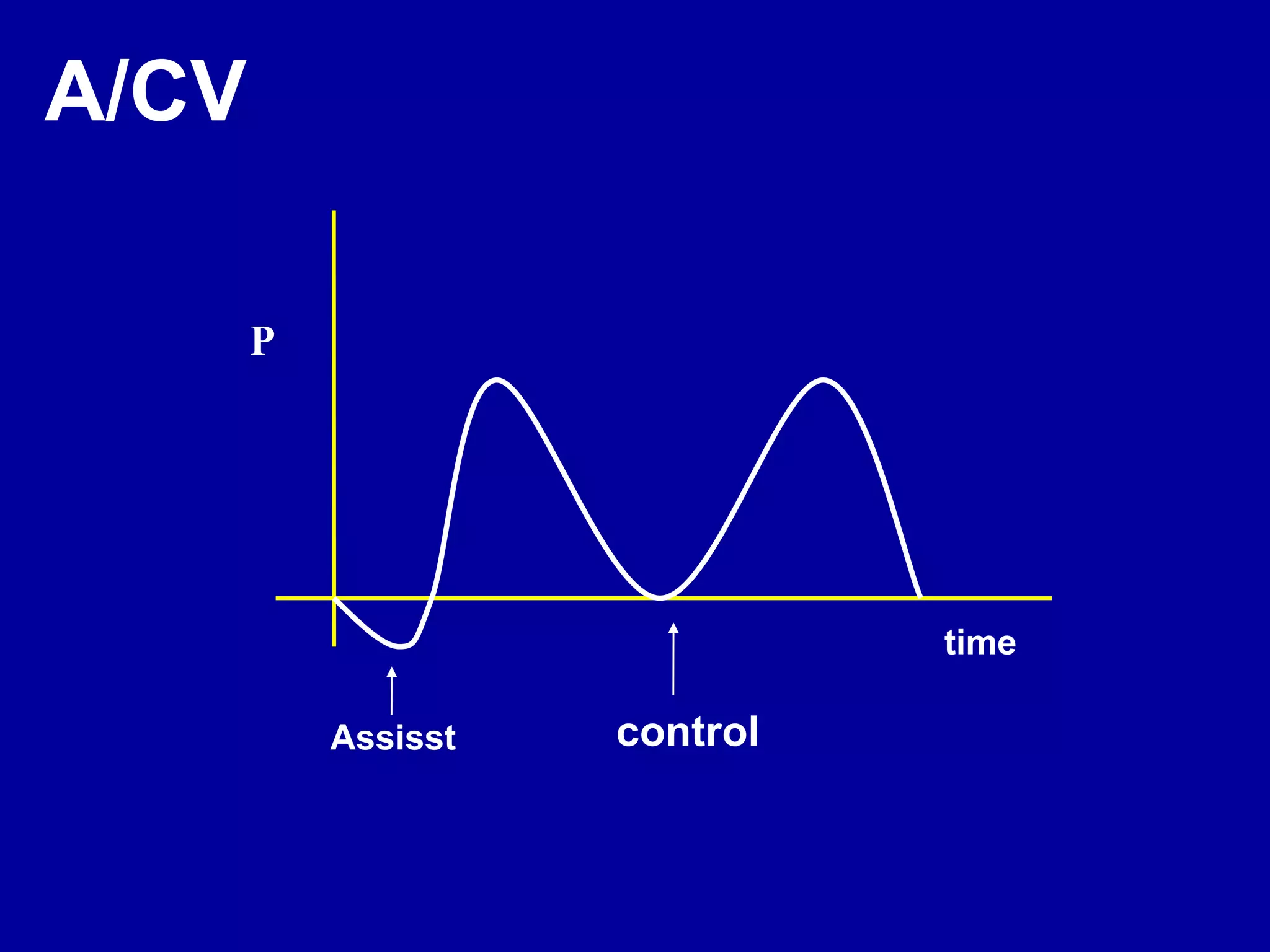
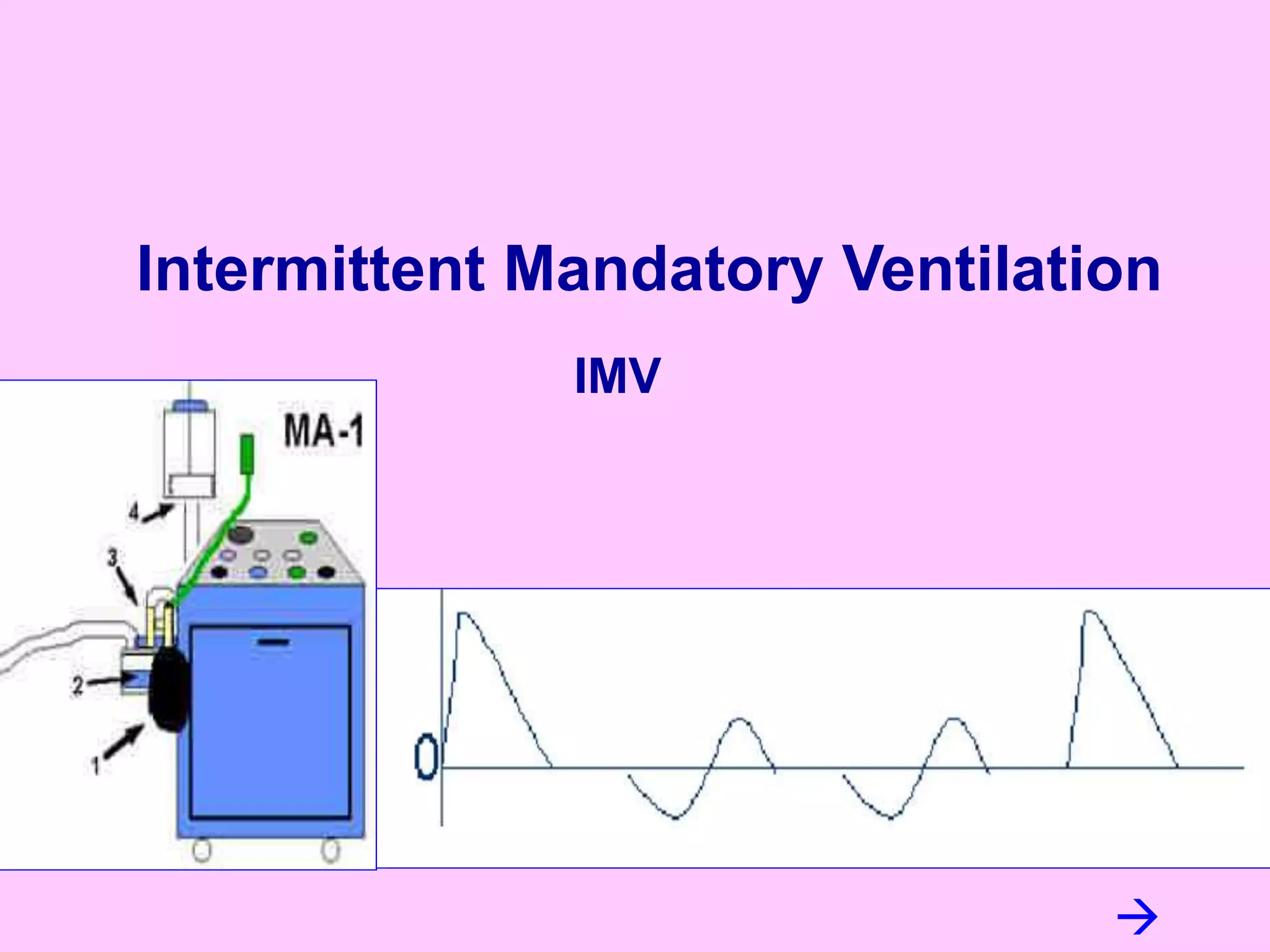
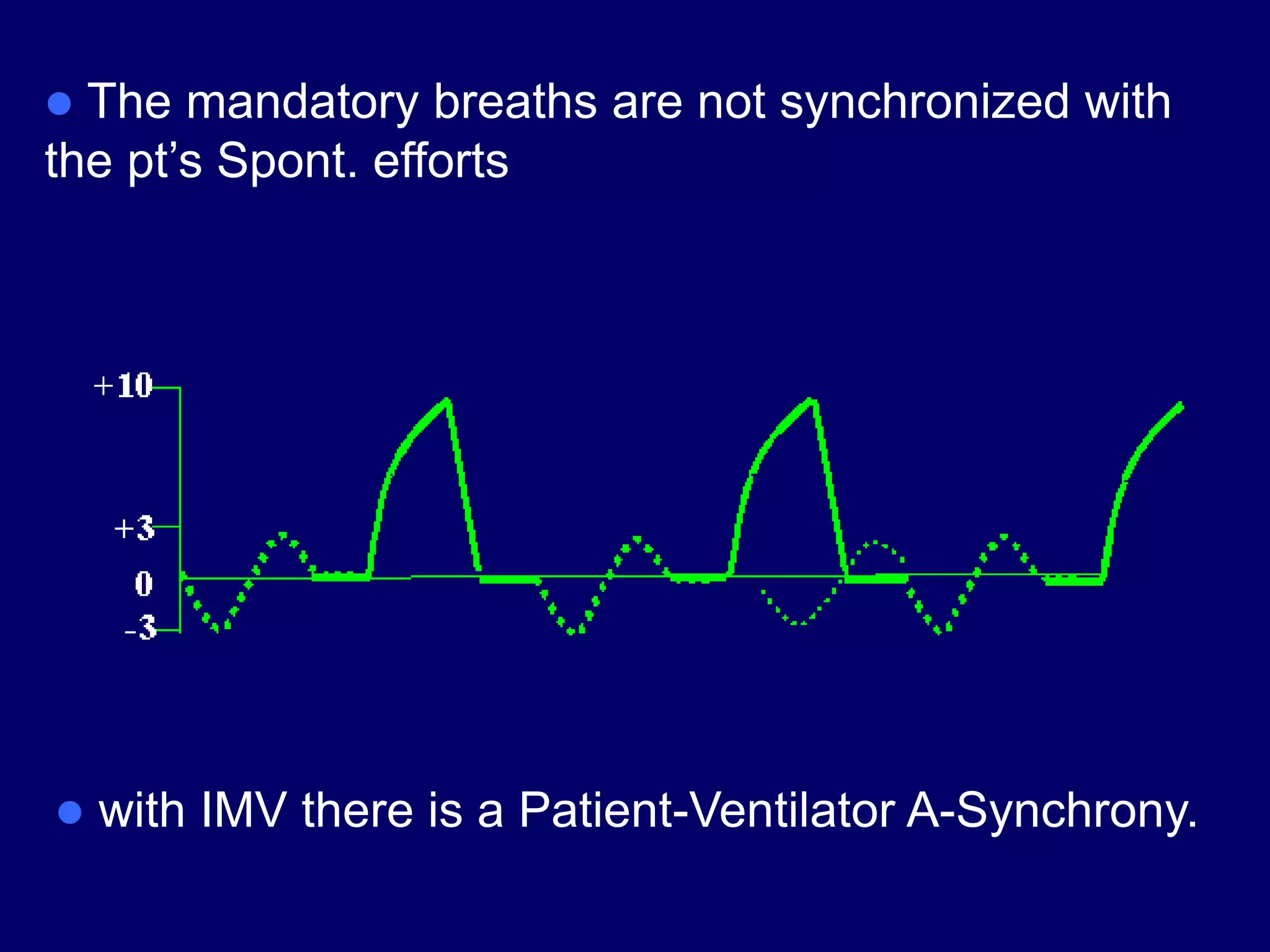
