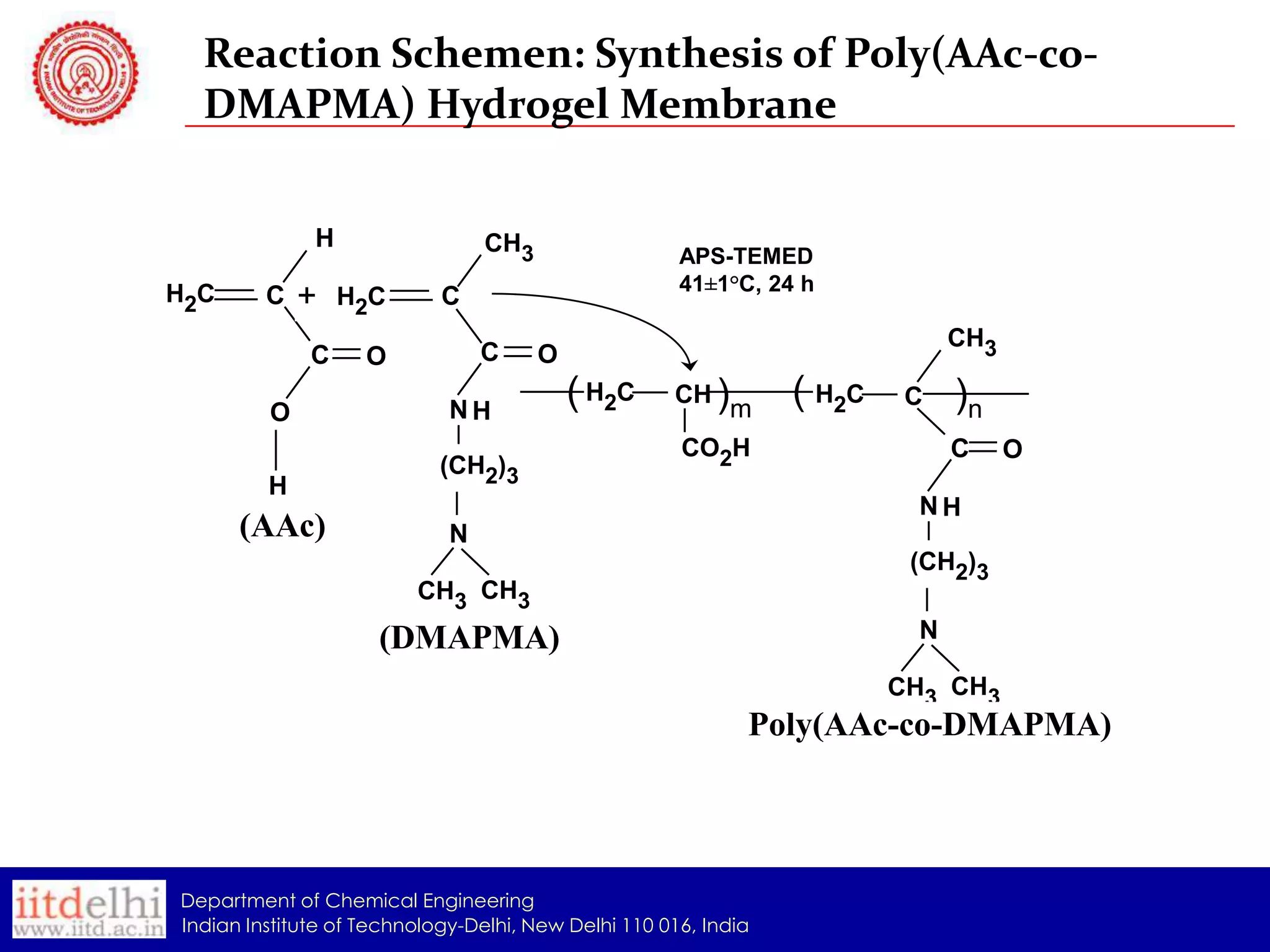
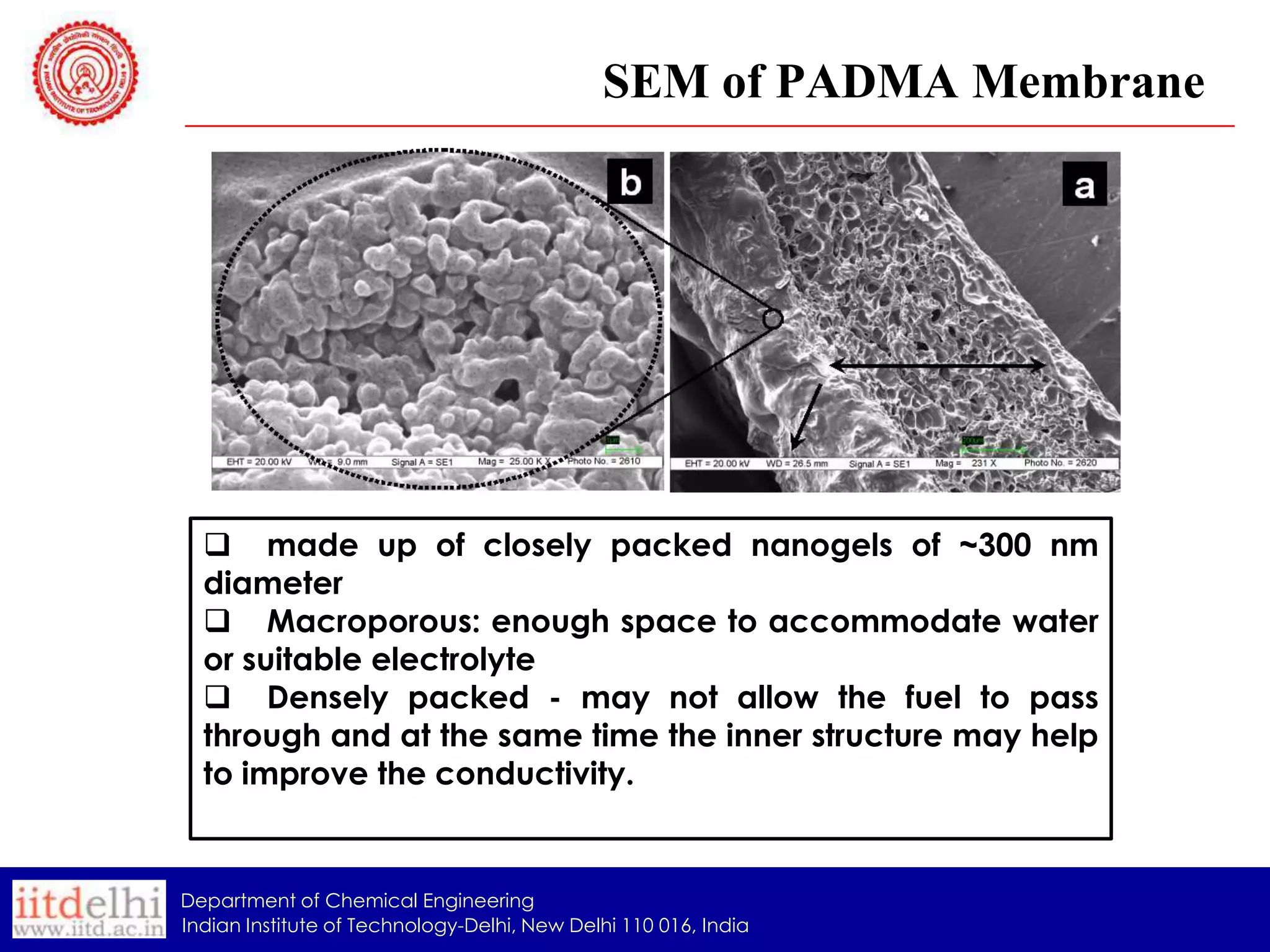
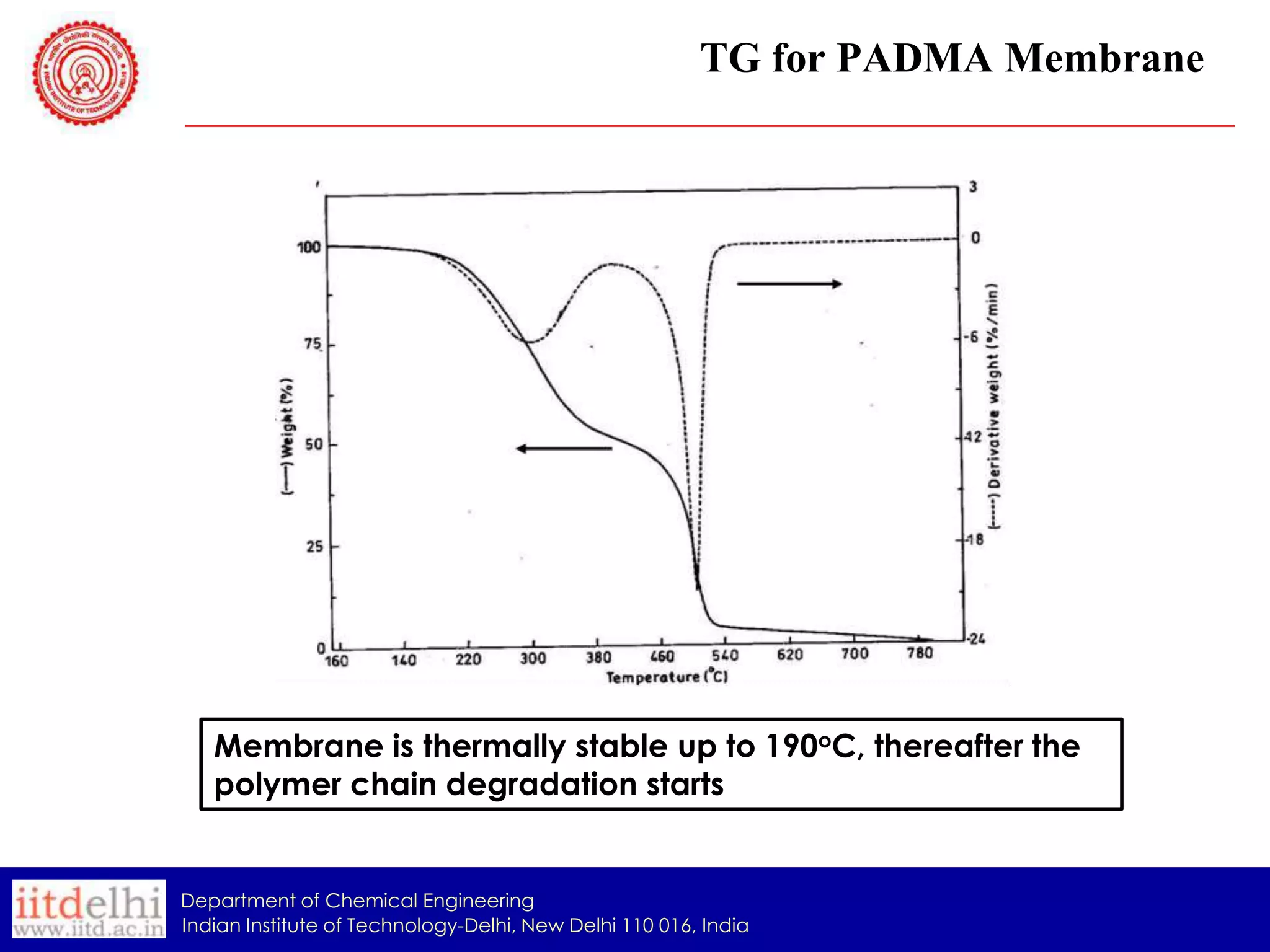
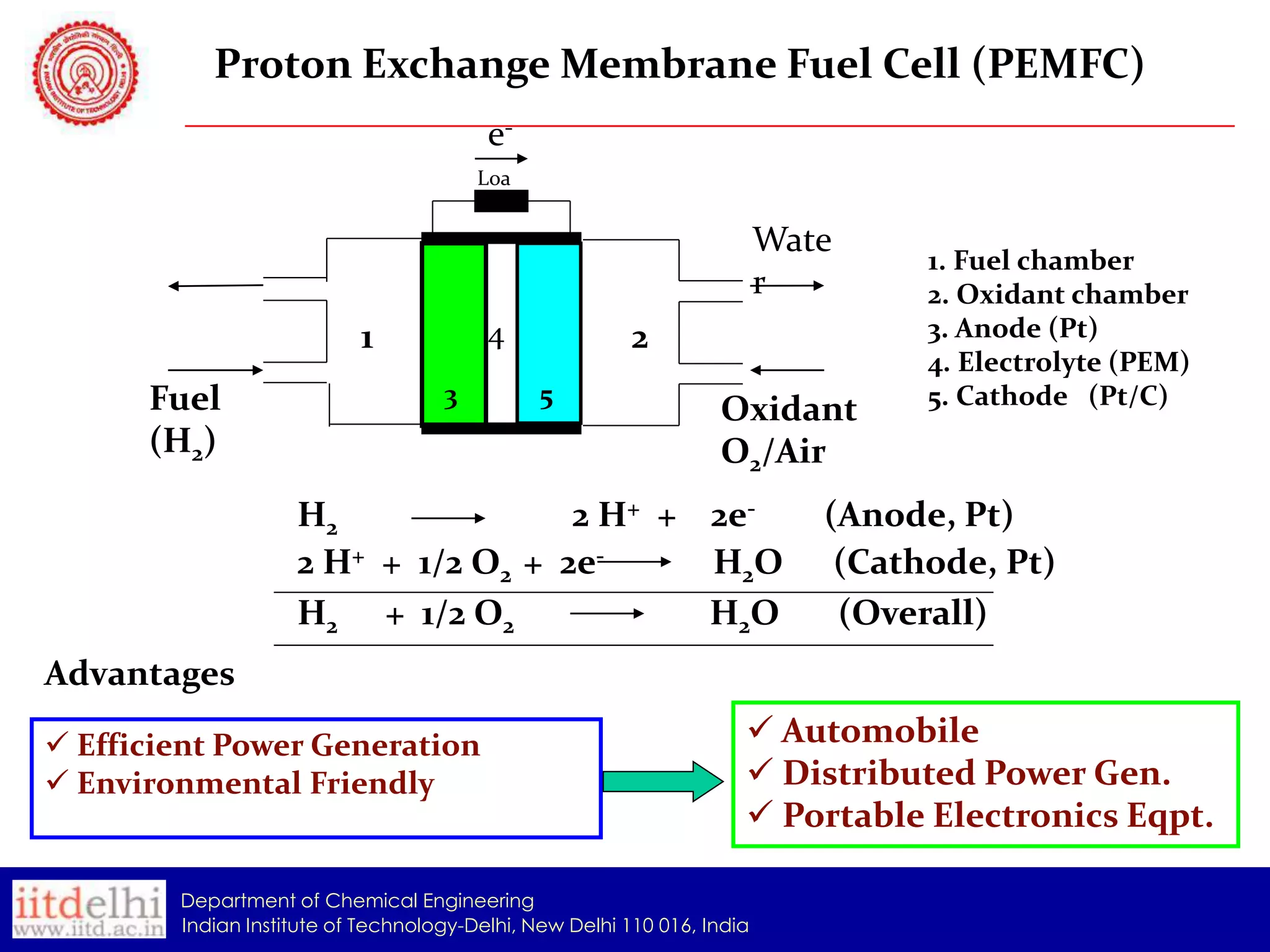
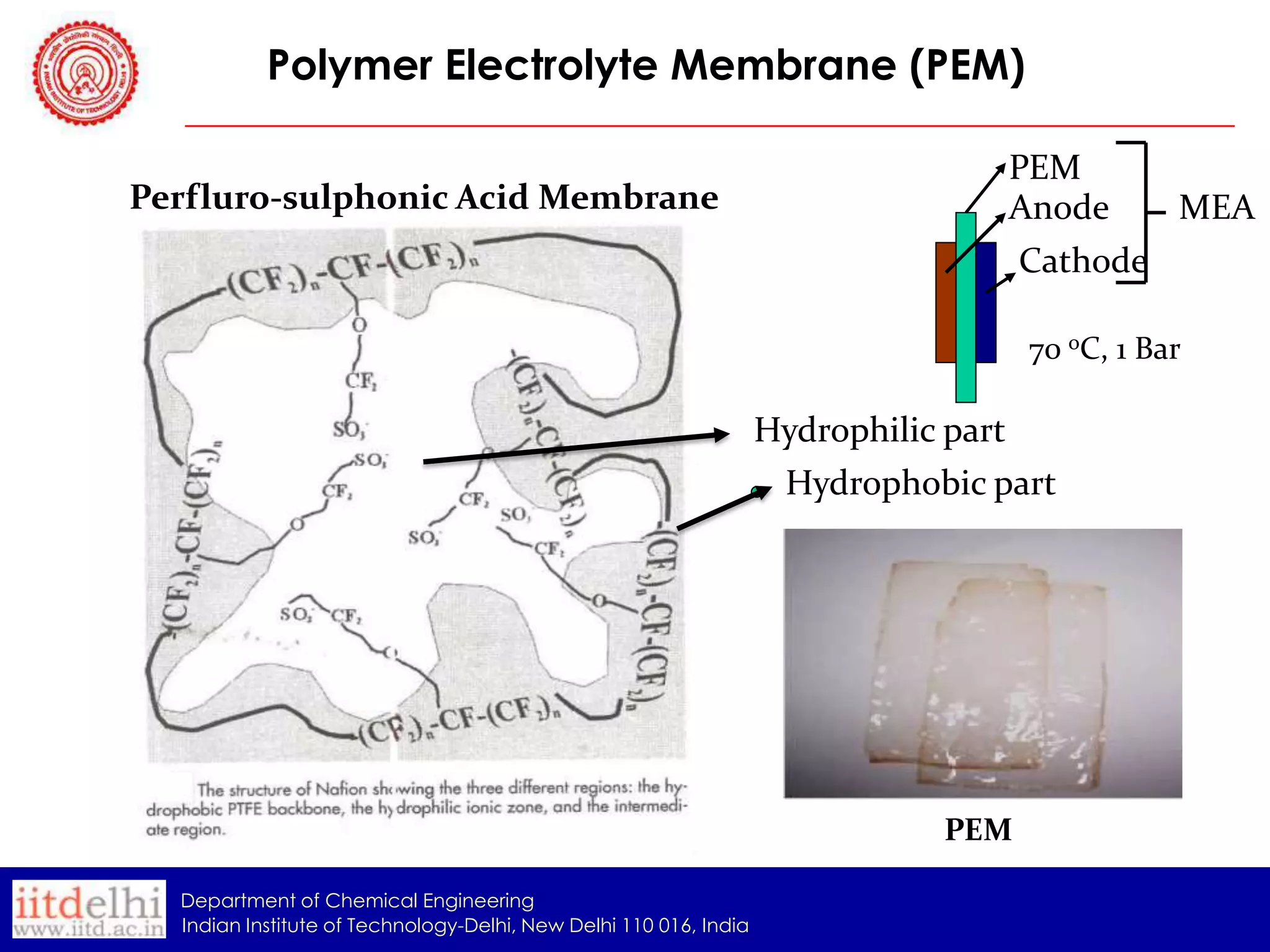
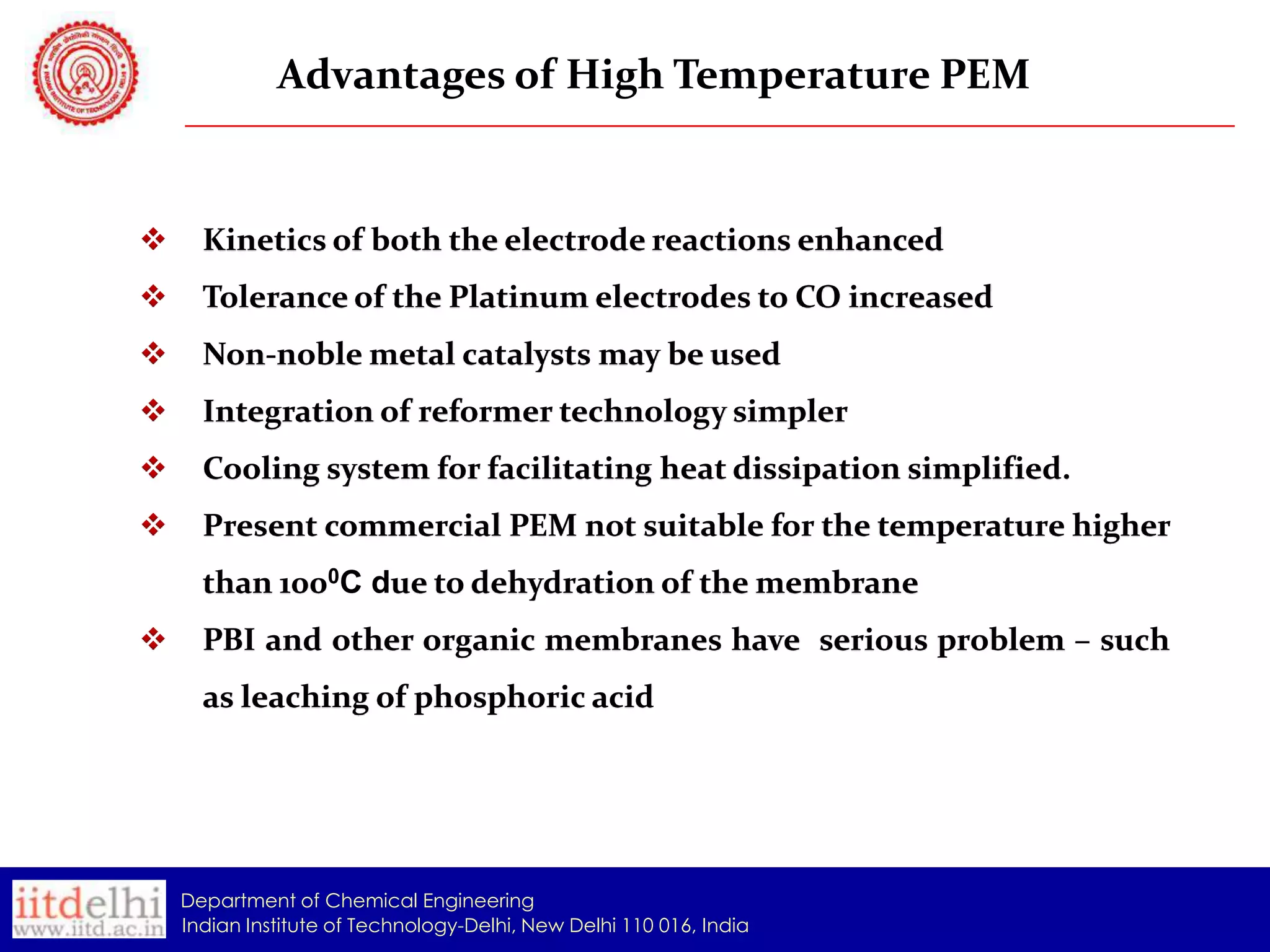
