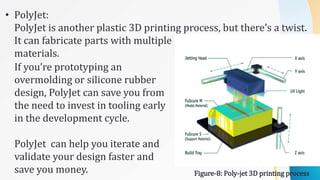
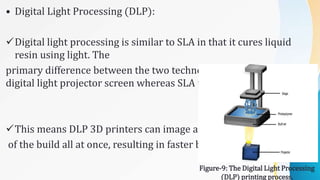
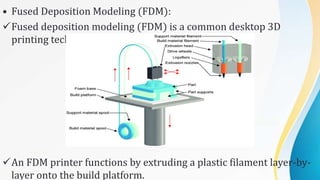
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of making three-dimensional solid objects from a digital file by successively depositing material layer by layer under computer control. It was invented in the 1980s and has since evolved to use a variety of materials such as plastics, metals, food, and concrete. 3D printing offers advantages over traditional manufacturing like reduced time and costs to produce prototypes and customized products in small batches. It has applications in many industries including aerospace, automotive, medical, art, architecture, and more.