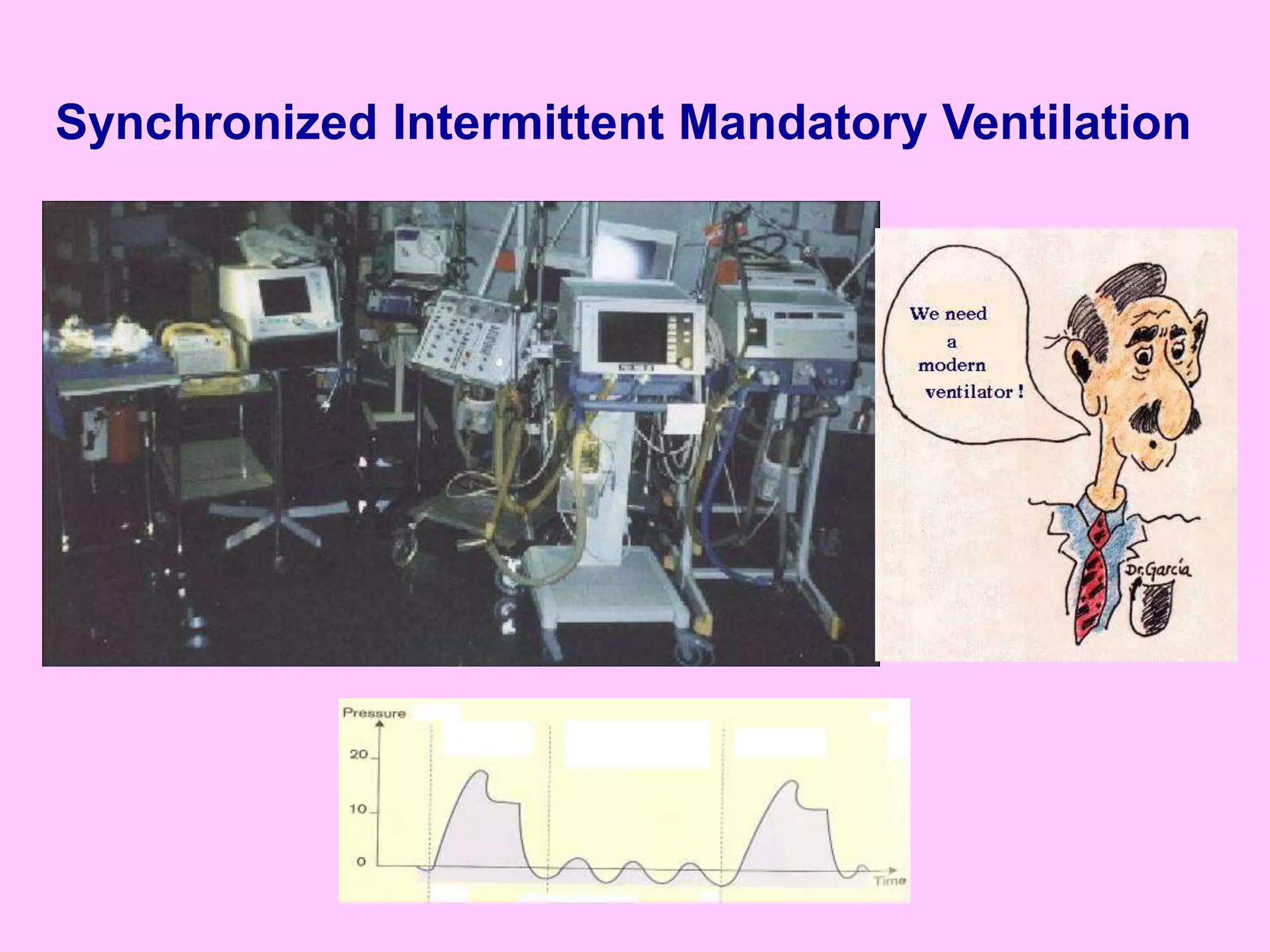
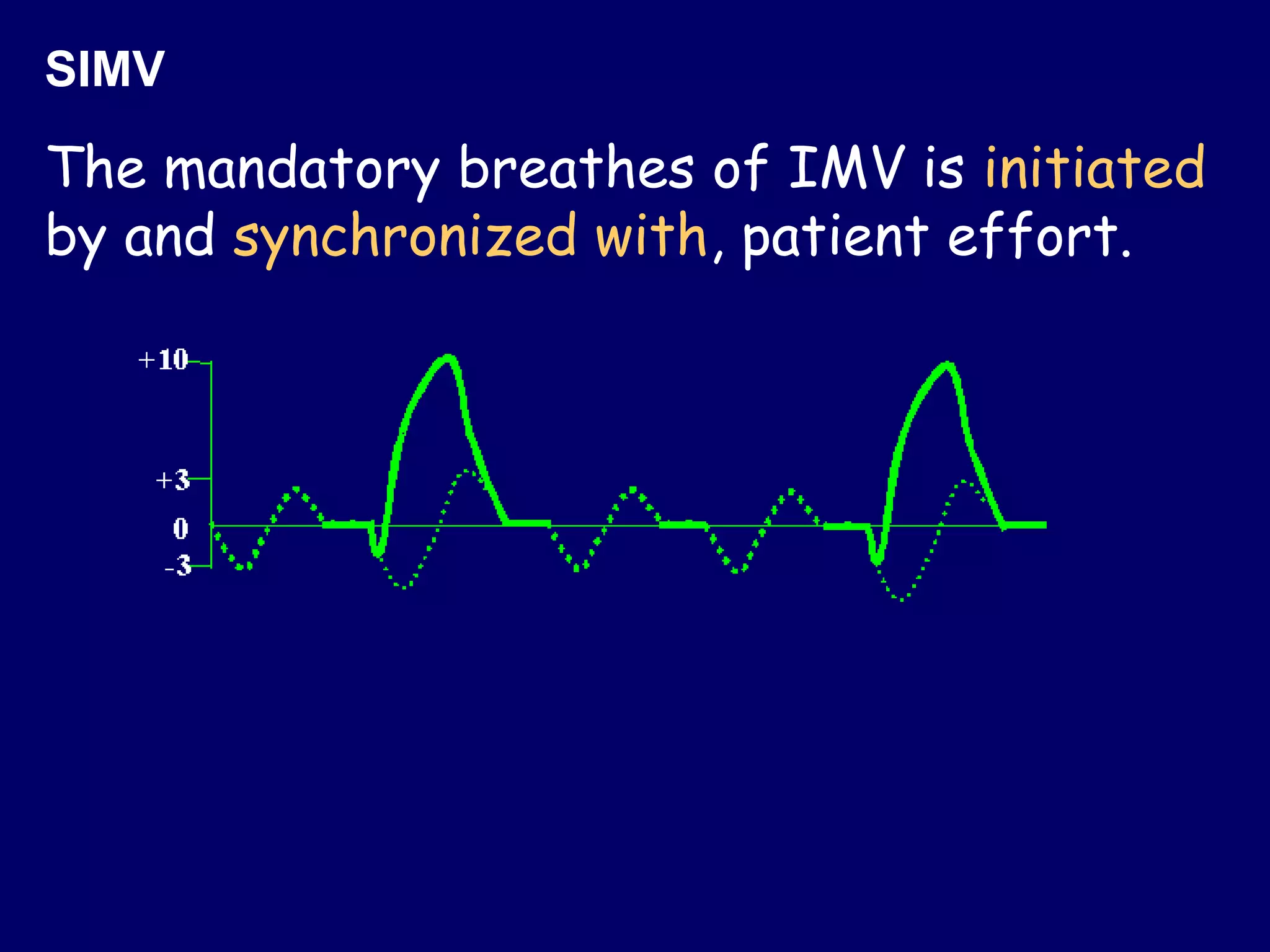
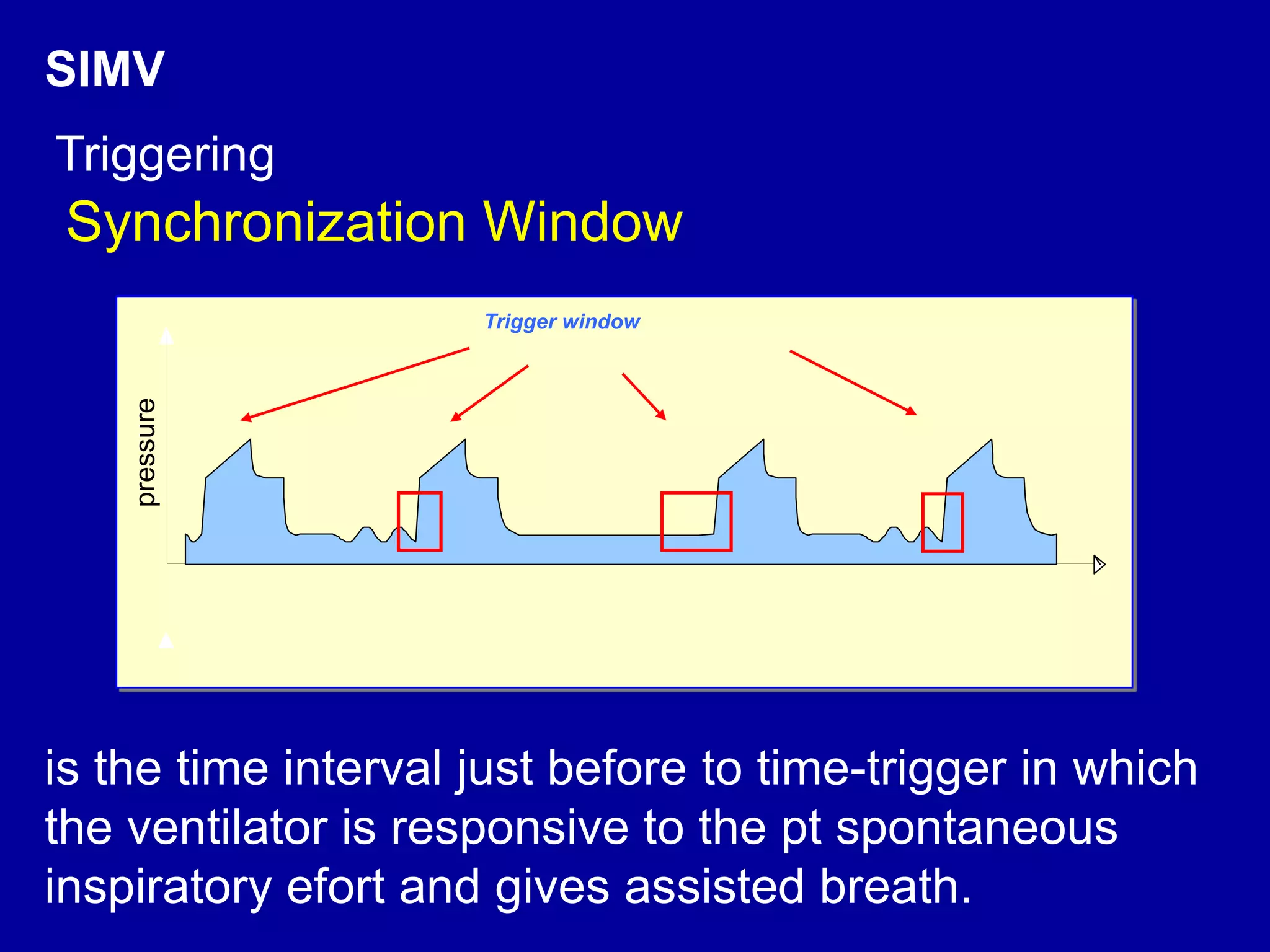
