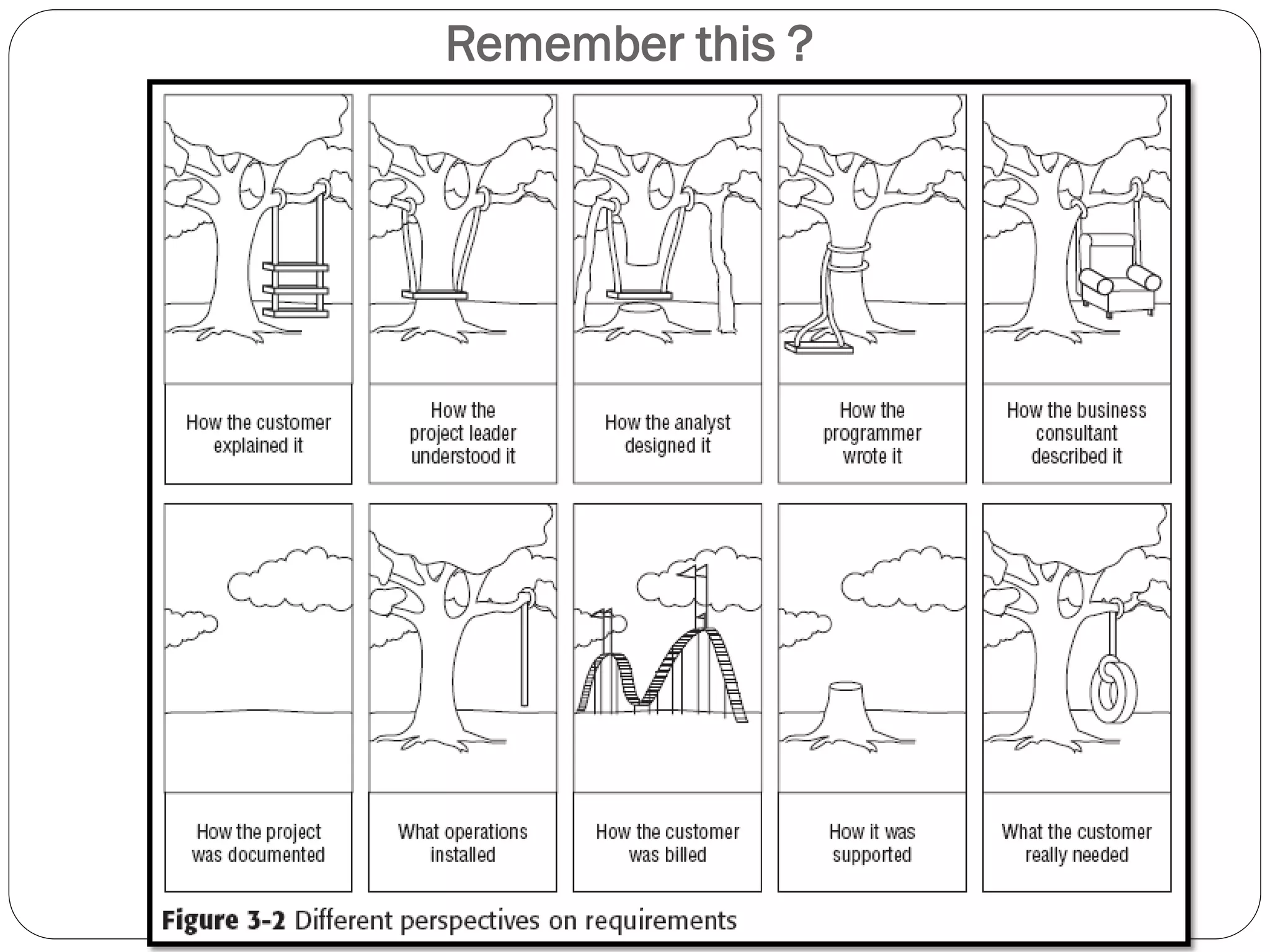
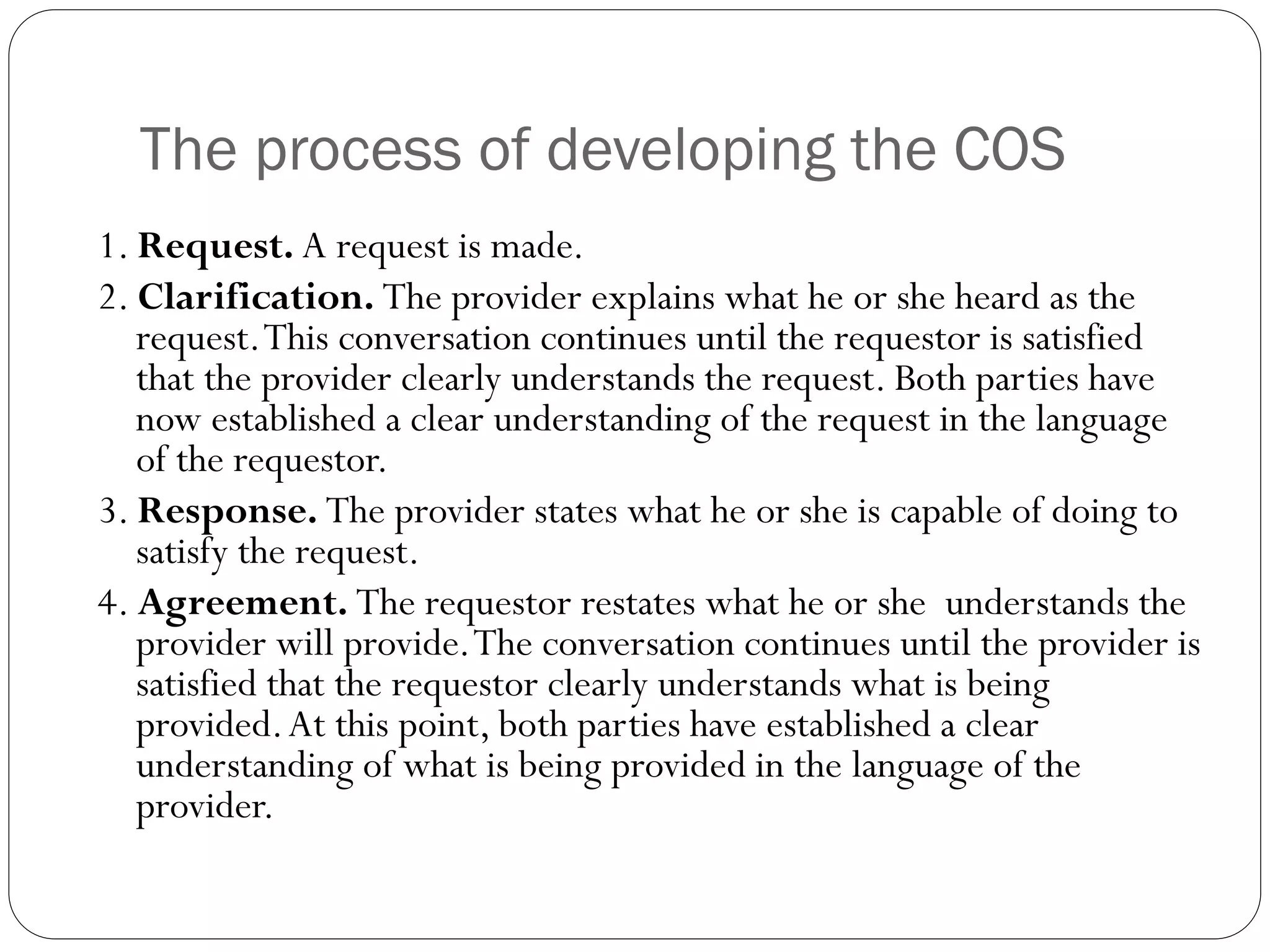
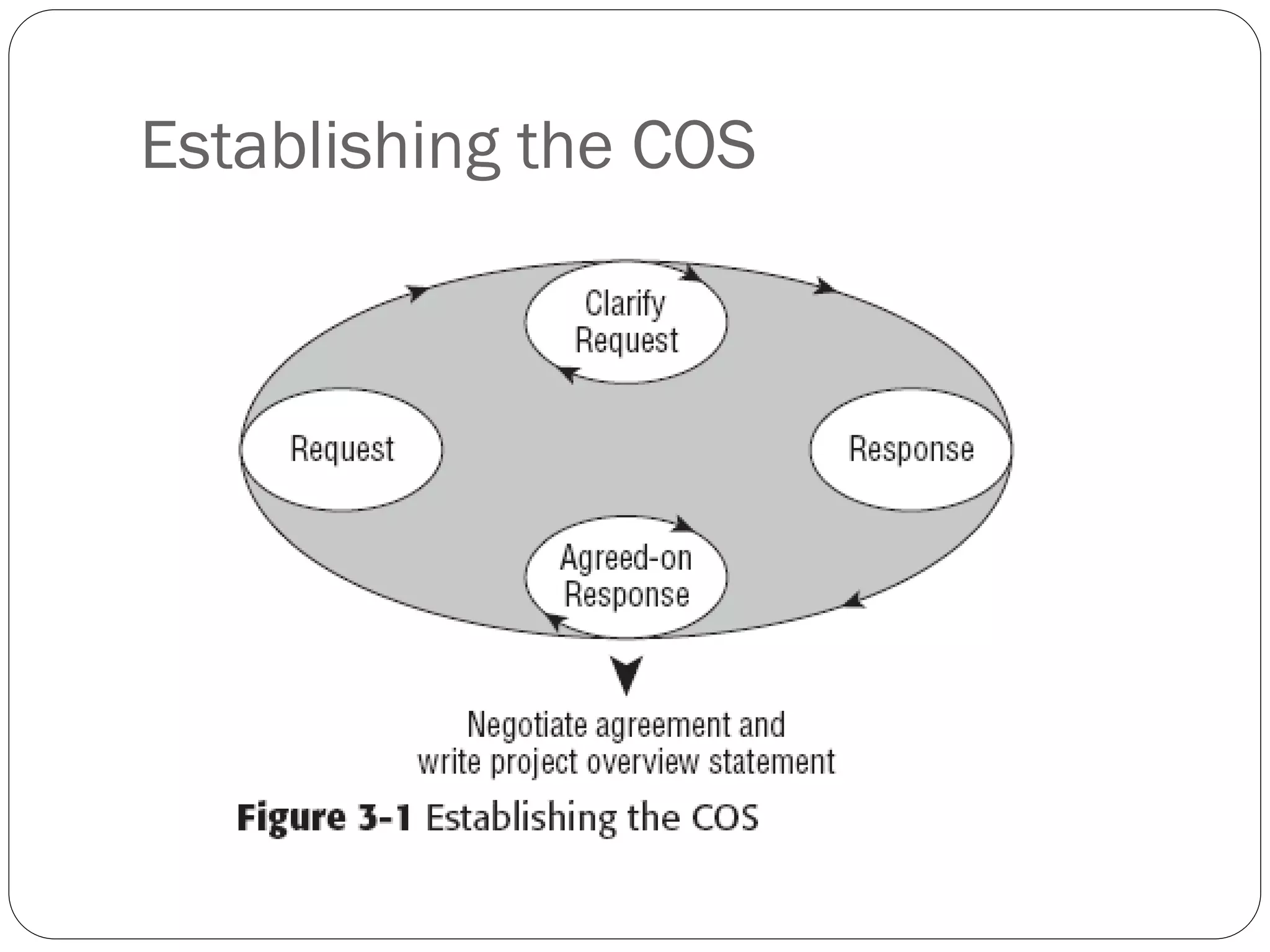
This document discusses managing client expectations for projects through establishing clear Conditions of Satisfaction (COS). The COS involves structured conversations between the client and project manager to develop a shared understanding of the request and response. This understanding is documented in a one-page Project Overview Statement (POS). The document then describes planning a project meeting to further develop the COS, POS, and project requirements and objectives. It outlines contents of the POS like the problem, goals, objectives, success criteria, risks, and attachments. Finally, it discusses getting senior management, customer, and team approval on the POS.