The document summarizes the synthesis and characterization of a Poly(AAc-co-DMAPMA) (PADMA) hydrogel membrane for use as an ion exchange membrane in fuel cells. PADMA membrane was synthesized via free radical polymerization and characterized using SEM, TGA, compression testing, and ionic conductivity measurements. SEM showed the membrane has a nanogel structure capable of accommodating water or electrolyte. TGA found it thermally stable to 190°C. Testing indicated the membrane could function as both a proton and hydroxyl ion conductor, making it a potential low-cost alternative to Nafion membranes.

![Experimental
Acrylic Acid (25.8 % mole) + [dimethylamino) propyl]-methacrylamide
(DMAPMA) (4.2 % mole) mixed in cold condition over magnetic stirrer
Distill water (70 % mole) added & mixed thoroughly
N2 gas purged for 15 min.
Added: conc. aq. solution of ammonium persulphate (APS – 0.50 mol % of
total monomer) as initiator and N,N,N’,N’-tetramethyl ethylene diamine
(TEMED -1 mol %) as accelerator.
Reaction mixture transferred into a mold of PTFE, placed in water bath at 41 ± 10C
Membrane removed from mold and cut into pieces
Washed in regularly changed distilled water for 3 days and dried in vacuum
Department of Chemical Engineering
Indian Institute of Technology-Delhi, New Delhi 110 016, India](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/320sbasu-131211234948-phpapp02/75/320-s-basu-7-2048.jpg)