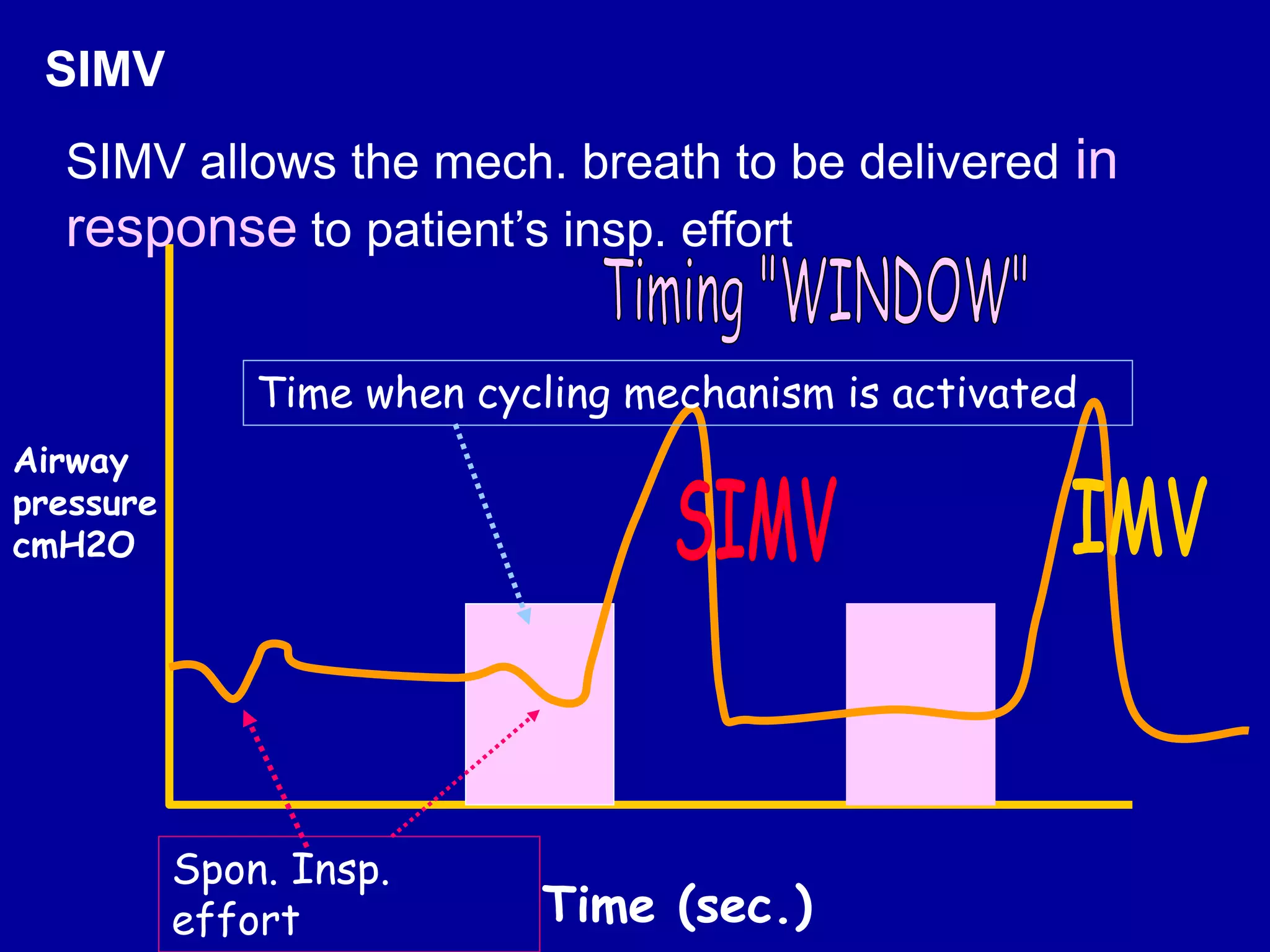
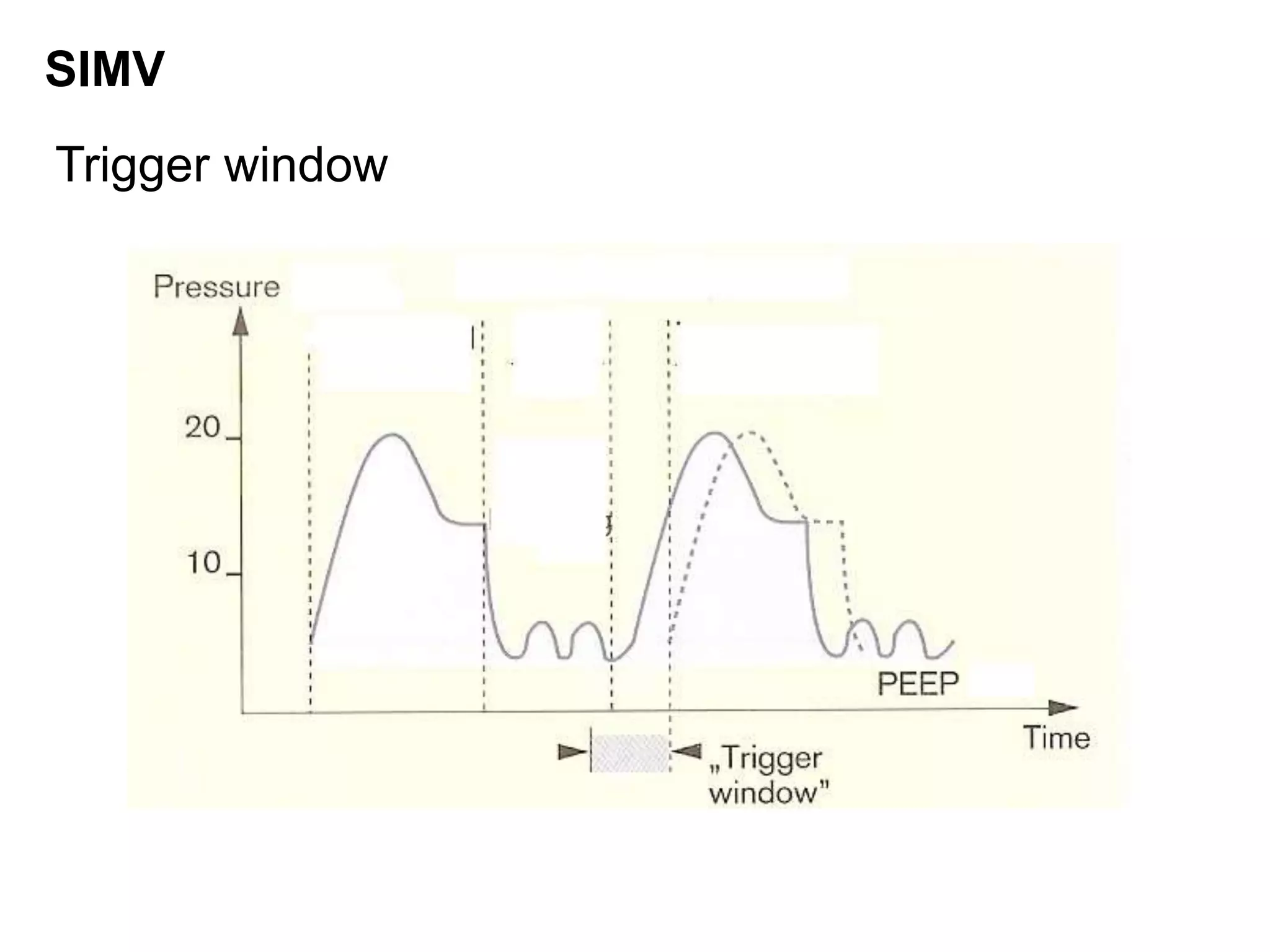
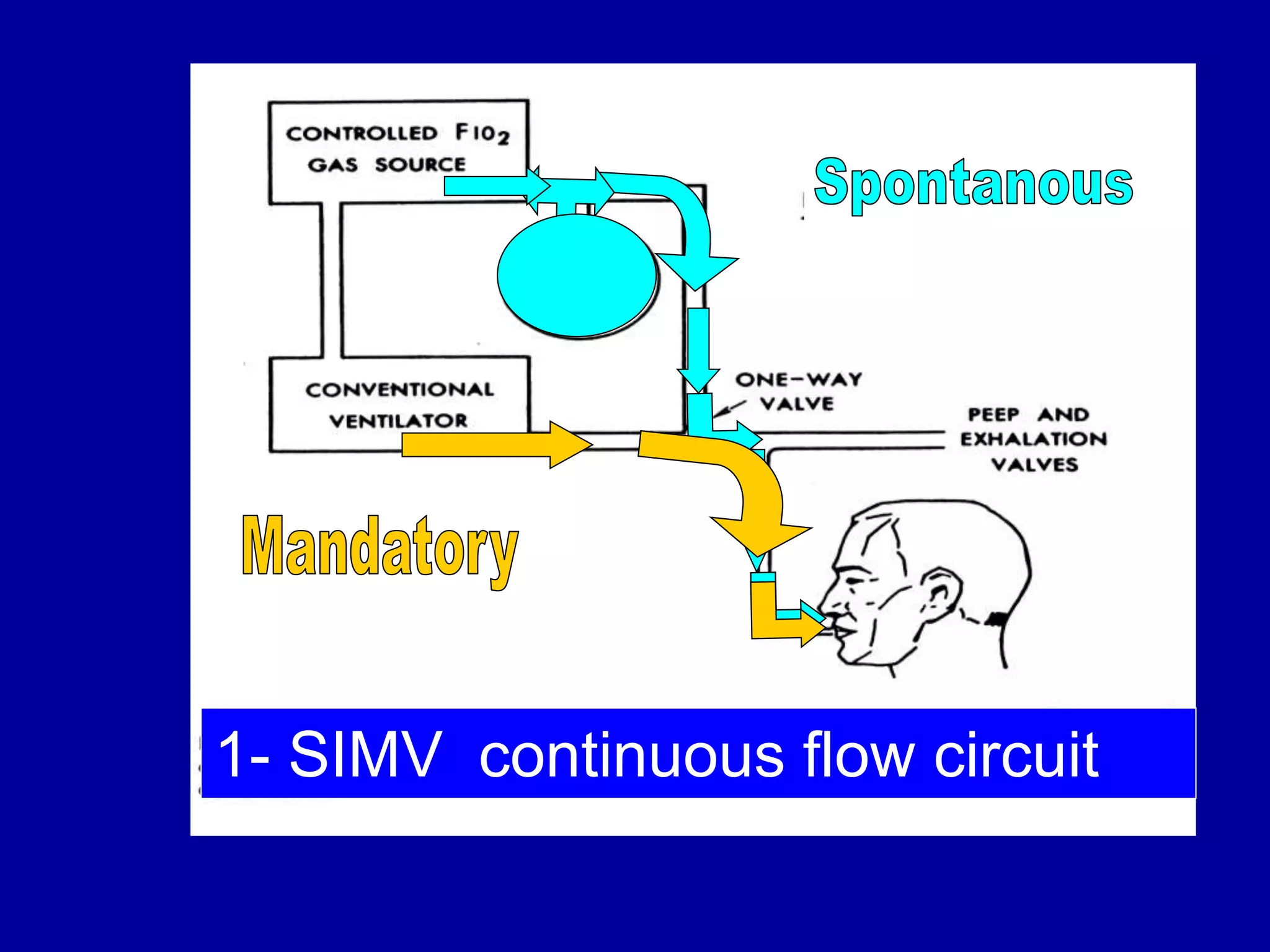
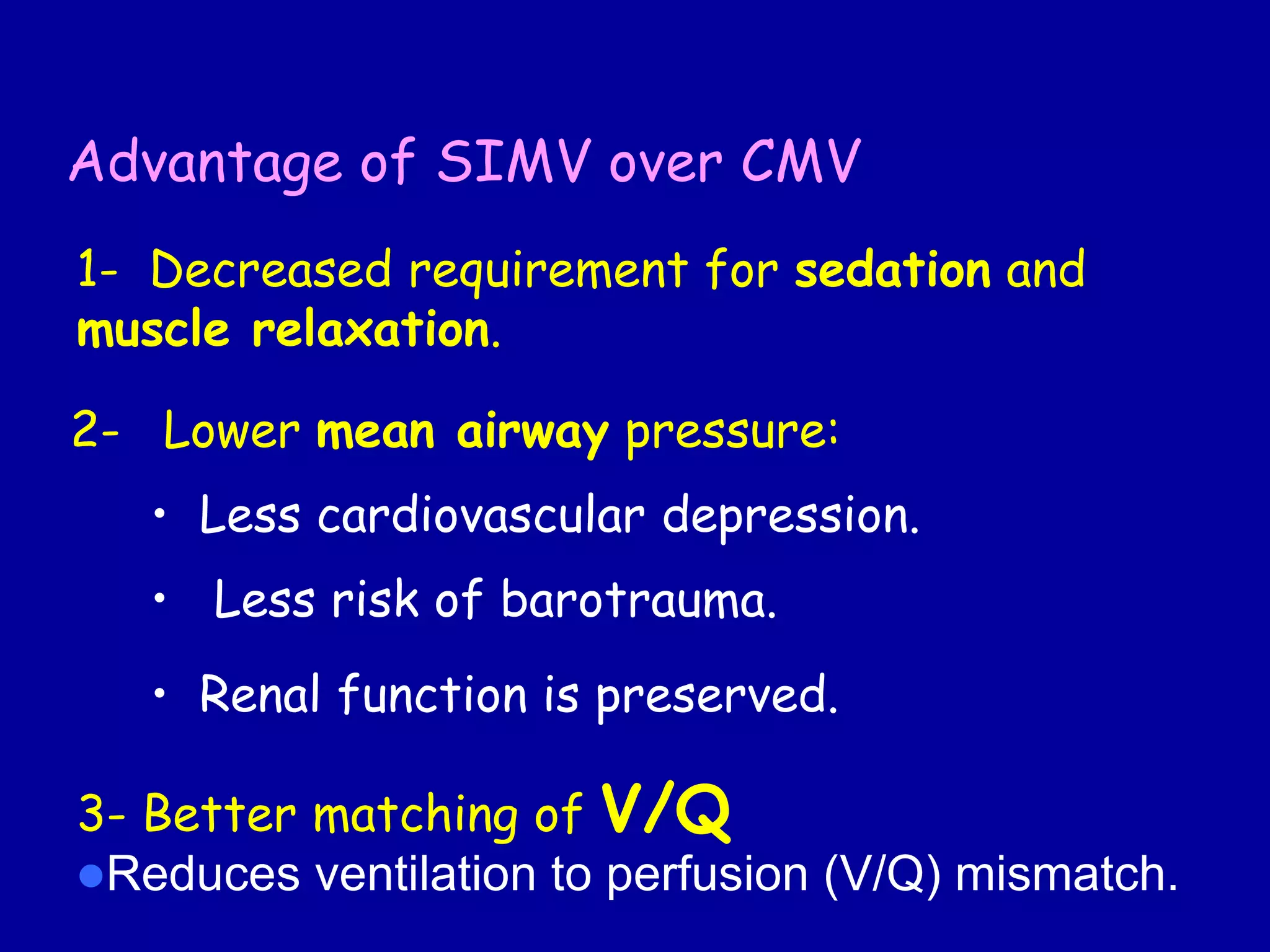
This document discusses various modes of mechanical ventilation including CMV, A/C, IMV, and SIMV. CMV provides full ventilatory support with no spontaneous breathing allowed. A/C allows patients to spontaneously breathe in addition to mandatory breaths. IMV delivers mandatory breaths on a timed cycle with spontaneous breathing allowed in between. SIMV improves on IMV by synchronizing mandatory breaths with patient effort to reduce asynchrony. SIMV has advantages over CMV like lower sedation needs and reduced risks of barotrauma and hemodynamic effects.